Professor of Oral Microbiology, King’s College London. Microbiome.
Reposted by William G. Wade
Reposted by Simon Roux, William G. Wade

While oral bacteria rarely colonize the healthy gut, they dominate the gut microbiome of patients with chronic liver disease. Here a bacterial gene encoded by microbial translocators is linked to gut barrier disruption and fibrosis
#MicroSky 🦠
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Reposted by William G. Wade

Reposted by Anne Applebaum, Timothy Snyder, Dorothy Bishop , and 19 more Anne Applebaum, Timothy Snyder, Dorothy Bishop, Simon Burgess, Mel Bartley, Gavin A. Schmidt, Christopher Wright, Michael A. Clemens, Maarten Vink, Leigh Sparks, Charles West, Robert C. Richards, Aaron Sojourner, Stephen D. Murphy, Marina Costa Lobo, Jonathan Birch, Ann Bartow, Georg Weizsäcker, Nathan Richardson, Christina Pagel, William G. Wade, Pam Jarvis
Reposted by Jesse M. Shapiro, Alan McNally, William G. Wade

Reposted by William G. Wade

Reposted by William G. Wade

Reposted by William G. Wade
Reposted by William G. Wade
Reposted by Mart Krupovìč, William G. Wade
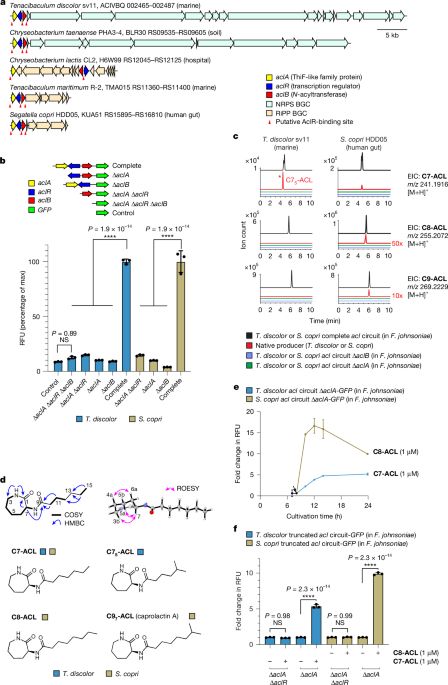
rdcu.be/erkkU
Reposted by Marc Strous, Andrew L. Jackson, William G. Wade
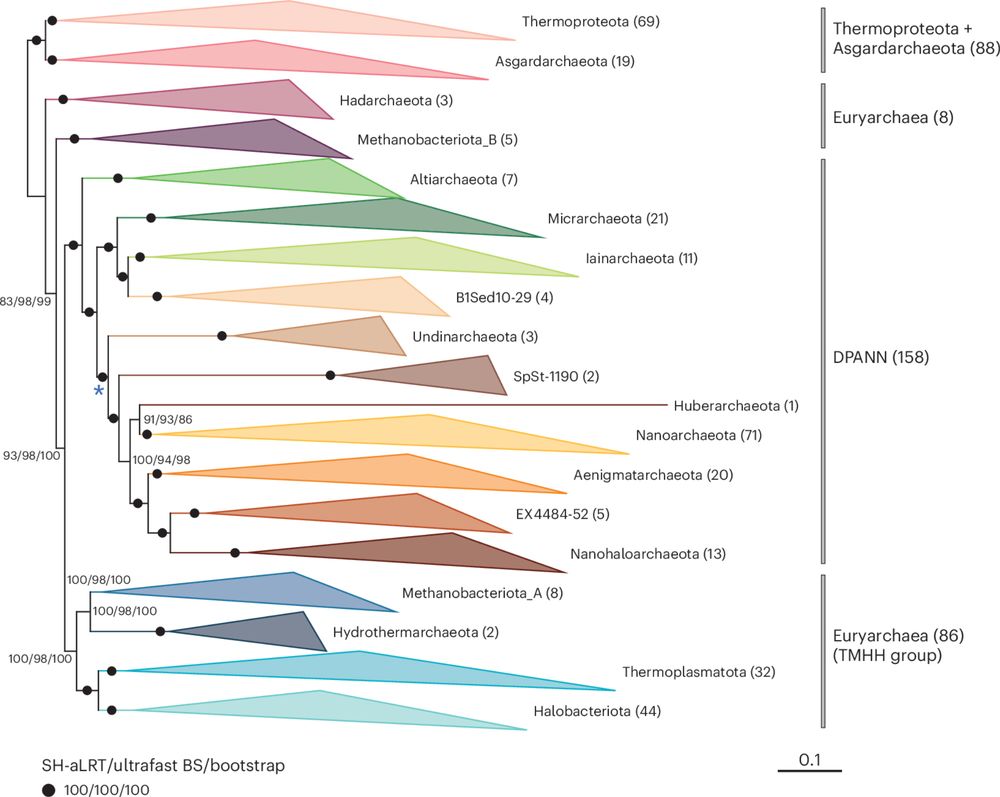
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
#MicroSKy #Microbiology
Reposted by Mya Breitbart, William G. Wade
Today, we jointly shed light on the mysterious world of archaeal extracellular vesicles from human gut archaea - published in @natcomms.nature.com in parallel with our precious colleagues around @mkrupovic.bsky.social 🇦🇹🤝🇫🇷.
Reposted by William G. Wade

