Kranzusch Lab
@kranzuschlab.bsky.social
Harvard Medical School, Dana Farber Cancer Institute
https://kranzuschlab.med.harvard.edu
https://kranzuschlab.med.harvard.edu
Reposted by Kranzusch Lab
🚨New preprint out!
We present a foundational genomic resource of human gut microbiome viruses. It delivers high-quality, deeply curated data spanning taxonomy, predicted hosts, structures, and functions, providing a reference for gut virome research. (1/8)
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
We present a foundational genomic resource of human gut microbiome viruses. It delivers high-quality, deeply curated data spanning taxonomy, predicted hosts, structures, and functions, providing a reference for gut virome research. (1/8)
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

November 6, 2025 at 5:26 PM
🚨New preprint out!
We present a foundational genomic resource of human gut microbiome viruses. It delivers high-quality, deeply curated data spanning taxonomy, predicted hosts, structures, and functions, providing a reference for gut virome research. (1/8)
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
We present a foundational genomic resource of human gut microbiome viruses. It delivers high-quality, deeply curated data spanning taxonomy, predicted hosts, structures, and functions, providing a reference for gut virome research. (1/8)
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Reposted by Kranzusch Lab
Bacteria can sense when a virus starts shredding their genome — by detecting methylated mononucleotides.
Here’s the story of how we discovered the Metis defense system 👇
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Here’s the story of how we discovered the Metis defense system 👇
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

November 6, 2025 at 5:00 AM
Bacteria can sense when a virus starts shredding their genome — by detecting methylated mononucleotides.
Here’s the story of how we discovered the Metis defense system 👇
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Here’s the story of how we discovered the Metis defense system 👇
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Reposted by Kranzusch Lab
from 2021. A new family of globally distributed lytic roseophages with unusual deoxythymidine to deoxyuridine substitution www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti... @cyanoney.bsky.social

A new family of globally distributed lytic roseophages with unusual deoxythymidine to deoxyuridine substitution
Marine bacterial viruses (bacteriophages) are abundant biological entities that are vital for shaping microbial diversity, impacting marine ecosystem …
www.sciencedirect.com
November 4, 2025 at 2:38 PM
from 2021. A new family of globally distributed lytic roseophages with unusual deoxythymidine to deoxyuridine substitution www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti... @cyanoney.bsky.social
Reposted by Kranzusch Lab
A membrane-bound nuclease directly cleaves phage DNA during genome injection https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2025.11.03.685801v1
November 3, 2025 at 4:16 PM
A membrane-bound nuclease directly cleaves phage DNA during genome injection https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2025.11.03.685801v1
Reposted by Kranzusch Lab
Hi everyone, a few years ago, we started a list of labs studying bacterial immunty for students, editors, conference organizers... (currently n=79).
Update time ! Send me a message to 1) add your lab or others 2) Correct info
docs.google.com/spreadsheets...
#Phagesky #Microsky
Update time ! Send me a message to 1) add your lab or others 2) Correct info
docs.google.com/spreadsheets...
#Phagesky #Microsky

Labs in bacterial immunity
docs.google.com
November 4, 2025 at 3:06 PM
Hi everyone, a few years ago, we started a list of labs studying bacterial immunty for students, editors, conference organizers... (currently n=79).
Update time ! Send me a message to 1) add your lab or others 2) Correct info
docs.google.com/spreadsheets...
#Phagesky #Microsky
Update time ! Send me a message to 1) add your lab or others 2) Correct info
docs.google.com/spreadsheets...
#Phagesky #Microsky
Reposted by Kranzusch Lab
Check out our latest work led by two talented postdocs, Madhura @mkulkarni.bsky.social and Chris. We find that CASP4/5 can cleave and activate CASP3/7, acting as initiators of both pyroptosis and apoptosis. Notably, both are needed for full pathogen defense!
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

