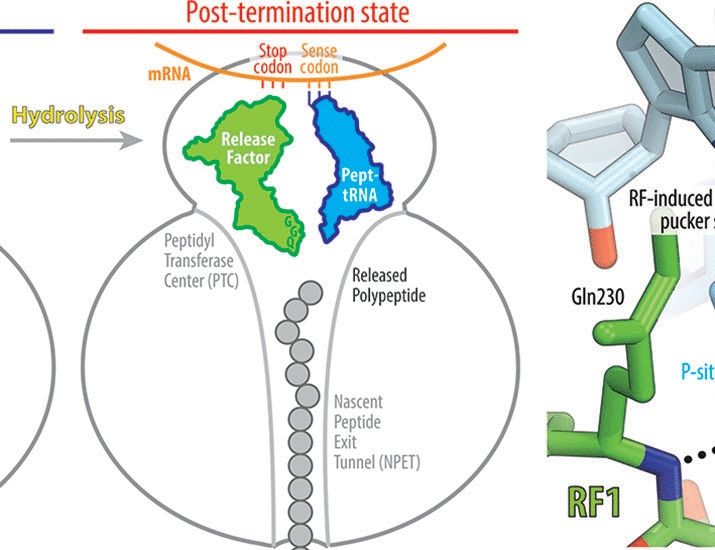
@amjjbonvin.bsky.social @bioinfo.se @lindorfflarsen.bsky.social #EMBOIntegMod25 ! 🍀🧿

@amjjbonvin.bsky.social @bioinfo.se @lindorfflarsen.bsky.social #EMBOIntegMod25 ! 🍀🧿
Check out these opportunities and consider becoming our new colleague at University of Copenhagen.
employment.ku.dk/faculty/?sho...

Check out these opportunities and consider becoming our new colleague at University of Copenhagen.
employment.ku.dk/faculty/?sho...
Deadline: 1 August
meetings.embo.org/event/25-ai-...
#LifeSciences #research #training #ProteinStructure #EMBOevents 🧪

Deadline: 1 August
meetings.embo.org/event/25-ai-...
#LifeSciences #research #training #ProteinStructure #EMBOevents 🧪

@xt117.bsky.social
biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

@xt117.bsky.social
biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Cyclic β-amino acid–based helical peptide library leads to stable, cell-permeable SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitors! New #RSCChemBio #advancearticle shows off RaPID selection power 💥
doi.org/10.1039/D5CB...

