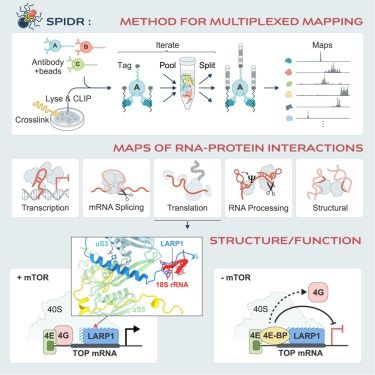
Delighted to share the story of two germline RBPs - one with little (DND1) and one with no (NANOS3) intrinsic sequence-specificity - that together build a continuous RNA binding surface recognizing a 7-mer (AUGAAUU) in target mRNA 3’UTRs, leading to deadenylation.
Delighted to share the story of two germline RBPs - one with little (DND1) and one with no (NANOS3) intrinsic sequence-specificity - that together build a continuous RNA binding surface recognizing a 7-mer (AUGAAUU) in target mRNA 3’UTRs, leading to deadenylation.

Delighted to share the story of two germline RBPs - one with little (DND1) and one with no (NANOS3) intrinsic sequence-specificity - that together build a continuous RNA binding surface recognizing a 7-mer (AUGAAUU) in target mRNA 3’UTRs, leading to deadenylation.

