www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...

www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
Thanks to wonderful coauthors/collaborators/friends, the whole @doudna-lab.bsky.social and everyone at @innovativegenomics.bsky.social

Thanks to wonderful coauthors/collaborators/friends, the whole @doudna-lab.bsky.social and everyone at @innovativegenomics.bsky.social
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
@unmc.bsky.social @uwbiochem.bsky.social

www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
@unmc.bsky.social @uwbiochem.bsky.social
Learn more in #ScienceImmunology: https://scim.ag/43ewTiV

Learn more in #ScienceImmunology: https://scim.ag/43ewTiV
@cedarssinai.bsky.social
rdcu.be/eNIFY

@cedarssinai.bsky.social
rdcu.be/eNIFY
Our memory T cells undergo a dramatic shift resulting in dysregulated B cell antibody production
@alleninstitute.org @nature.com
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

Our memory T cells undergo a dramatic shift resulting in dysregulated B cell antibody production
@alleninstitute.org @nature.com
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Enhanced DNA repair
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
erictopol.substack.com/p/a-long-awa...

Enhanced DNA repair
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
erictopol.substack.com/p/a-long-awa...
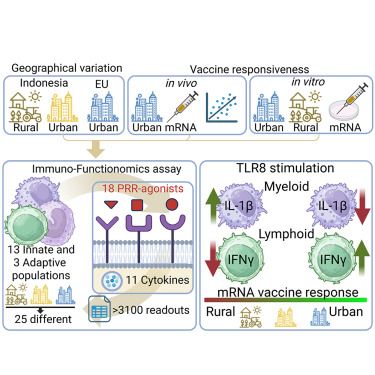
Check out our latest Oligo investigation led by @pryprk.bsky.social !
Read our two companion papers:
🔹 www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
🔹 www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
🧵 Highlights below!
Check out our latest Oligo investigation led by @pryprk.bsky.social !
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Caviar for RNA-Seq nerds! Check this out

www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Caviar for RNA-Seq nerds! Check this out
Today, we report the discovery of telomerase homologs in a family of antiviral RTs, revealing an unexpected evolutionary origin in bacteria.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

Today, we report the discovery of telomerase homologs in a family of antiviral RTs, revealing an unexpected evolutionary origin in bacteria.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
A fantastic collaboration with Antoine, with Jovana Kaljevic' initiated the collaboration and drives the project.

A fantastic collaboration with Antoine, with Jovana Kaljevic' initiated the collaboration and drives the project.
@science.org
science.org/doi/10.1126/...
science.org/doi/10.1126/...
www.nature.com/articles/d41...

@science.org
science.org/doi/10.1126/...
science.org/doi/10.1126/...
www.nature.com/articles/d41...
~27,000 predicted viral protein monomers & homodimers
Conserved folds across bacteria, archaea & eukaryotic viruses
New toxin–antitoxin system KreTA uncovered
Vast “functional darkness” remains uncharted
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...

~27,000 predicted viral protein monomers & homodimers
Conserved folds across bacteria, archaea & eukaryotic viruses
New toxin–antitoxin system KreTA uncovered
Vast “functional darkness” remains uncharted
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
🔗 www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

🔗 www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
🧬 💻 🧪
academic.oup.com/mbe/article/...
pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC...

🧬 💻 🧪
academic.oup.com/mbe/article/...
pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC...
It was a huge privilege when @shenwei356.bsky.social
joined our group for a year on an @embl.org sabbatical.
While here, he developed a new way of aligning to
millions of bacteria, called LexicMap 1/n
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

It was a huge privilege when @shenwei356.bsky.social
joined our group for a year on an @embl.org sabbatical.
While here, he developed a new way of aligning to
millions of bacteria, called LexicMap 1/n
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

Our approach allows silencing defense systems of choice. We show how this approach enables programming of “untransformable” bacteria, and how it can enhance phage therapy applications
Congrats Jeremy Garb!
tinyurl.com/Syttt
🧵

Our approach allows silencing defense systems of choice. We show how this approach enables programming of “untransformable” bacteria, and how it can enhance phage therapy applications
Congrats Jeremy Garb!
tinyurl.com/Syttt
🧵
www.cell.com/cell/fulltex...

www.cell.com/cell/fulltex...
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
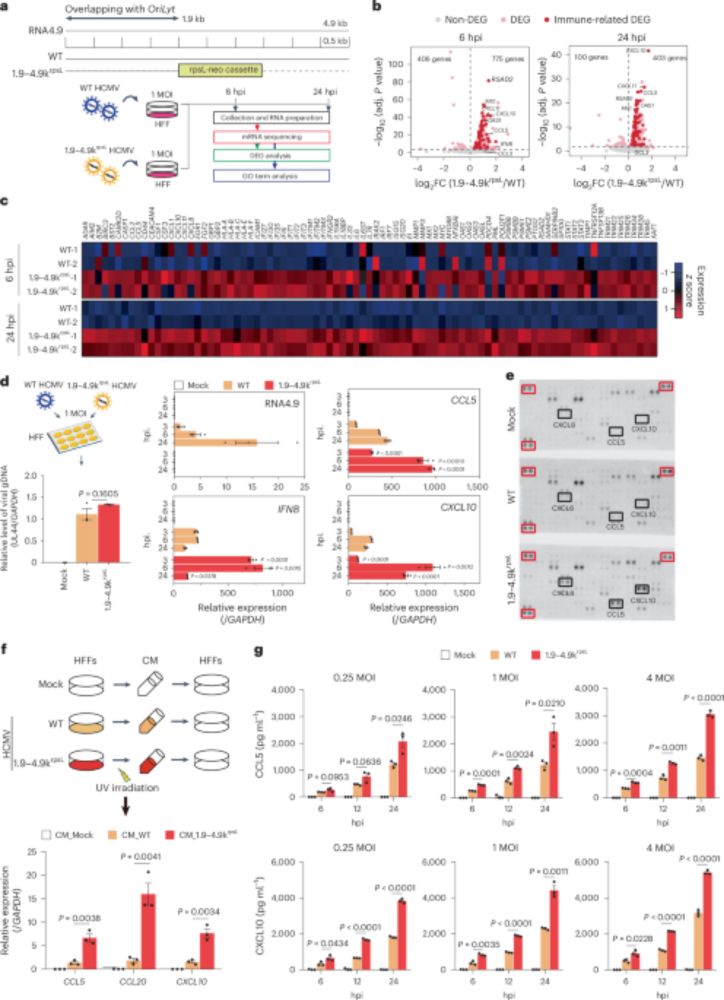
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