Cyclic β-amino acid–based helical peptide library leads to stable, cell-permeable SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitors! New #RSCChemBio #advancearticle shows off RaPID selection power 💥
doi.org/10.1039/D5CB...
Engineering E. coli bacteria to turn plastic waste into paracetamol (Tylenol)
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
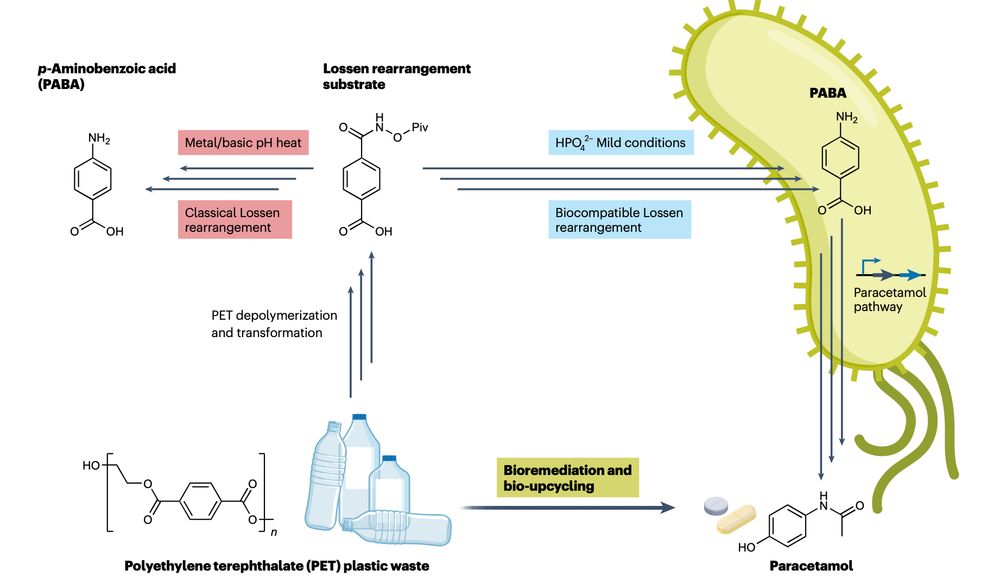
Engineering E. coli bacteria to turn plastic waste into paracetamol (Tylenol)
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
rdcu.be/eq975
rdcu.be/eq975
@nejm.org
nejm.org/doi/full/10....
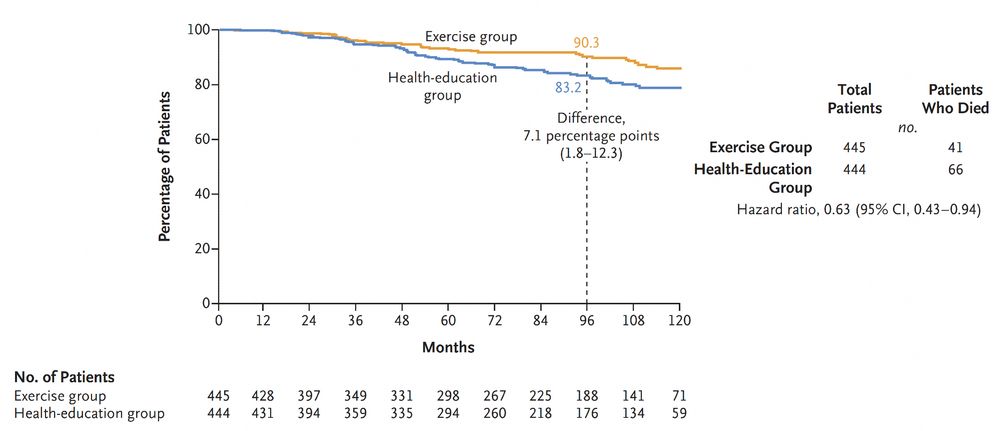
@nejm.org
nejm.org/doi/full/10....
Now out in its final form in @angewandtechemie.bsky.social as a 'Very Important Paper' 🔥 (1/🧵) #chemsky
onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/...
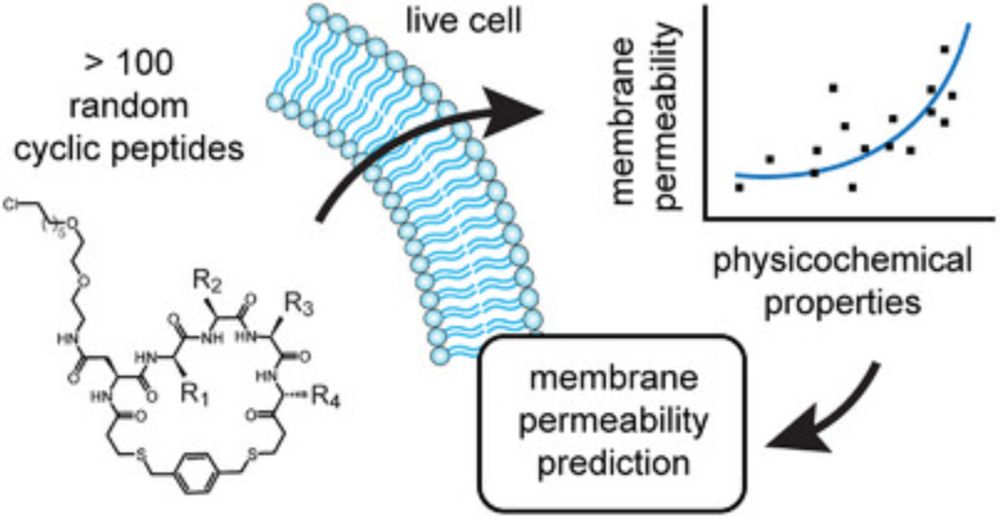
Now out in its final form in @angewandtechemie.bsky.social as a 'Very Important Paper' 🔥 (1/🧵) #chemsky
onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/...
@dereklowe.bsky.social writes about how Csaba Szabo was contacted by a paper mill and offered money if he could help them write more junk papers.
www.science.org/content/blog...