Human non-canonical inflammasomes activate CASP3 to limit intracellular Salmonella replication in macrophages.
Inflammasomes are multiprotein signaling platforms that activate inflammatory caspases to induce pyroptosis. In humans, canonical inflammasomes activate CASP1, which cleaves the pore-forming protein g...
www.biorxiv.org
November 3, 2025 at 10:09 PM
Check out our latest work led by two talented postdocs, Madhura @mkulkarni.bsky.social and Chris. We find that CASP4/5 can cleave and activate CASP3/7, acting as initiators of both pyroptosis and apoptosis. Notably, both are needed for full pathogen defense!
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Reposted by Kranzusch Lab
#microsky #phagesky #phage defence
Novel bacterial ubiquitination-like pathway!
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Novel bacterial ubiquitination-like pathway!
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

Mechanistic basis for protein conjugation in a diverged bacterial ubiquitination pathway - Nature Structural & Molecular Biology
Ye et al. define the structure and mechanisms of a bacterial pathway that performs ubiquitination-like protein conjugation, revealing new insights into the evolution and biological roles of ubiquitina...
www.nature.com
November 3, 2025 at 8:56 PM
#microsky #phagesky #phage defence
Novel bacterial ubiquitination-like pathway!
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Novel bacterial ubiquitination-like pathway!
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Reposted by Kranzusch Lab
Our new preprint is out 🥳🥳🥳
Henipaviruses, like Nipah and Hendra, package their genomes inside helical shells built by thousands of nucleoproteins. These nucleocapsids are essential to protect the viral RNA, but how do they ever let the polymerase in to read the sequence?
👇
Henipaviruses, like Nipah and Hendra, package their genomes inside helical shells built by thousands of nucleoproteins. These nucleocapsids are essential to protect the viral RNA, but how do they ever let the polymerase in to read the sequence?
👇

November 3, 2025 at 12:26 PM
Our new preprint is out 🥳🥳🥳
Henipaviruses, like Nipah and Hendra, package their genomes inside helical shells built by thousands of nucleoproteins. These nucleocapsids are essential to protect the viral RNA, but how do they ever let the polymerase in to read the sequence?
👇
Henipaviruses, like Nipah and Hendra, package their genomes inside helical shells built by thousands of nucleoproteins. These nucleocapsids are essential to protect the viral RNA, but how do they ever let the polymerase in to read the sequence?
👇
Reposted by Kranzusch Lab
Last year it was discovered that a single bacterial NLR-like protein can recognize multiple, structurally unrelated phage proteins (Béchon et al, Kibby et al)
Now, a new study shows the same for a plant NLR. Another example how principles of immunity remain conserved from bacteria to eukaryotes
Now, a new study shows the same for a plant NLR. Another example how principles of immunity remain conserved from bacteria to eukaryotes
A wheat NLR conferring broad-spectrum resistance against powdery mildew by recognizing two structurally diverse AVR effectors. Interested? Check out our newest preprint: www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

Dual recognition of structurally unrelated mildew effectors underlies the broad-spectrum resistance of Pm3e in wheat
Broad-spectrum resistance genes are highly valuable for sustainable crop protection, yet the molecular basis of their activity is often unknown. The Pm3 allelic series in wheat encodes NLR receptors t...
www.biorxiv.org
November 2, 2025 at 6:34 PM
Last year it was discovered that a single bacterial NLR-like protein can recognize multiple, structurally unrelated phage proteins (Béchon et al, Kibby et al)
Now, a new study shows the same for a plant NLR. Another example how principles of immunity remain conserved from bacteria to eukaryotes
Now, a new study shows the same for a plant NLR. Another example how principles of immunity remain conserved from bacteria to eukaryotes
Reposted by Kranzusch Lab
The Wilkinson Lab is open for science! @mskcancercenter.bsky.social
🧬We'll be finding funky new RNA biology, mainly by looking at reverse transcriptases (i.e. the Best Enzymes In The World)🧬
annnd: I'm hiring - come join! Especially postdocs and PhD students - please get in touch (NYC is great)
🧬We'll be finding funky new RNA biology, mainly by looking at reverse transcriptases (i.e. the Best Enzymes In The World)🧬
annnd: I'm hiring - come join! Especially postdocs and PhD students - please get in touch (NYC is great)