Reposted by William G. Wade, Alan W. Walker
Read it here: www.nature.com/articles/s41...
#microsky #microbiomesky 🧪
Reposted by William G. Wade
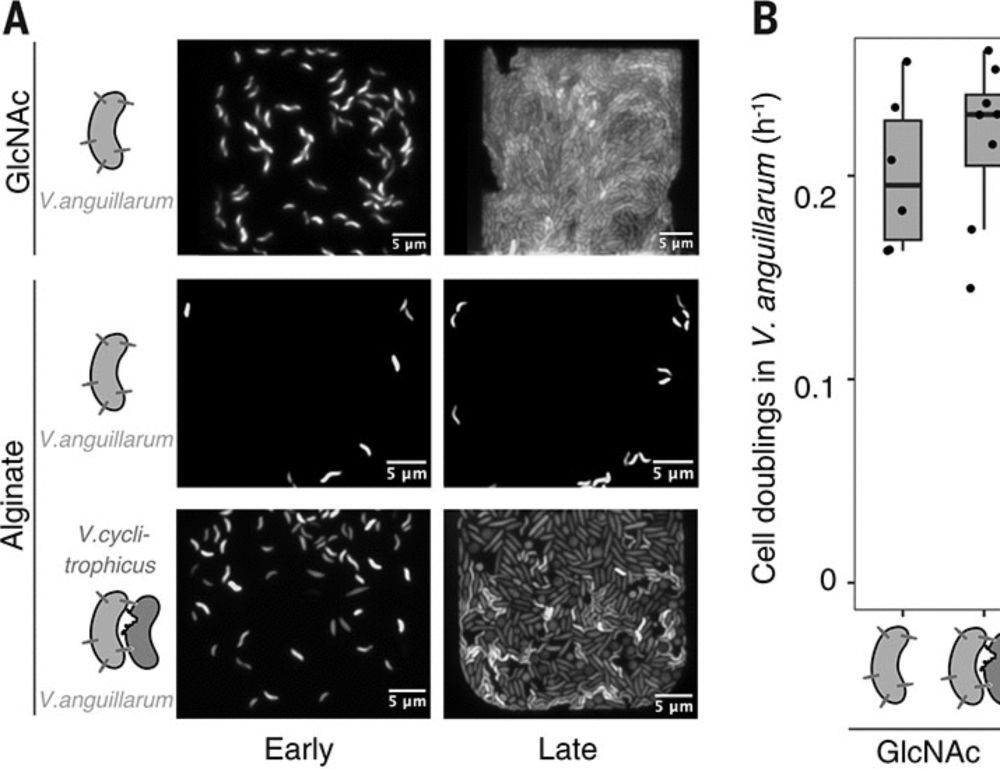
May protect against infections and preterm birth.
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Reposted by William G. Wade
Reposted by William G. Wade
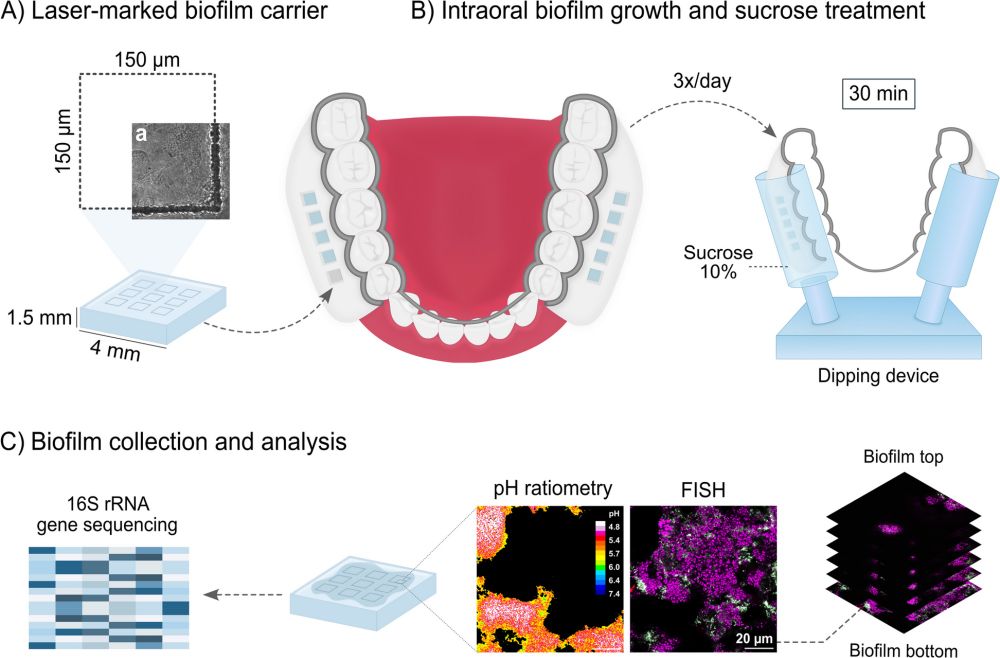
🌟 Exciting news! Our latest collaborative research with team @aarhusuni.bsky.social introduces pH-FISH, a novel technique combining pH ratiometry and FISH to simultaneously unravel microbial identity and local biofilm pH. 🔬 🧪 #MicroSky
link.springer.com/article/10.1...
#Microbiome #Biofilms
Reposted by William G. Wade