@dereklowe.bsky.social writes about how Csaba Szabo was contacted by a paper mill and offered money if he could help them write more junk papers.
www.science.org/content/blog...
Experience in protein biochemistry and/or molecular neuroscience preferred.
Share: 🙏
mbg.au.dk/aktuelt/ledi...

Experience in protein biochemistry and/or molecular neuroscience preferred.
Share: 🙏
mbg.au.dk/aktuelt/ledi...
Collaboration and Tour de Force with Richard Wheeler @zephyris-science.bsky.social and many other coauthors.
Big congratulations and thank you to anyone involved!
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
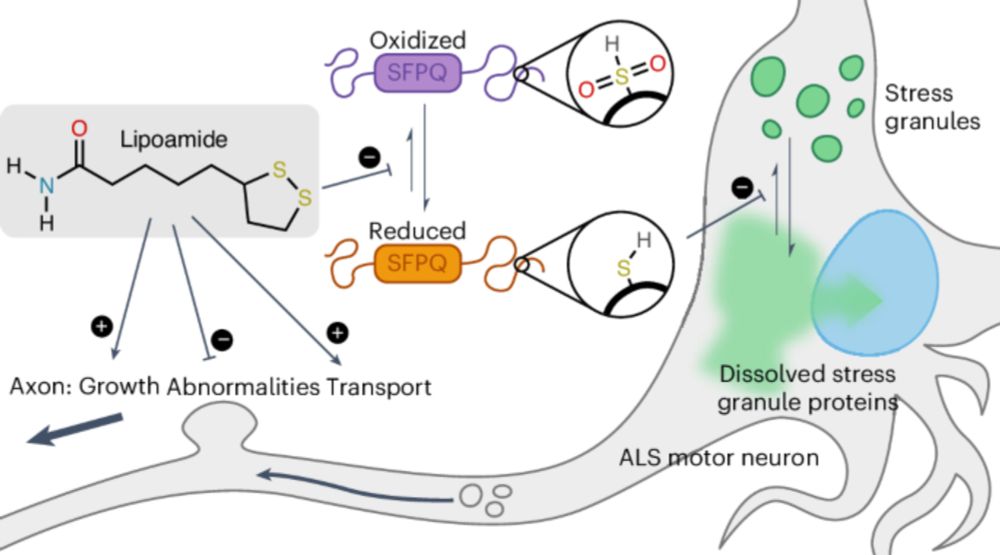
Collaboration and Tour de Force with Richard Wheeler @zephyris-science.bsky.social and many other coauthors.
Big congratulations and thank you to anyone involved!
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Applications coming soon!
@flatironinstitute.org

Applications coming soon!
@flatironinstitute.org
If structure ends up big & central, u’ll render it with PyMol et al, but for a truly schematic depiction u want a biorender-style icon, but for YOUR protein.
Think I’ve finally found a way.
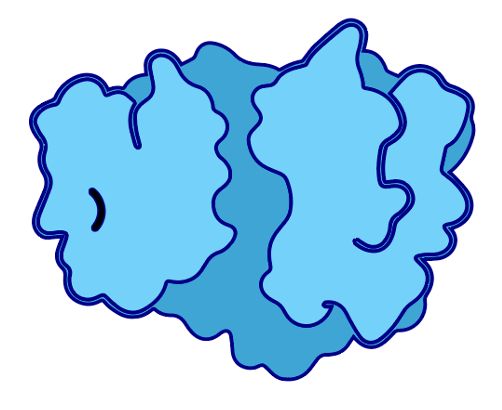

If structure ends up big & central, u’ll render it with PyMol et al, but for a truly schematic depiction u want a biorender-style icon, but for YOUR protein.
Think I’ve finally found a way.
Building AI models or the data to train them?
Core funding of >$130M a year for a faculty of ~30.
www.nature.com/naturecareer...
acrobat.adobe.com/id/urn:aaid:...
pls RT!

