https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1054-2124
https://sites.temple.edu/voelzlab
Great collab w/ Weiping Tang! Congrats to Yue & co-authors!
chemrxiv.org/doi/full/10....
-

Great collab w/ Weiping Tang! Congrats to Yue & co-authors!
chemrxiv.org/doi/full/10....
-
pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10....

pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10....

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.6...

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.6...
www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/...
www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/...


apply.careers.microsoft.com/careers/job/...

apply.careers.microsoft.com/careers/job/...
Your one-stop shop for everything related to our conference community. 🎉
BTW, registration is now open, so head over to secure your spot! We'll be sharing updates and details about the event.
Bookmark it as there's plenty more to come!
Your one-stop shop for everything related to our conference community. 🎉
BTW, registration is now open, so head over to secure your spot! We'll be sharing updates and details about the event.
Bookmark it as there's plenty more to come!
pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10....

pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10....
In collaboration with our industry partners, we ran benchmarking simulations of our hybrid-topology RBFE protocol on a large collection of both public and private protein-ligand binding datasets.
#compchem

In collaboration with our industry partners, we ran benchmarking simulations of our hybrid-topology RBFE protocol on a large collection of both public and private protein-ligand binding datasets.
#compchem
Learn more here: buff.ly/gInH6VV
#SBGrid #SBGridSoftware #StructuralBiology

Learn more here: buff.ly/gInH6VV
#SBGrid #SBGridSoftware #StructuralBiology
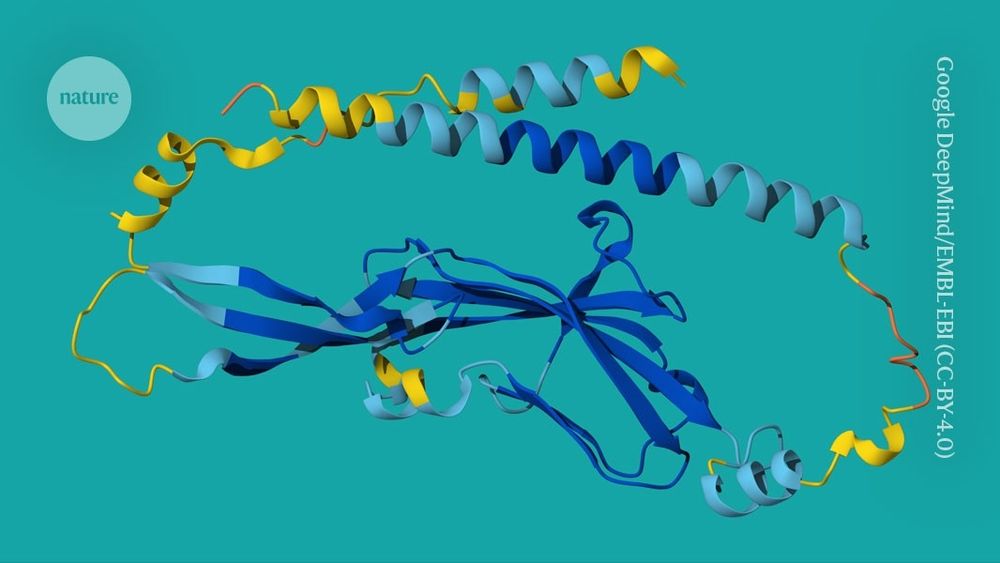
Experiment-guided AlphaFold3 resolves accurate protein ensembles.
doi.org/10.1101/2025...
AlphaFold3 is incredible, but has crucial limitations: it typically collapses to a single conformation, ignoring the inherent dynamics of proteins. And it can be wrong. Here's a solution. 🧵👇

Experiment-guided AlphaFold3 resolves accurate protein ensembles.
doi.org/10.1101/2025...
AlphaFold3 is incredible, but has crucial limitations: it typically collapses to a single conformation, ignoring the inherent dynamics of proteins. And it can be wrong. Here's a solution. 🧵👇
Check out this new interview with Pat in Nature Reviews Drug Discovery:
www.nature.com/articles/d41...

Check out this new interview with Pat in Nature Reviews Drug Discovery:
www.nature.com/articles/d41...

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/...

pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/...
from www.linkedin.com/in/ullah-sam...
www.youtube.com/watch?v=A5ph...
PyPI pypi.org/project/ipsae/
His github fork github.com/ullahsamee/I...
My github github.com/DunbrackLab/...
Paper www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
For designed protein binders www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

from www.linkedin.com/in/ullah-sam...
www.youtube.com/watch?v=A5ph...
PyPI pypi.org/project/ipsae/
His github fork github.com/ullahsamee/I...
My github github.com/DunbrackLab/...
Paper www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
For designed protein binders www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Named after Quetzalcoatl, the Aztec god of creation, Quetzal is a simple yet scalable model for building 3D molecules atom by atom.
📜 arxiv.org/abs/2505.13791
[1/4]
Named after Quetzalcoatl, the Aztec god of creation, Quetzal is a simple yet scalable model for building 3D molecules atom by atom.
📜 arxiv.org/abs/2505.13791
[1/4]
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
We used molecular dynamics simulations and solid-state NMR (@fmp-berlin.de) to look at calcium binding to the pore domain of the calcium-gated K+ channel MthK. @wojciechkopec.bsky.social @compbiophys.bsky.social
We used molecular dynamics simulations and solid-state NMR (@fmp-berlin.de) to look at calcium binding to the pore domain of the calcium-gated K+ channel MthK. @wojciechkopec.bsky.social @compbiophys.bsky.social