julkaisufoorumi.fi/en/news/chan...
Reposted by William G. Wade
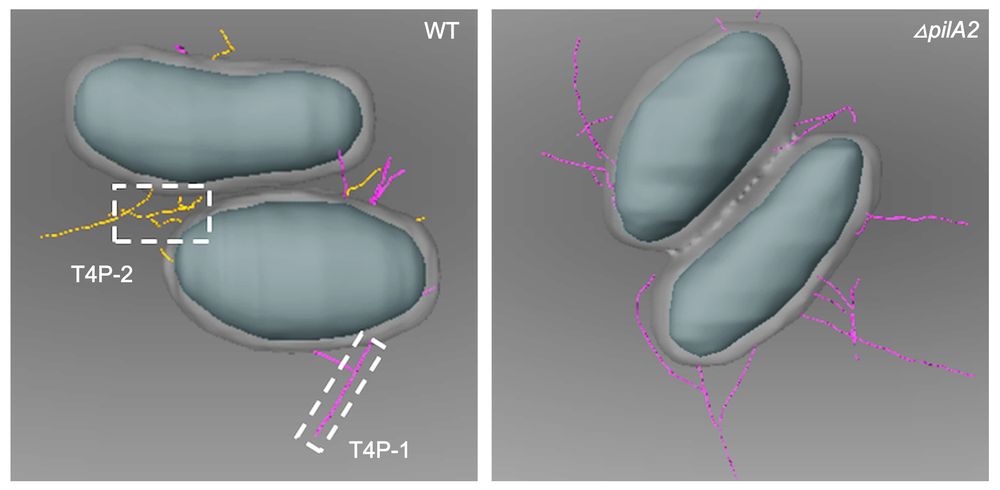
Reposted by Victor A. Albert, William G. Wade