Building AI models or the data to train them?
Core funding of >$130M a year for a faculty of ~30.
www.nature.com/naturecareer...
acrobat.adobe.com/id/urn:aaid:...
pls RT!
connecting ‘cell surface RNA biology’ to cancer biology
@natbiotech.nature.com
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
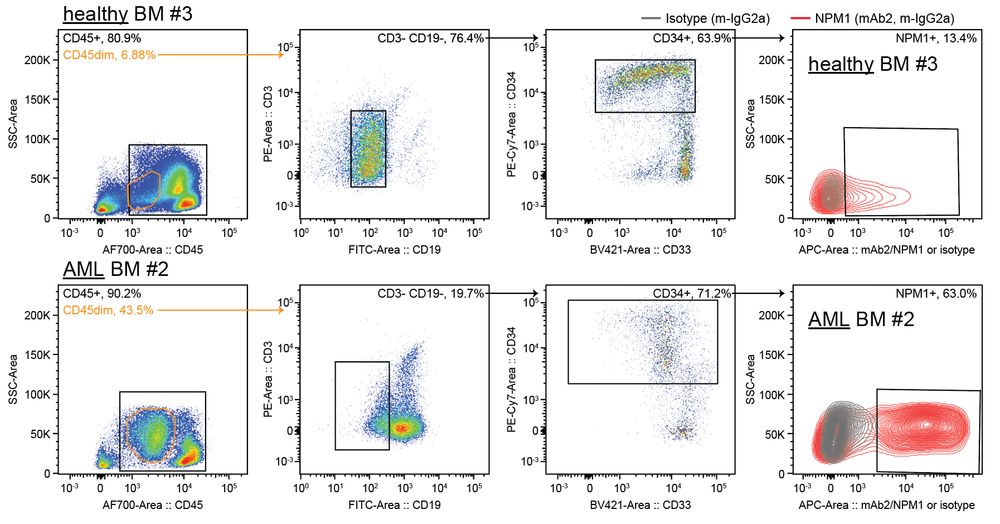
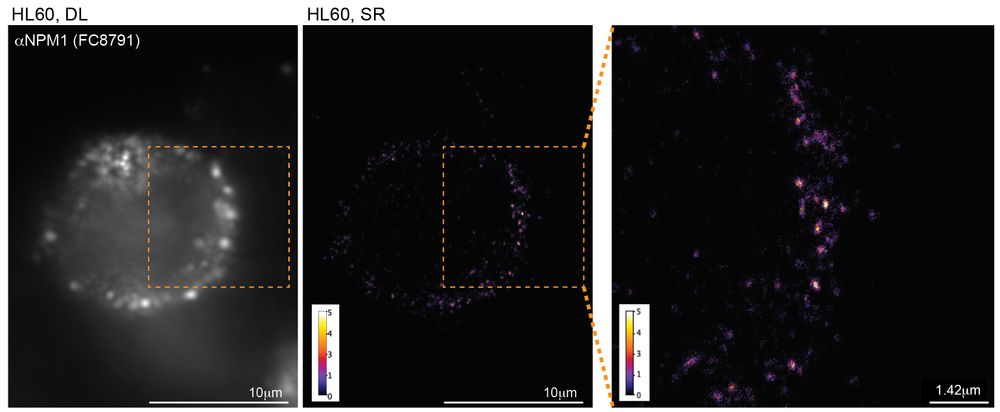
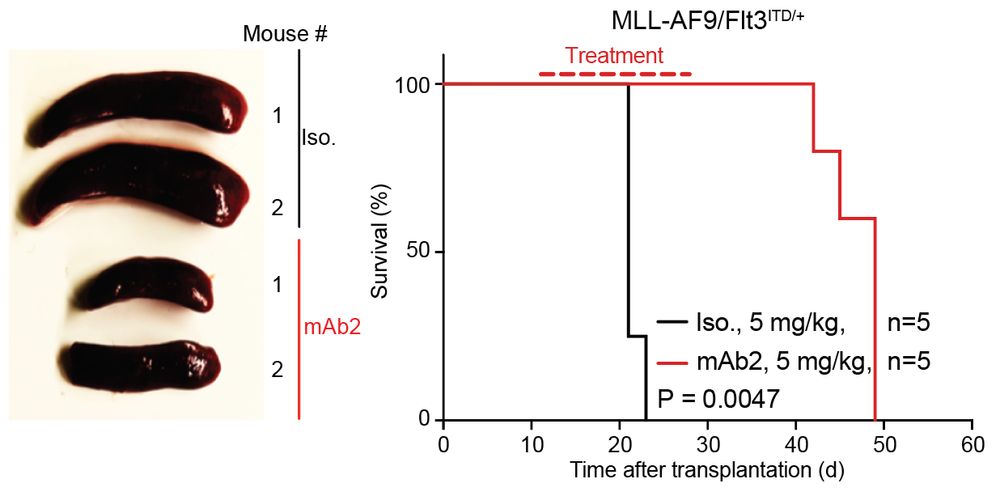
connecting ‘cell surface RNA biology’ to cancer biology
