CRISPR-Cas system, defense system, TA system, phage and microbes.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Thanks to wonderful coauthors/collaborators/friends, the whole @doudna-lab.bsky.social and everyone at @innovativegenomics.bsky.social

Predicting host- #phage interactions from genomics.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

Predicting host- #phage interactions from genomics.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Anti-CRISPR protein hijacks host’s enolase to tackle and block CRISPR-Cas
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

Anti-CRISPR protein hijacks host’s enolase to tackle and block CRISPR-Cas
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
@cp-trendsmicrobiol.bsky.social Spotlight by Kotaro Kiga and Rodrigo Ibarra-Chávez
www.cell.com/trends/micro...

@cp-trendsmicrobiol.bsky.social Spotlight by Kotaro Kiga and Rodrigo Ibarra-Chávez
www.cell.com/trends/micro...

Here’s the story of how we discovered the Metis defense system 👇
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

Here’s the story of how we discovered the Metis defense system 👇
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
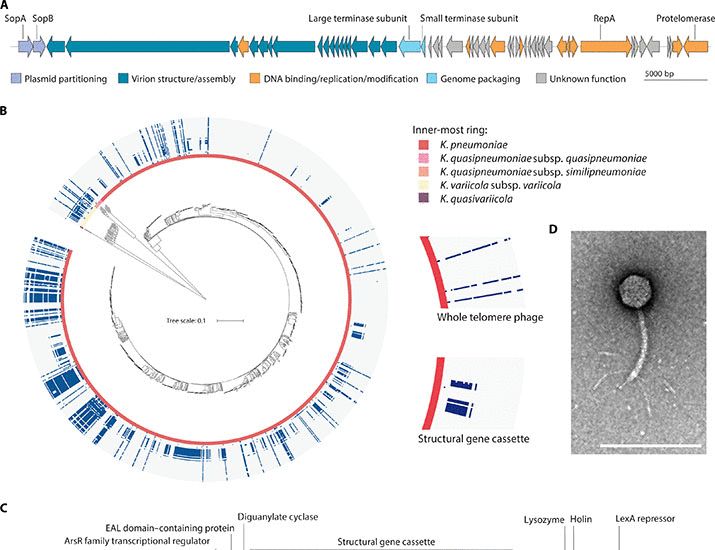
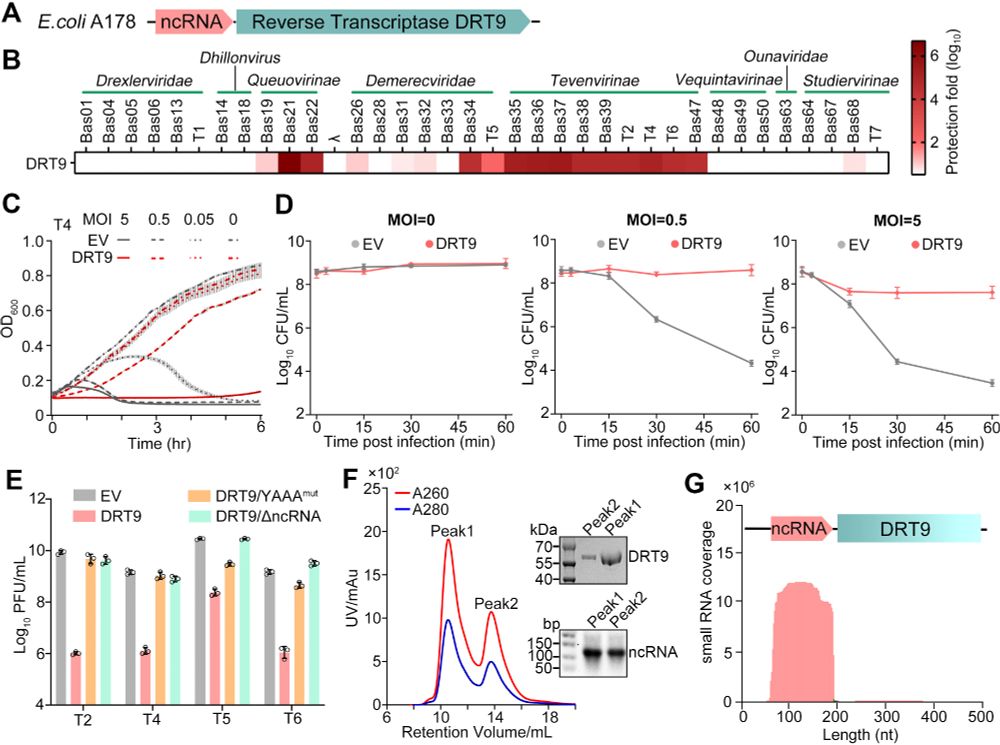
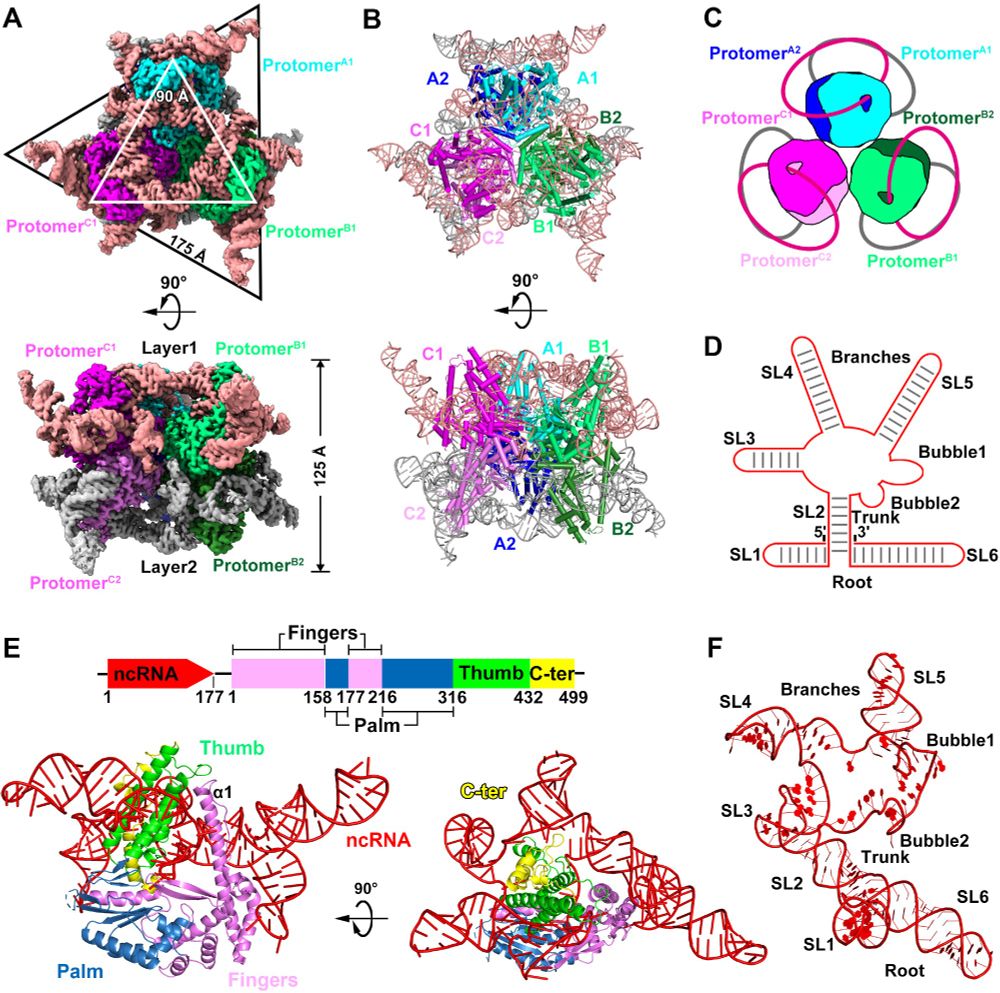
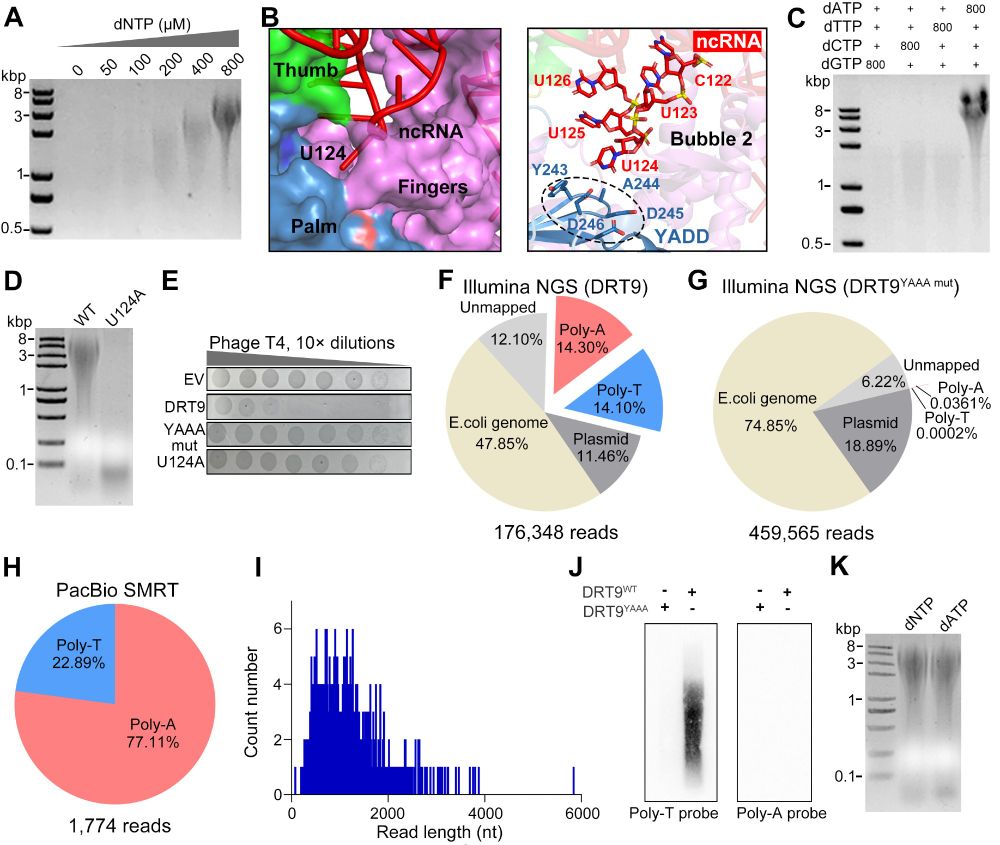
Today, we report the discovery of telomerase homologs in a family of antiviral RTs, revealing an unexpected evolutionary origin in bacteria.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