Reposted by William G. Wade

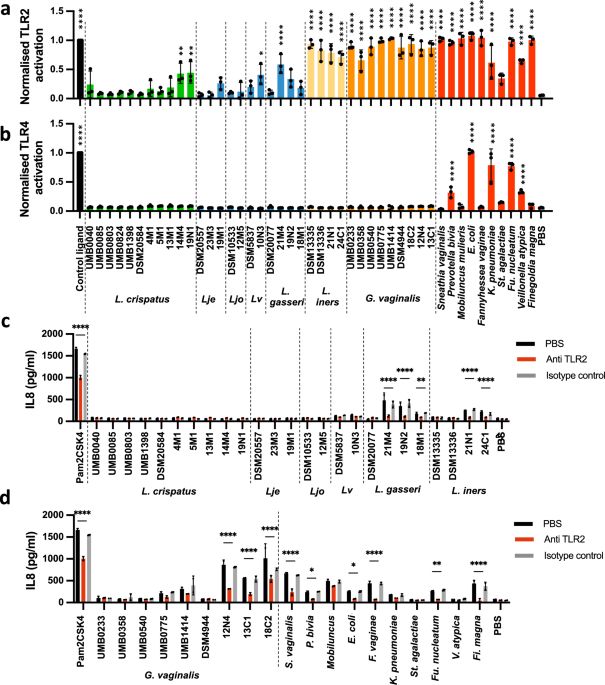
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
🔓 rdcu.be/d0hBg
#GastroSky #Microsky
Reposted by William G. Wade
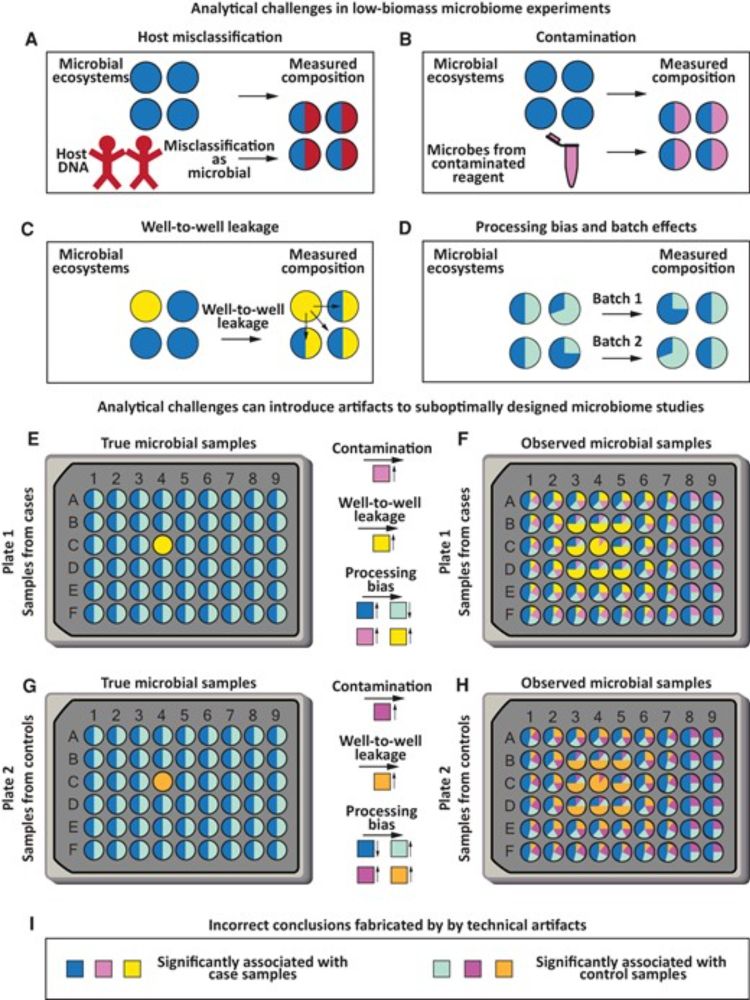
Reposted by William G. Wade

www.nature.com/articles/s41...