@natbiotech.nature.com
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
chemsymposia.com
chemsymposia.com
"InstaNovo enables diffusion-powered de novo peptide sequencing in large-scale proteomics experiments"
🔗 www.nature.com/articles/s42...
👇 Thread 🧵
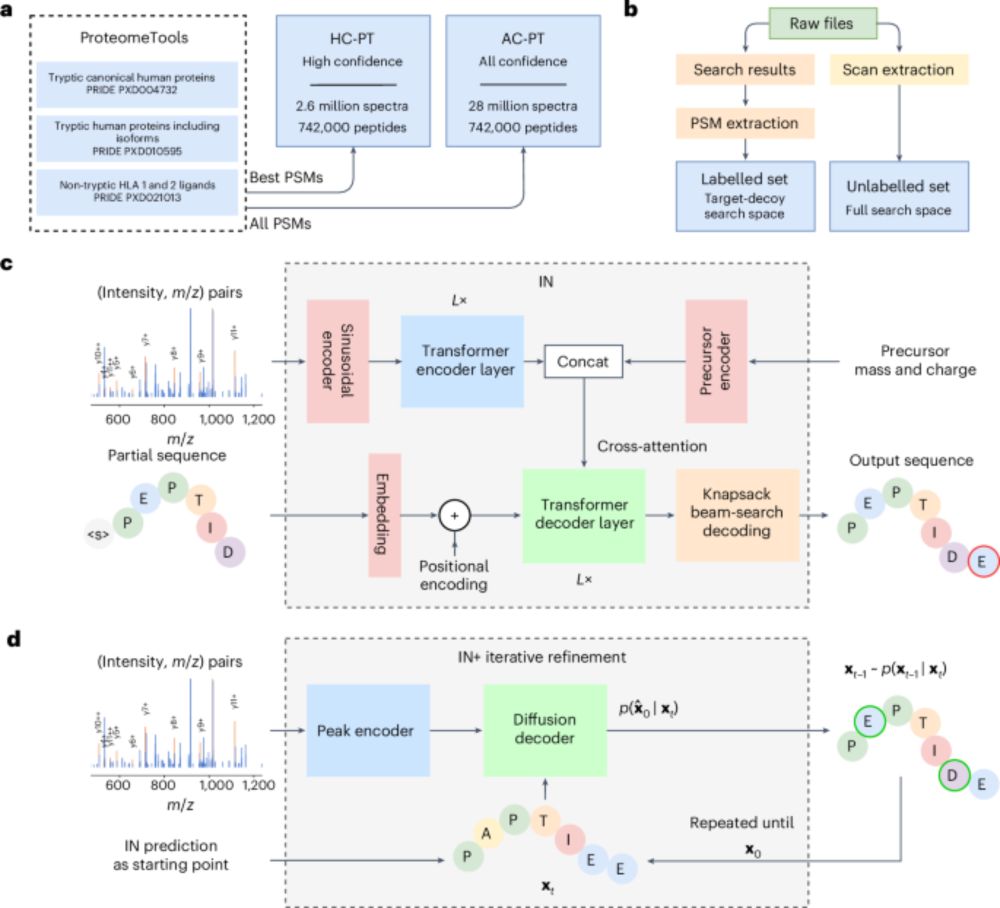
"InstaNovo enables diffusion-powered de novo peptide sequencing in large-scale proteomics experiments"
🔗 www.nature.com/articles/s42...
👇 Thread 🧵
