Translation in bacteria, mammal| Ribosome | Host-Microbe |


In @natmethods.nature.com we propose using "Translon" for any region decoded by the ribosome

In @natmethods.nature.com we propose using "Translon" for any region decoded by the ribosome
go.nature.com/4mmSygd

go.nature.com/4mmSygd


More than 2700 human 3′UTRs are highly conserved. These 3′UTRs are essential components in mRNA templates, as their deletion decreases protein activity without changing protein abundance. Highly conserved 3′UTRs help the folding of proteins with long IDRs.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
More than 2700 human 3′UTRs are highly conserved. These 3′UTRs are essential components in mRNA templates, as their deletion decreases protein activity without changing protein abundance. Highly conserved 3′UTRs help the folding of proteins with long IDRs.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
We find (>800!) 30S binding sites in hundreds of 5'UTRs, but also new dynamic steps of translation initiation.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Congrats to all co-authors at the RNA control of gene expression lab, IBPC CNRS
(Thread, 1/6)

We find (>800!) 30S binding sites in hundreds of 5'UTRs, but also new dynamic steps of translation initiation.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Congrats to all co-authors at the RNA control of gene expression lab, IBPC CNRS
(Thread, 1/6)

www.cell.com/cell/fulltex...
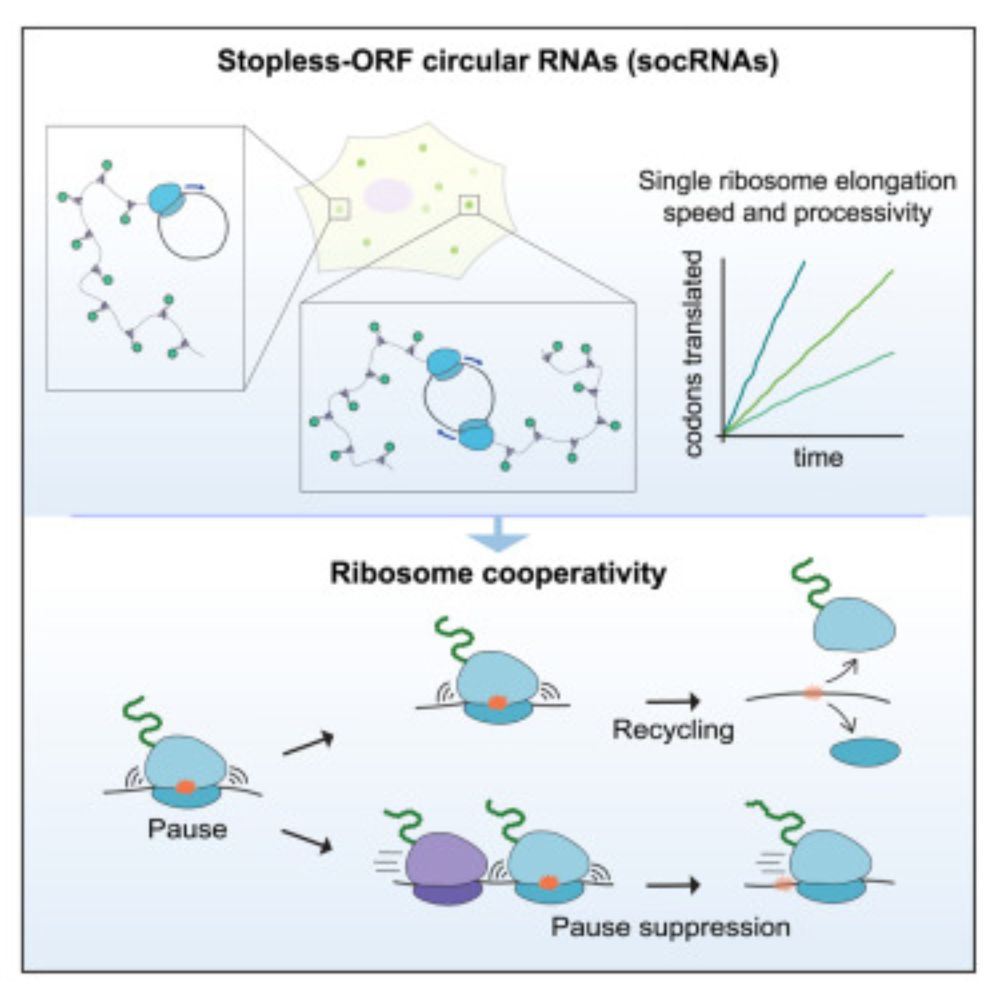
www.cell.com/cell/fulltex...
Highly multiplexed spatial transcriptomics in bacteria | Science www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
#microsky #microbial #microbiology #genomics
#transcriptomic 🦠🧫

