
[alternative splicing]
MD-PhD student @jacksonlab.bsky.social, @uconnresearch.bsky.social

Our virtual course offers exposure to clinical decision-making in #PrecisionOncology: www.jax.org/news-and-ins...

Our virtual course offers exposure to clinical decision-making in #PrecisionOncology: www.jax.org/news-and-ins...
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...



I cannot emphasize enough how dangerous it is to dismantle our disease surveillance infrastructure.
I cannot emphasize enough how dangerous it is to dismantle our disease surveillance infrastructure.

@jamiehackett.bsky.social et al @embl.org see transcriptome changes in offspring after fertilisation by fathers exposed to gut dysbiosis or western diet
www.embopress.org/doi/full/10....

@jamiehackett.bsky.social et al @embl.org see transcriptome changes in offspring after fertilisation by fathers exposed to gut dysbiosis or western diet
www.embopress.org/doi/full/10....
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
The results revealed 𝐜𝐨𝐦𝐩𝐥𝐞𝐱 regulation & 𝐬𝐢𝐦𝐩𝐥𝐞 organizing principles:
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
🧵

The results revealed 𝐜𝐨𝐦𝐩𝐥𝐞𝐱 regulation & 𝐬𝐢𝐦𝐩𝐥𝐞 organizing principles:
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
🧵

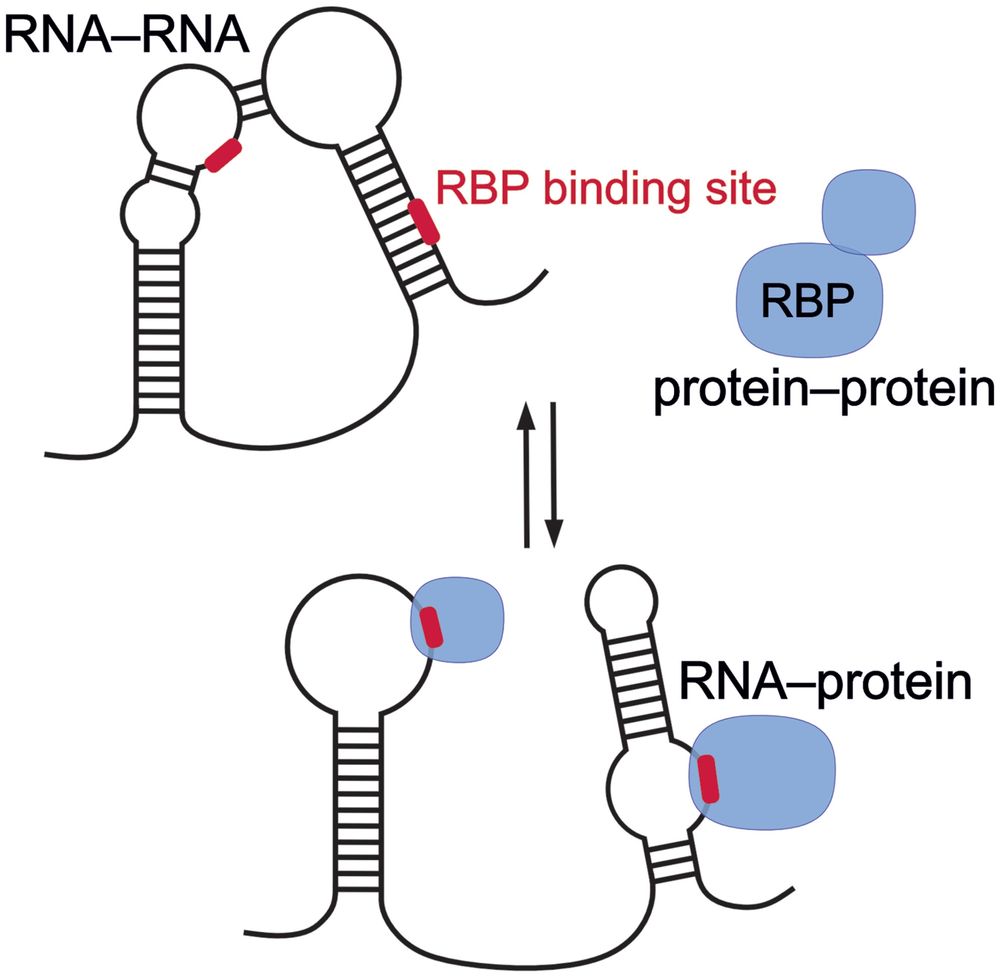
Delighted to share the story of two germline RBPs - one with little (DND1) and one with no (NANOS3) intrinsic sequence-specificity - that together build a continuous RNA binding surface recognizing a 7-mer (AUGAAUU) in target mRNA 3’UTRs, leading to deadenylation.

Delighted to share the story of two germline RBPs - one with little (DND1) and one with no (NANOS3) intrinsic sequence-specificity - that together build a continuous RNA binding surface recognizing a 7-mer (AUGAAUU) in target mRNA 3’UTRs, leading to deadenylation.

The regulation of most proteins is dominated by different regulatory mechanisms across cell types.
Gratifyingly, this complex regulation defines simple rules ⬇️
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

The regulation of most proteins is dominated by different regulatory mechanisms across cell types.
Gratifyingly, this complex regulation defines simple rules ⬇️
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Dissection of CDX2 regulatory elements identifies a repressive element that converts to an enhancer with a nuclear receptor motif switch
www.cell.com/developmenta...

Dissection of CDX2 regulatory elements identifies a repressive element that converts to an enhancer with a nuclear receptor motif switch
www.cell.com/developmenta...

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

A great collaboration with @kurianlab.bsky.social that began with how an RBP (QKI) controls cardiomyocyte function, and led to uncovering a unique mechanism of direct interaction with U6 & the tri-snRNP at weak 5'SS

A great collaboration with @kurianlab.bsky.social that began with how an RBP (QKI) controls cardiomyocyte function, and led to uncovering a unique mechanism of direct interaction with U6 & the tri-snRNP at weak 5'SS
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...