Wilkinson Lab
We discover and study reverse transcriptases
wilkinsonlab.bio
October 31, 2025 at 7:00 PM
The Wilkinson Lab is open for science! @mskcancercenter.bsky.social
🧬We'll be finding funky new RNA biology, mainly by looking at reverse transcriptases (i.e. the Best Enzymes In The World)🧬
annnd: I'm hiring - come join! Especially postdocs and PhD students - please get in touch (NYC is great)
🧬We'll be finding funky new RNA biology, mainly by looking at reverse transcriptases (i.e. the Best Enzymes In The World)🧬
annnd: I'm hiring - come join! Especially postdocs and PhD students - please get in touch (NYC is great)
Reposted by Kranzusch Lab
Excited to share: DNA glycosylases are diverse antiviral effectors. They recognize phage base modifications and initiate genome destruction. A structure‑guided approach made the scope of this discovery possible! 🧪 #phagesky doi.org/10.1101/2025... #phage #microbiology

Antiviral Defence is a Conserved Function of Diverse DNA Glycosylases
Bacteria are frequently attacked by viruses, known as phages, and rely on diverse defence systems like restriction endonucleases and CRISPR-Cas to survive. While phages can evade these defences by cov...
doi.org
October 30, 2025 at 12:16 PM
Excited to share: DNA glycosylases are diverse antiviral effectors. They recognize phage base modifications and initiate genome destruction. A structure‑guided approach made the scope of this discovery possible! 🧪 #phagesky doi.org/10.1101/2025... #phage #microbiology
Reposted by Kranzusch Lab
By the @cellsensing.bsky.social and Zipfel labs: The plant receptor kinase HSL3 senses a cyclic, disulfide-bond stabilized peptide phytocytokine. www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

October 25, 2025 at 7:19 AM
By the @cellsensing.bsky.social and Zipfel labs: The plant receptor kinase HSL3 senses a cyclic, disulfide-bond stabilized peptide phytocytokine. www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Reposted by Kranzusch Lab
How does life evolve to adapt to modern cities?
Out now in Science, my PhD work with @lindymcbr.bsky.social uncovers the ancient origin of the “London Underground mosquito” – one of the most iconic examples of urban adaptation.
🧵(1/n)
@science.org
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.ady4515
Out now in Science, my PhD work with @lindymcbr.bsky.social uncovers the ancient origin of the “London Underground mosquito” – one of the most iconic examples of urban adaptation.
🧵(1/n)
@science.org
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.ady4515

Ancient origin of an urban underground mosquito
Understanding how life is adapting to urban environments represents an important challenge in evolutionary biology. In this work, we investigate a widely cited example of urban adaptation, Culex pipie...
www.science.org
October 25, 2025 at 4:46 AM
How does life evolve to adapt to modern cities?
Out now in Science, my PhD work with @lindymcbr.bsky.social uncovers the ancient origin of the “London Underground mosquito” – one of the most iconic examples of urban adaptation.
🧵(1/n)
@science.org
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.ady4515
Out now in Science, my PhD work with @lindymcbr.bsky.social uncovers the ancient origin of the “London Underground mosquito” – one of the most iconic examples of urban adaptation.
🧵(1/n)
@science.org
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.ady4515
Reposted by Kranzusch Lab
Excited to share some new work from the lab, led by @shelbyeandersen.bsky.social where we developed a method and computational pipeline to identify antiphage defenses across diverse bacterial phyla.
Serine recombinases are conserved genetic markers of antiphage defense systems https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2025.10.07.681051v1
October 20, 2025 at 5:49 PM
Excited to share some new work from the lab, led by @shelbyeandersen.bsky.social where we developed a method and computational pipeline to identify antiphage defenses across diverse bacterial phyla.
Reposted by Kranzusch Lab
🚨 Systems Virology Journal Club – 8th Series! 🚨
#BillSchneider and I are delighted to announce another round of cutting-edge talks in #SystemsVirology! 🦠💡
Join us and an outstanding lineup of speakers, starting Oct 30.
Free registration: shiraweingartengabbay.com/systems-viro... 🔬✨
#BillSchneider and I are delighted to announce another round of cutting-edge talks in #SystemsVirology! 🦠💡
Join us and an outstanding lineup of speakers, starting Oct 30.
Free registration: shiraweingartengabbay.com/systems-viro... 🔬✨