Highly multiplexed spatial transcriptomics in bacteria | Science www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
#microsky #microbial #microbiology #genomics
#transcriptomic 🦠🧫
Answering a two-centuries old question about a membraneless organelle that forms in #oocytes from insects to humans: the Balbiani body (Bb).
Now in
@currentbiology.bsky.social
:
cell.com/current-biol...
>
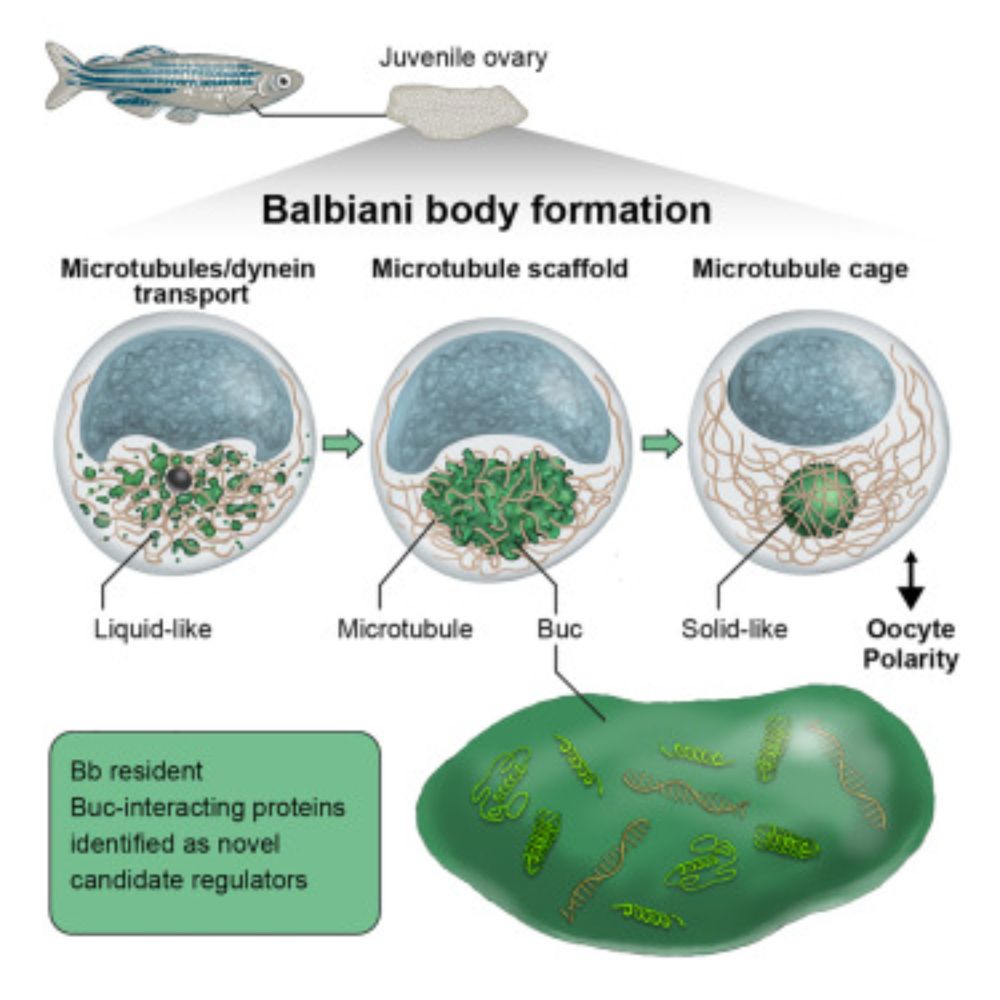
Answering a two-centuries old question about a membraneless organelle that forms in #oocytes from insects to humans: the Balbiani body (Bb).
Now in
@currentbiology.bsky.social
:
cell.com/current-biol...
>
遺伝子間の共起パターンを使用した言語モデルによって目的の機能を持つ新規配列を生成する手法(Evo)を開発。既知のタンパク質と相同性の低い全く新しい毒素やantiCRISPRを作ることができるらしい。AI生成ゲノム配列も作成
すごすぎて、、

遺伝子間の共起パターンを使用した言語モデルによって目的の機能を持つ新規配列を生成する手法(Evo)を開発。既知のタンパク質と相同性の低い全く新しい毒素やantiCRISPRを作ることができるらしい。AI生成ゲノム配列も作成
すごすぎて、、