We know proteins fluctuate between different conformations- but by how much? How does it vary from protein to protein? Can highly stable domains have low stability segments? @ajrferrari.bsky.social experimentally tested >5,000 domains to find out!
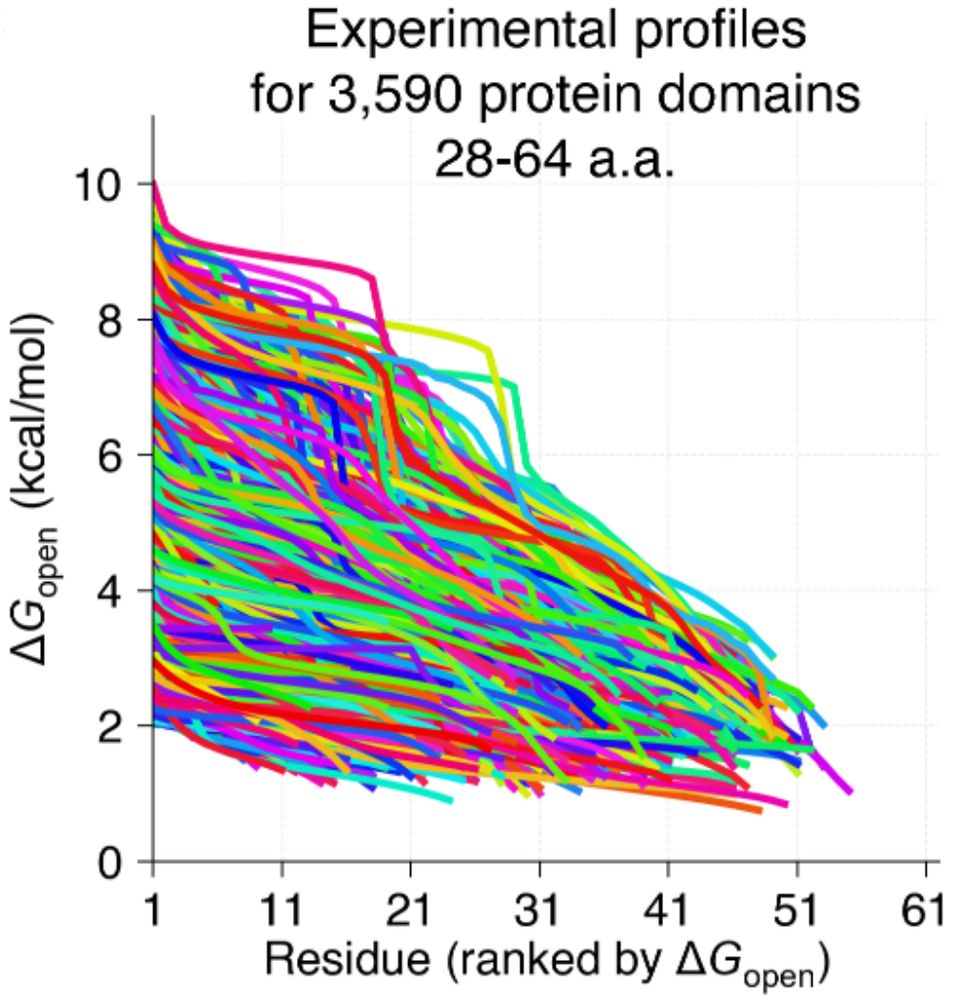
We know proteins fluctuate between different conformations- but by how much? How does it vary from protein to protein? Can highly stable domains have low stability segments? @ajrferrari.bsky.social experimentally tested >5,000 domains to find out!