October 20, 2025 at 2:55 PM
🚨 Systems Virology Journal Club – 8th Series! 🚨
#BillSchneider and I are delighted to announce another round of cutting-edge talks in #SystemsVirology! 🦠💡
Join us and an outstanding lineup of speakers, starting Oct 30.
Free registration: shiraweingartengabbay.com/systems-viro... 🔬✨
#BillSchneider and I are delighted to announce another round of cutting-edge talks in #SystemsVirology! 🦠💡
Join us and an outstanding lineup of speakers, starting Oct 30.
Free registration: shiraweingartengabbay.com/systems-viro... 🔬✨
Reposted by Kranzusch Lab
Genome maintenance by telomerase is a fundamental process in nearly all eukaryotes. But where does it come from?
Today, we report the discovery of telomerase homologs in a family of antiviral reverse transcriptases, revealing an unexpected evolutionary origin in bacteria.
doi.org/10.1101/2025...
Today, we report the discovery of telomerase homologs in a family of antiviral reverse transcriptases, revealing an unexpected evolutionary origin in bacteria.
doi.org/10.1101/2025...

October 17, 2025 at 12:47 PM
Genome maintenance by telomerase is a fundamental process in nearly all eukaryotes. But where does it come from?
Today, we report the discovery of telomerase homologs in a family of antiviral reverse transcriptases, revealing an unexpected evolutionary origin in bacteria.
doi.org/10.1101/2025...
Today, we report the discovery of telomerase homologs in a family of antiviral reverse transcriptases, revealing an unexpected evolutionary origin in bacteria.
doi.org/10.1101/2025...
Reposted by Kranzusch Lab
1/10 Genome maintenance by telomerase is a fundamental process in nearly all eukaryotes. But where does it come from?
Today, we report the discovery of telomerase homologs in a family of antiviral RTs, revealing an unexpected evolutionary origin in bacteria.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Today, we report the discovery of telomerase homologs in a family of antiviral RTs, revealing an unexpected evolutionary origin in bacteria.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

Antiviral reverse transcriptases reveal the evolutionary origin of telomerase
Defense-associated reverse transcriptases (DRTs) employ diverse and distinctive mechanisms of cDNA synthesis to protect bacteria against viral infection. However, much of DRT family diversity remains ...
www.biorxiv.org
October 17, 2025 at 5:22 PM
1/10 Genome maintenance by telomerase is a fundamental process in nearly all eukaryotes. But where does it come from?
Today, we report the discovery of telomerase homologs in a family of antiviral RTs, revealing an unexpected evolutionary origin in bacteria.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Today, we report the discovery of telomerase homologs in a family of antiviral RTs, revealing an unexpected evolutionary origin in bacteria.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Perfect timing in the field for a beautiful review on NAD+ in bacterial immunity by @hugovaysset.bsky.social and @audeber.bsky.social @cp-molcell.bsky.social
#MicroSky
www.cell.com/molecular-ce...
#MicroSky
www.cell.com/molecular-ce...

October 16, 2025 at 2:58 PM
Perfect timing in the field for a beautiful review on NAD+ in bacterial immunity by @hugovaysset.bsky.social and @audeber.bsky.social @cp-molcell.bsky.social
#MicroSky
www.cell.com/molecular-ce...
#MicroSky
www.cell.com/molecular-ce...
Reposted by Kranzusch Lab
Very excited for Jeannette Tenthorey! @packardfdn.bsky.social @ucsfhealth.bsky.social

Jeannette Tenthorey • The David and Lucile Packard Foundation
A staggering 8% of the human genome derives from endogenous retroviruses, ancient evolutionary fossils that have been dismissed as vestiges. Yet recent work has revealed that some of these viral genes...
www.packard.org
October 16, 2025 at 1:47 AM
Very excited for Jeannette Tenthorey! @packardfdn.bsky.social @ucsfhealth.bsky.social
Reposted by Kranzusch Lab
The IFIT2–IFIT3 antiviral complex targets short 5’ untranslated regions on viral mRNAs for translation inhibition
By Dustin Glasner, Matthew Daugherty & colleagues.
#microsky
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
By Dustin Glasner, Matthew Daugherty & colleagues.
#microsky
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