Today, we report the discovery of telomerase homologs in a family of antiviral RTs, revealing an unexpected evolutionary origin in bacteria.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
But how does piRNA-guided target interaction translate into silencing?
PhD student Júlia Portell Montserrat has an intriguing answer
www.cell.com/molecular-ce...

We report in @science.org the discovery of a human homolog of SIR2 antiphage proteins that participates in the TLR pathway of animal innate immunity.
Co-led wt @enzopoirier.bsky.social by D. Bonhomme and @hugovaysset.bsky.social
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
We report in @science.org the discovery of a human homolog of SIR2 antiphage proteins that participates in the TLR pathway of animal innate immunity.
Co-led wt @enzopoirier.bsky.social by D. Bonhomme and @hugovaysset.bsky.social
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
academic.oup.com/nar/article/...
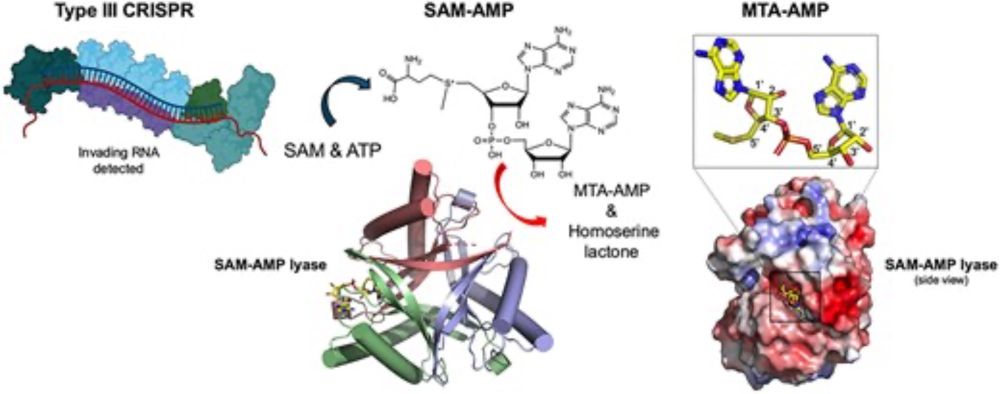
academic.oup.com/nar/article/...