Delighted to share the story of two germline RBPs - one with little (DND1) and one with no (NANOS3) intrinsic sequence-specificity - that together build a continuous RNA binding surface recognizing a 7-mer (AUGAAUU) in target mRNA 3’UTRs, leading to deadenylation.
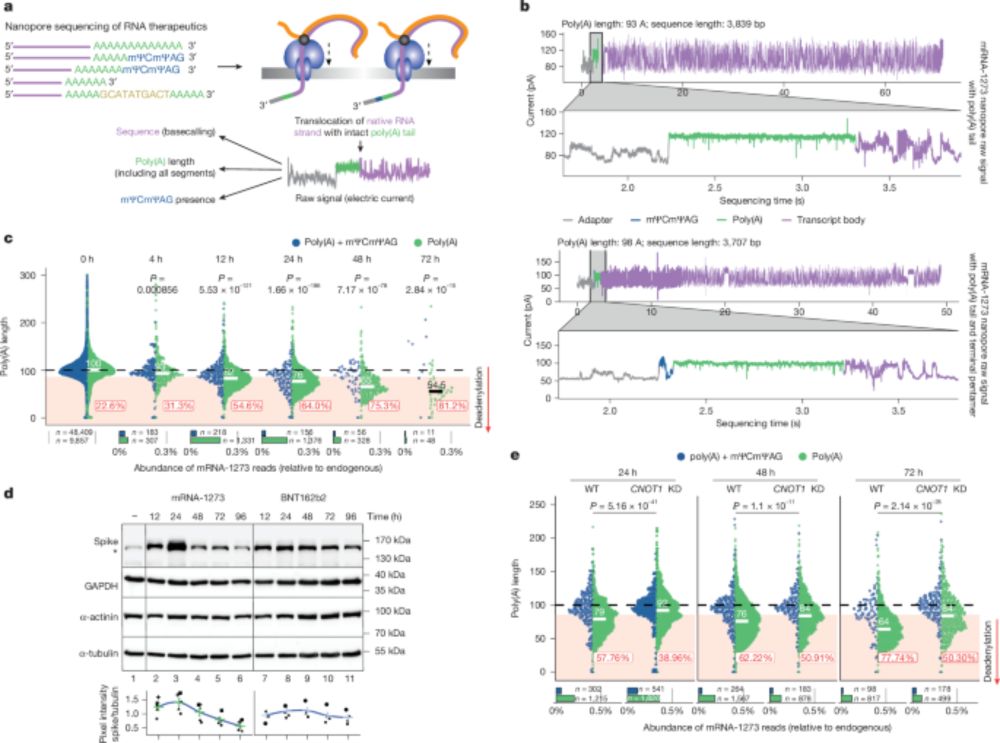
Paper 1 -- an AI model trained to predict translation rates from mRNA sequences: rdcu.be/exN1l
Paper 1 -- an AI model trained to predict translation rates from mRNA sequences: rdcu.be/exN1l
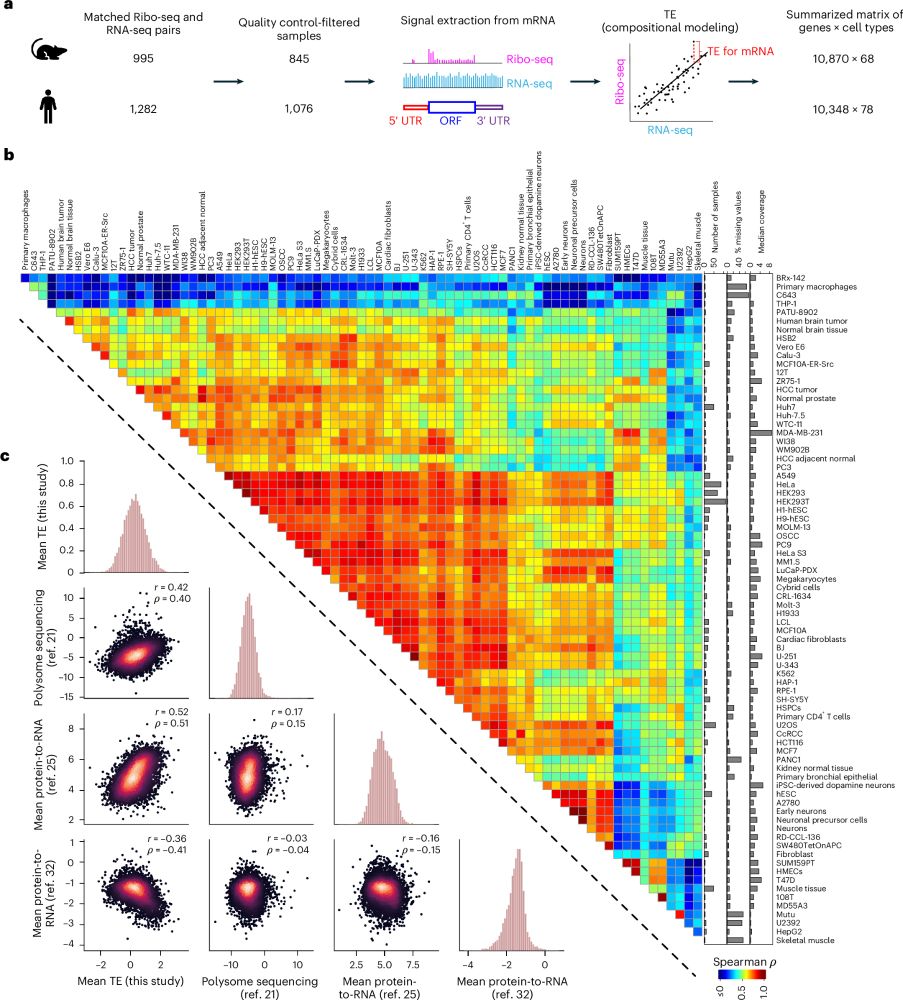
www.nature.com/articles/s41... Intracellular pathogen effector reprograms host gene expression by inhibiting mRNA decay | Nature Communications
www.nature.com/articles/s41... Intracellular pathogen effector reprograms host gene expression by inhibiting mRNA decay | Nature Communications