The IFIT2–IFIT3 antiviral complex targets short 5’ untranslated regions on viral mRNAs for translation inhibition - Nature Microbiology
Viruses generally have compact genomes, resulting in many viral mRNAs with short 5’ untranslated regions. An antiviral complex exploits this feature of viral mRNAs to selectively inhibit viral protein...
www.nature.com
October 15, 2025 at 4:59 PM
The IFIT2–IFIT3 antiviral complex targets short 5’ untranslated regions on viral mRNAs for translation inhibition
By Dustin Glasner, Matthew Daugherty & colleagues.
#microsky
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
By Dustin Glasner, Matthew Daugherty & colleagues.
#microsky
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Reposted by Kranzusch Lab
Two intensive sampling periods of oyster-associated vibrio and their phage, 4 years apart, and many surprises. Despite being washed by the Atlantic, wide tides, and vibrio (almost?) disappearing most of the year, we can find the exact same virulent phages 4 years later (down to 0 SNP)! preprint👇

October 14, 2025 at 4:08 PM
Two intensive sampling periods of oyster-associated vibrio and their phage, 4 years apart, and many surprises. Despite being washed by the Atlantic, wide tides, and vibrio (almost?) disappearing most of the year, we can find the exact same virulent phages 4 years later (down to 0 SNP)! preprint👇
Reposted by Kranzusch Lab
Happy that the final version of our Lamassu work @yli18smc.bsky.social is now out:
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Thanks again to our awesome collaborators @mblokesch.bsky.social and David and co and Mark Szczelkun and @steven-shaw.bsky.social and the DCI Lausanne @fbm-unil.bsky.social
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Thanks again to our awesome collaborators @mblokesch.bsky.social and David and co and Mark Szczelkun and @steven-shaw.bsky.social and the DCI Lausanne @fbm-unil.bsky.social
Glad to share the work of @yli18smc.bsky.social and co on Lamassu, a bacterial defense system related to Rad50/Mre11 (RM). While RM carefully trims DNA ends for repair, Lamassu chops up the host chromosome. Our study reveals how it is regulated to minimize damage, activating only during infection.
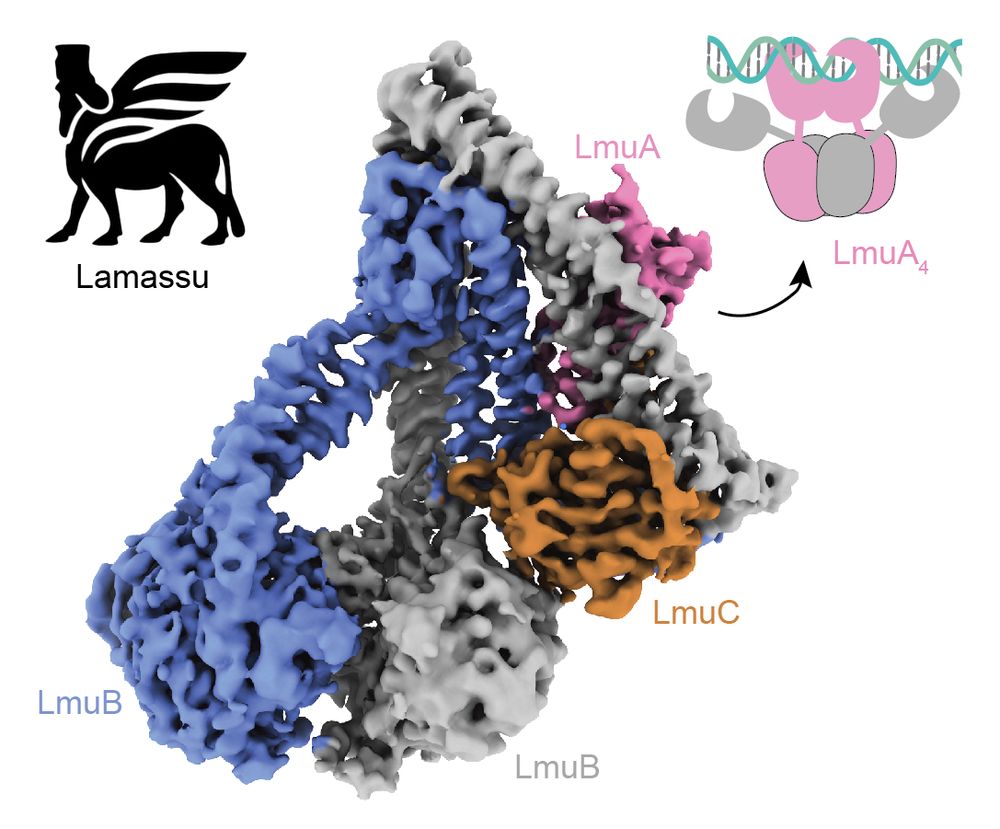
October 14, 2025 at 9:28 AM
Happy that the final version of our Lamassu work @yli18smc.bsky.social is now out:
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Thanks again to our awesome collaborators @mblokesch.bsky.social and David and co and Mark Szczelkun and @steven-shaw.bsky.social and the DCI Lausanne @fbm-unil.bsky.social
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Thanks again to our awesome collaborators @mblokesch.bsky.social and David and co and Mark Szczelkun and @steven-shaw.bsky.social and the DCI Lausanne @fbm-unil.bsky.social
Reposted by Kranzusch Lab
Phages evolve fast, or do they?
In oysters, some stay identical for years.
With >1,200 phages & 600 Vibrio genomes, we reveal long-term stability and new mobile elements.
Proud of this collaborative work across our teams (Roscoff-UdeM and @epcrocha.bsky.social www.biorxiv.org/cgi/content/...
In oysters, some stay identical for years.
With >1,200 phages & 600 Vibrio genomes, we reveal long-term stability and new mobile elements.
Proud of this collaborative work across our teams (Roscoff-UdeM and @epcrocha.bsky.social www.biorxiv.org/cgi/content/...