plos.io/4koXP60
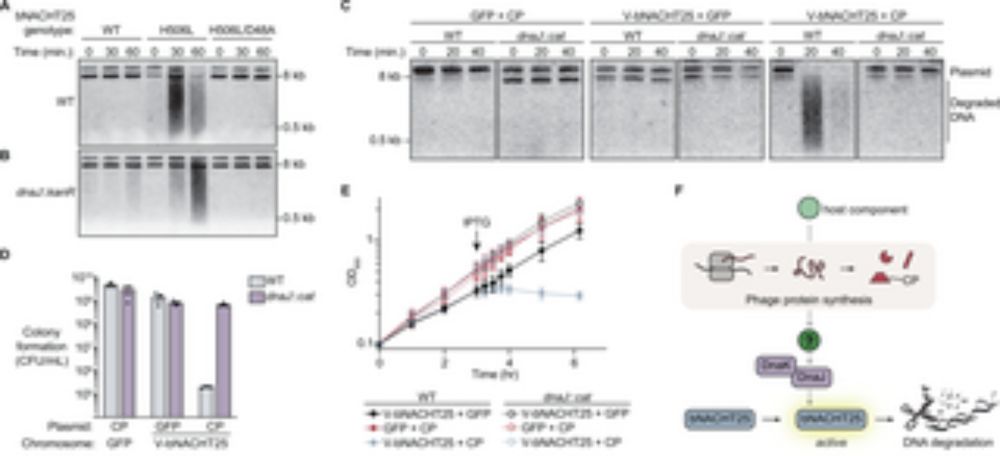
plos.io/4koXP60
We show that a sub-lineage of 7th pandemic V. cholerae has acquired mobile genetic elements packed with phage defense systems—rendering it multi-phage resistant 😳 ..... 1/3
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
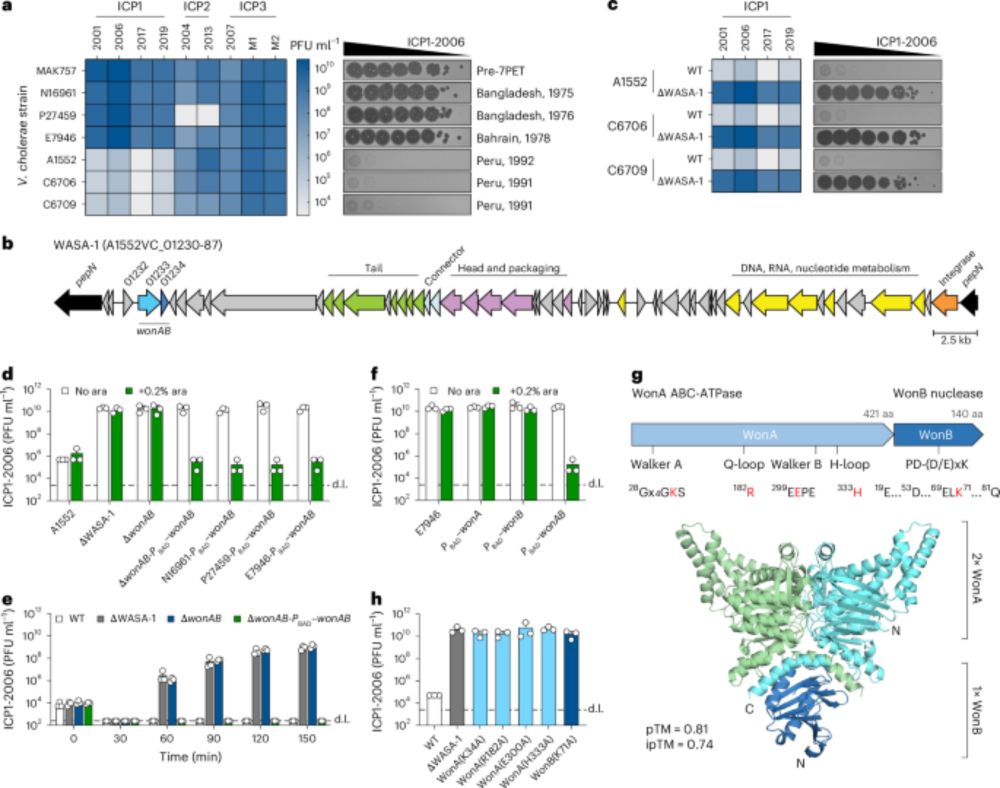
We show that a sub-lineage of 7th pandemic V. cholerae has acquired mobile genetic elements packed with phage defense systems—rendering it multi-phage resistant 😳 ..... 1/3
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Many thanks to everyone involved, especially my supervisor @epcrocha.bsky.social
bsky.app/profile/bapt...
In collaboration with the Rocha lab, we show in our new paper that cassettes of these large platforms encode many known anti-phage defenses, and uncovered 16 new ones.
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
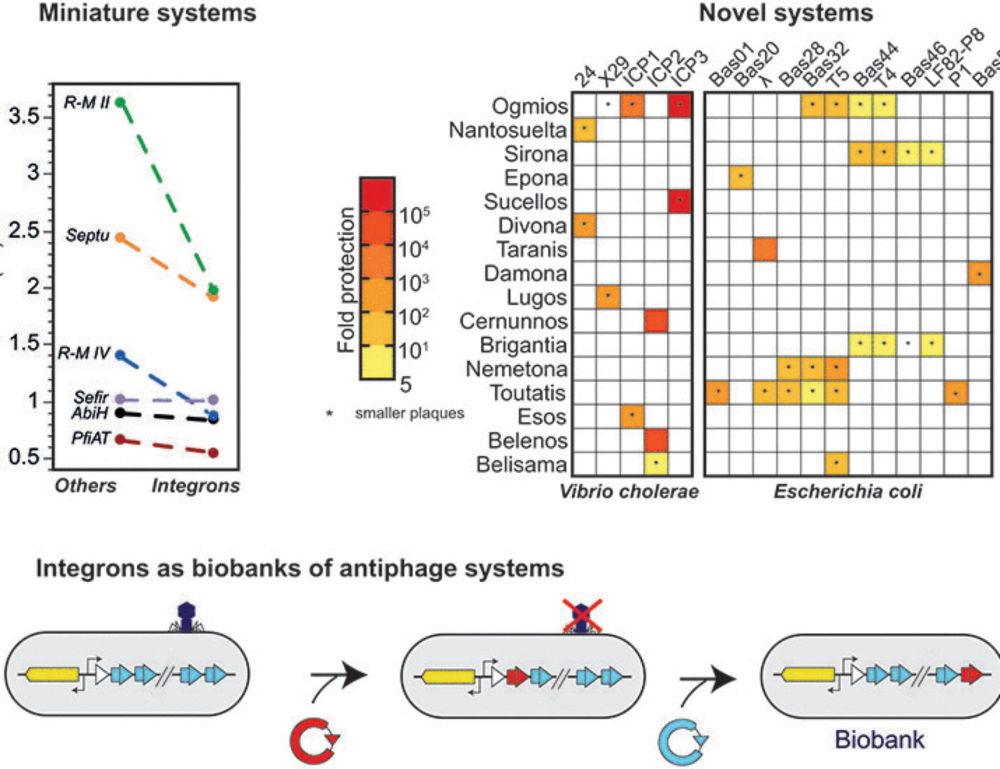
Many thanks to everyone involved, especially my supervisor @epcrocha.bsky.social
bsky.app/profile/bapt...