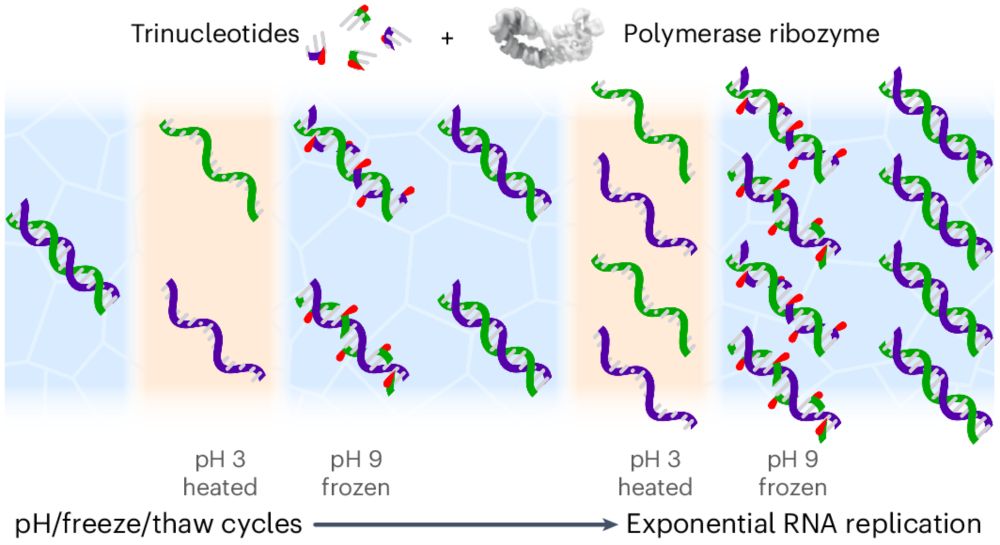
www.cell.com/cell/fulltex...
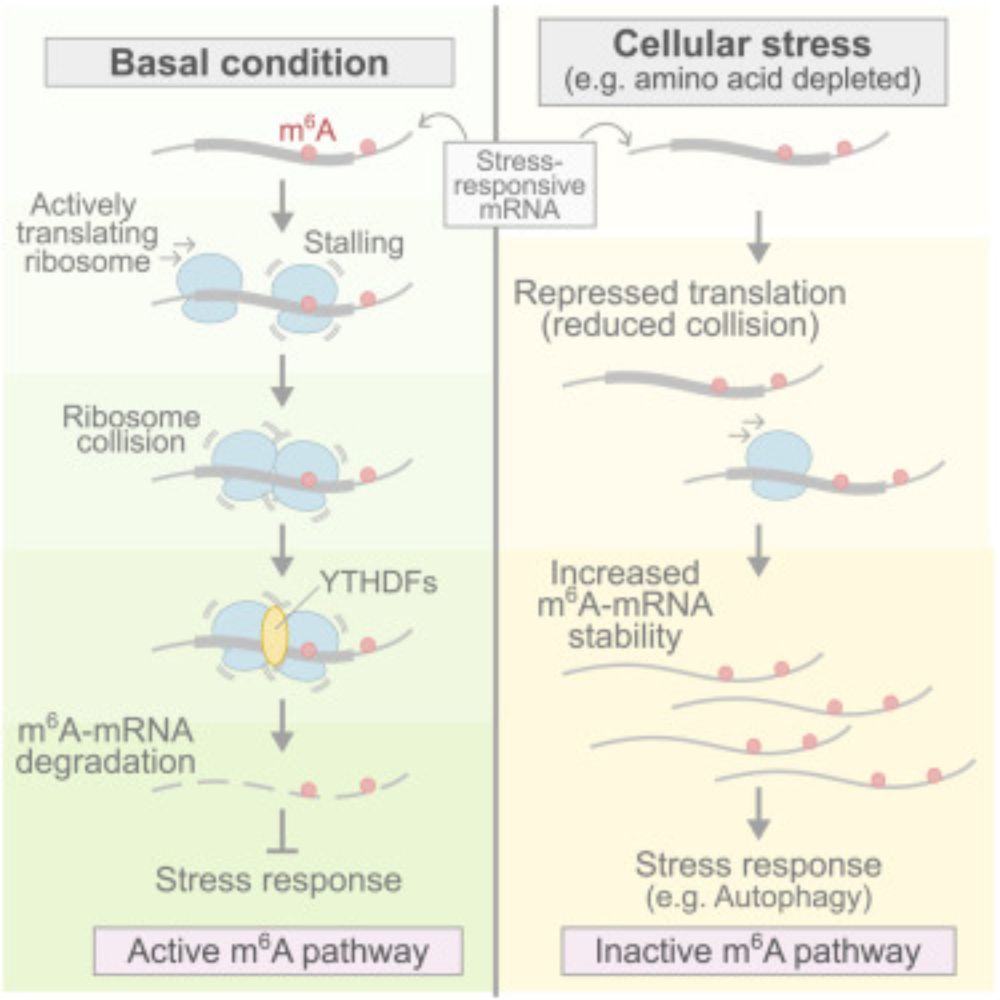
www.cell.com/cell/fulltex...
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...

www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
Learn more about her fascinating work investigating #phenotypic plasticity & chemo resistance in colorectal cancer here: www.abstractsonline.com/pp8/#!/20273...