Ecological constraints foster both extreme viral-host lineage stability and mobile element diversity in a marine community
Phages are typically viewed as very rapidly evolving biological entities. Little is known, however, about whether and how phages can establish long-term genetic stability. We addressed this eco-evolut...
www.biorxiv.org
October 12, 2025 at 9:16 PM
Phages evolve fast, or do they?
In oysters, some stay identical for years.
With >1,200 phages & 600 Vibrio genomes, we reveal long-term stability and new mobile elements.
Proud of this collaborative work across our teams (Roscoff-UdeM and @epcrocha.bsky.social www.biorxiv.org/cgi/content/...
In oysters, some stay identical for years.
With >1,200 phages & 600 Vibrio genomes, we reveal long-term stability and new mobile elements.
Proud of this collaborative work across our teams (Roscoff-UdeM and @epcrocha.bsky.social www.biorxiv.org/cgi/content/...
Differential activation of cGAS in naked mole rats! An exciting addition to our understanding of species-specific mutations tailoring the cGAS-STING pathway in individual organisms
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...

A cGAS-mediated mechanism in naked mole-rats potentiates DNA repair and delays aging
Efficient DNA repair might make possible the longevity of naked mole-rats. However, whether they have distinctive mechanisms to optimize functions of DNA repair suppressors is unclear. We find that na...
www.science.org
October 9, 2025 at 6:40 PM
Differential activation of cGAS in naked mole rats! An exciting addition to our understanding of species-specific mutations tailoring the cGAS-STING pathway in individual organisms
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
Thank you to the Blavatnik Family Foundation and The New York Academy of Sciences for honoring our research uniting human innate immunity and bacterial anti-phage defense at @danafarber.bsky.social @harvardmicro.bsky.social @harvard.edu
bit.ly/4pZUDkF
blavatnikawards.org/news/items/t...
bit.ly/4pZUDkF
blavatnikawards.org/news/items/t...

October 9, 2025 at 4:44 PM
Thank you to the Blavatnik Family Foundation and The New York Academy of Sciences for honoring our research uniting human innate immunity and bacterial anti-phage defense at @danafarber.bsky.social @harvardmicro.bsky.social @harvard.edu
bit.ly/4pZUDkF
blavatnikawards.org/news/items/t...
bit.ly/4pZUDkF
blavatnikawards.org/news/items/t...