Finally out after peer review, our work showing that "Mobile #Integrons carry Phage Defense Systems" is now published in Science 🎉
Short 🧵
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...

Finally out after peer review, our work showing that "Mobile #Integrons carry Phage Defense Systems" is now published in Science 🎉
Short 🧵
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
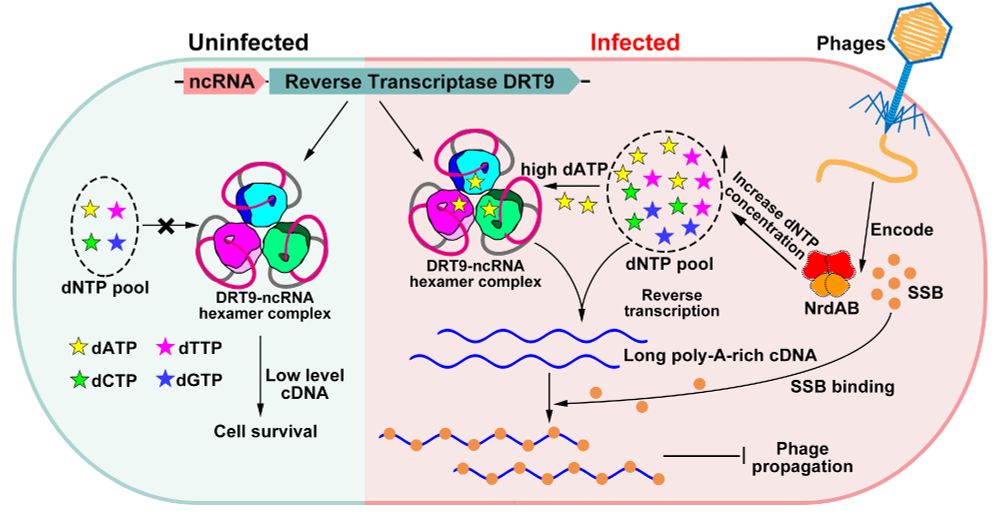
Histidine+ADP-ribose = His-ADPR
New bacterial “danger” molecule made during phage infection
Produced by TIR domains, recognized by Macro domains, and blocked by viral evasion proteins
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

Histidine+ADP-ribose = His-ADPR
New bacterial “danger” molecule made during phage infection
Produced by TIR domains, recognized by Macro domains, and blocked by viral evasion proteins
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
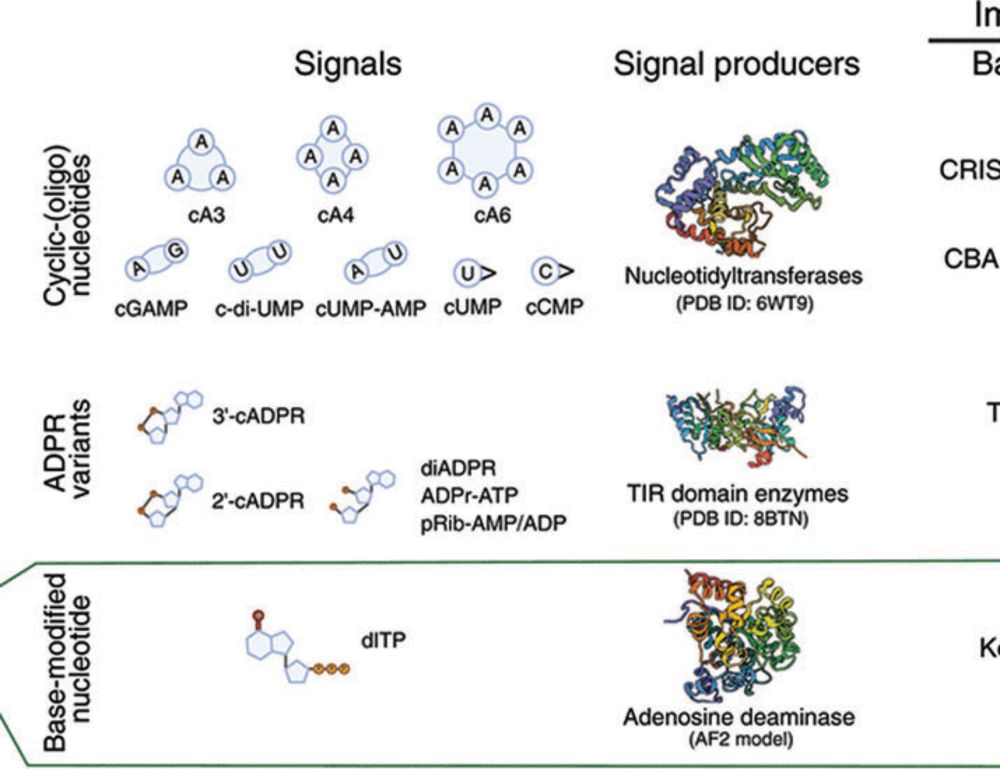
Base-modified nucleotides mediate immune signaling in bacteria
@science.org #microsky
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...

Base-modified nucleotides mediate immune signaling in bacteria
@science.org #microsky
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
But scientists have only begun to unlock the secrets of this ancient arms race
https://go.nature.com/4lD4LOa
But scientists have only begun to unlock the secrets of this ancient arms race
https://go.nature.com/4lD4LOa