Learn more about her fascinating work investigating #phenotypic plasticity & chemo resistance in colorectal cancer here: www.abstractsonline.com/pp8/#!/20273...
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Yizhuang Zhang et al show that loss of maternal Rbm24a causes complete degradation of germ granules and disappearance of primordial germ cells
www.embopress.org/doi/full/10....

Yizhuang Zhang et al show that loss of maternal Rbm24a causes complete degradation of germ granules and disappearance of primordial germ cells
www.embopress.org/doi/full/10....
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

"The integrated stress response pathway controls cytokine production in tissue-resident memory CD4+ T cells"
@natureportfolio.nature.com
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

"The integrated stress response pathway controls cytokine production in tissue-resident memory CD4+ T cells"
@natureportfolio.nature.com
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

@cancer-inst-purdue.bsky.social danzhou-yang.com #DNA #StructuralBiology
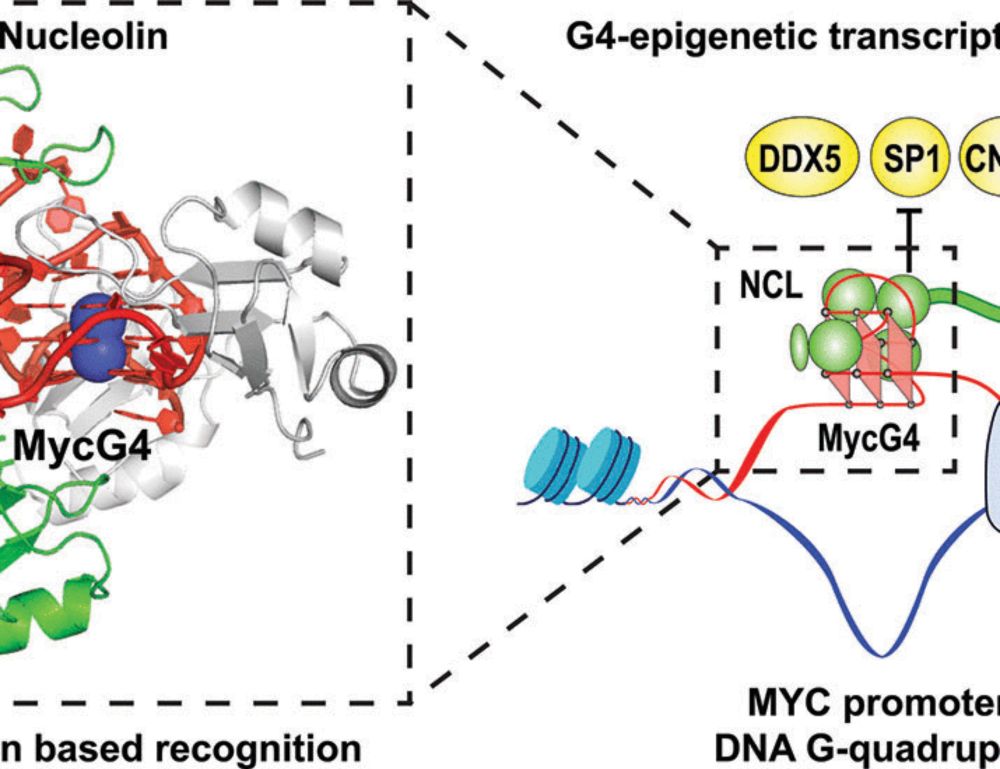
@cancer-inst-purdue.bsky.social danzhou-yang.com #DNA #StructuralBiology
#RNA #Ribosome
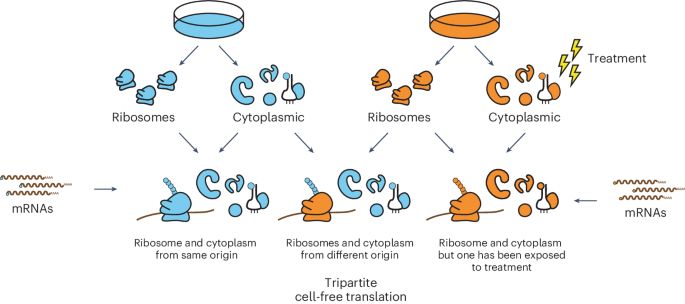
@nature.com
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

@nature.com
www.nature.com/articles/s41...