
📷: Sicilian landscape
Preprint: www.biorxiv.org/content/10.6...
Models/data (UbiqCore website): dunbrack.fccc.edu/ubiqcore

Preprint: www.biorxiv.org/content/10.6...
Models/data (UbiqCore website): dunbrack.fccc.edu/ubiqcore
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
co-first with: @andschwarz.bsky.social
with: @lea-dietrich.bsky.social, @sgiando.bsky.social, @erin-schuman.bsky.social and many more
🧵 0/6
#MolBio 🧪
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
co-first with: @andschwarz.bsky.social
with: @lea-dietrich.bsky.social, @sgiando.bsky.social, @erin-schuman.bsky.social and many more
🧵 0/6
#MolBio 🧪
Link: www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Link: www.nature.com/articles/s41...
I’m delighted to share that registration is now open for the UK Proteostasis Meeting 2026, hosted by The Francis Crick Institute on 20–21 July 2026 .
Please register here(lnkd.in/ervXMzWN) and through Eventbrite for payment (lnkd.in/eTxqjnQy)

I’m delighted to share that registration is now open for the UK Proteostasis Meeting 2026, hosted by The Francis Crick Institute on 20–21 July 2026 .
Please register here(lnkd.in/ervXMzWN) and through Eventbrite for payment (lnkd.in/eTxqjnQy)
go.nature.com/4kwdCRy

go.nature.com/4kwdCRy
link.springer.com/article/10.1...

link.springer.com/article/10.1...

What’s new?
New1 (eEF3 homolog) stops ribosomes from stalling at C-terminal AAA/AGG/CGU codons. No New1 = collisions + Hel2 recruitment + Cue2-mediated no-go decay.
What’s new?
New1 (eEF3 homolog) stops ribosomes from stalling at C-terminal AAA/AGG/CGU codons. No New1 = collisions + Hel2 recruitment + Cue2-mediated no-go decay.

TL;DR: We use CRISPR screens in iPSC-derived neurons to find a new tau E3 ligase and a relationship between oxidative stress, the proteasome, and tau proteolytic fragments.
More below 👇

TL;DR: We use CRISPR screens in iPSC-derived neurons to find a new tau E3 ligase and a relationship between oxidative stress, the proteasome, and tau proteolytic fragments.
More below 👇
CRISPR screens in iPSC-derived neurons reveal principles of tau proteostasis
www.cell.com/cell/fulltex...
Great collaborative effort - read more from first author @asamelson.bsky.social below:
CRISPR screens in iPSC-derived neurons reveal principles of tau proteostasis
www.cell.com/cell/fulltex...
Great collaborative effort - read more from first author @asamelson.bsky.social below:

https://doi:10.1111/febs.70259
The SARS-CoV-2 spike protein interacts with HAX1 to modulate cellular stress responses through activation of the UPR
https://doi:10.1111/febs.70259
The SARS-CoV-2 spike protein interacts with HAX1 to modulate cellular stress responses through activation of the UPR
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

www.nature.com/articles/s41...

Artwork by the incredibly talented @doroteaartscience.bsky.social 👇
Cover: Flexibility of #autophagy initiation
👉🏼Review on #metabolism in #embryogenesis #devbio
👉🏼Review on #DNArepair
🔬 #ribosomes #neurodevelopment #mitophagy #ferroptosis #stemcells #epigenetics #leukemia #antitumor immunity & more!
www.nature.com/ncb/volumes/...

Artwork by the incredibly talented @doroteaartscience.bsky.social 👇
👇 for @zaffagg3 's detailed explanation
www.embopress.org/doi/full/10....
👇 for @zaffagg3 's detailed explanation
www.embopress.org/doi/full/10....
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
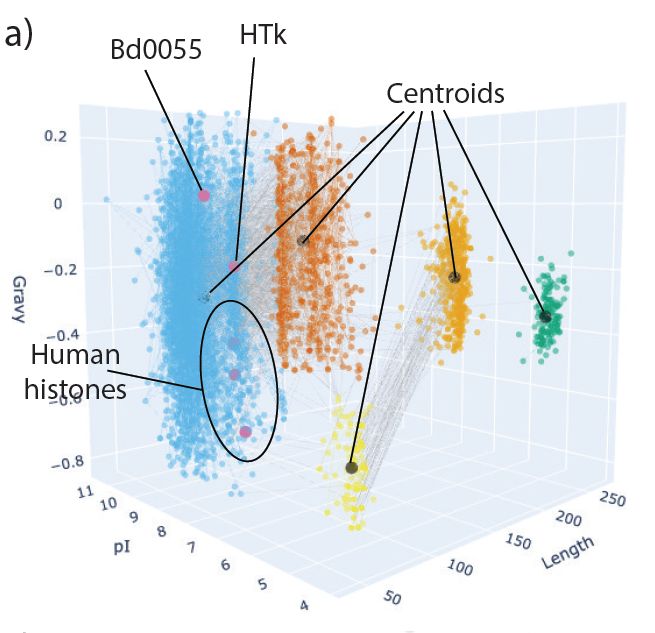
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...



