A big step for precision medicine!
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

A big step for precision medicine!
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

The SPRQ-Nx chemistry, now in beta access, delivers complete genomes for under $300 at scale.
View the press release: bit.ly/4o06eyH

The SPRQ-Nx chemistry, now in beta access, delivers complete genomes for under $300 at scale.
View the press release: bit.ly/4o06eyH
We have ingested the full dataset of over 13 million enhancer-gene regulatory interactions in the human genome across 1,458 DNase-seq experiments covering 369 cell types and tissues from the ENCODE-rE2G model
blog.opentargets.org/open-targets...

We have ingested the full dataset of over 13 million enhancer-gene regulatory interactions in the human genome across 1,458 DNase-seq experiments covering 369 cell types and tissues from the ENCODE-rE2G model
blog.opentargets.org/open-targets...



Kelli Letho, a new ERC Starting Grantee at the University of Tartu will dissect the causal mechanisms of adult ADHD features
More 👉 buff.ly/nci5eve
#ERCStG #FontierResearch @klehto.bsky.social

Maternal and paternal alleles can have distinct — even opposite — effects on human traits, revealing a hidden layer of genetic architecture that standard GWAS miss.
🔗 www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Highlights below!
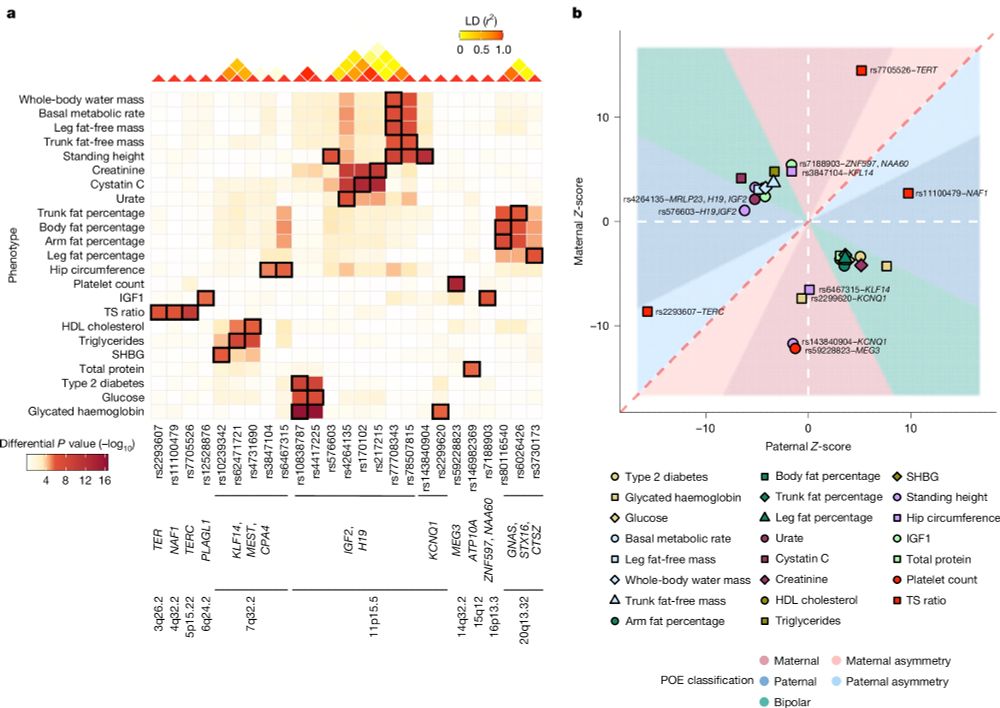
Maternal and paternal alleles can have distinct — even opposite — effects on human traits, revealing a hidden layer of genetic architecture that standard GWAS miss.
🔗 www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Highlights below!
Polygenic and pharmacogenomic contributions to medication dosing: a real-world longitudinal biobank study
🔗 tinyurl.com/25u3a5j7
(thread below) 👇

Polygenic and pharmacogenomic contributions to medication dosing: a real-world longitudinal biobank study
🔗 tinyurl.com/25u3a5j7
(thread below) 👇
We investigated genetic factors linked to antidepressant side effects in 13,000 individuals from the @estbiobank.bsky.social , leveraging data from questionnaires and clinical notes using NLP.
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

We investigated genetic factors linked to antidepressant side effects in 13,000 individuals from the @estbiobank.bsky.social , leveraging data from questionnaires and clinical notes using NLP.
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
@naturemedicine.bsky.social by my team @scripps.edu
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

@naturemedicine.bsky.social by my team @scripps.edu
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Assessment of a Polygenic Risk Score in Screening for Prostate Cancer www.nejm.org/doi/full/10....

Assessment of a Polygenic Risk Score in Screening for Prostate Cancer www.nejm.org/doi/full/10....
We highlight the unique features of the biobank and the conducted scientific research it has enabled, including the many recall studies that have been carried out over the years!
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

We highlight the unique features of the biobank and the conducted scientific research it has enabled, including the many recall studies that have been carried out over the years!
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
We explored this by analyzing 20 years of digital drug dispensing data linked to the @ESTbiobank which hosts 212,000 genotyped participants. 🧵
📄 doi.org/10.1101/2025...

We explored this by analyzing 20 years of digital drug dispensing data linked to the @ESTbiobank which hosts 212,000 genotyped participants. 🧵
📄 doi.org/10.1101/2025...
👉 www.nature.com/articles/s41...
We mapped & characterized genetic risk factors for 42 female reproductive health diagnoses. What we found & why it matters? 👇🧵
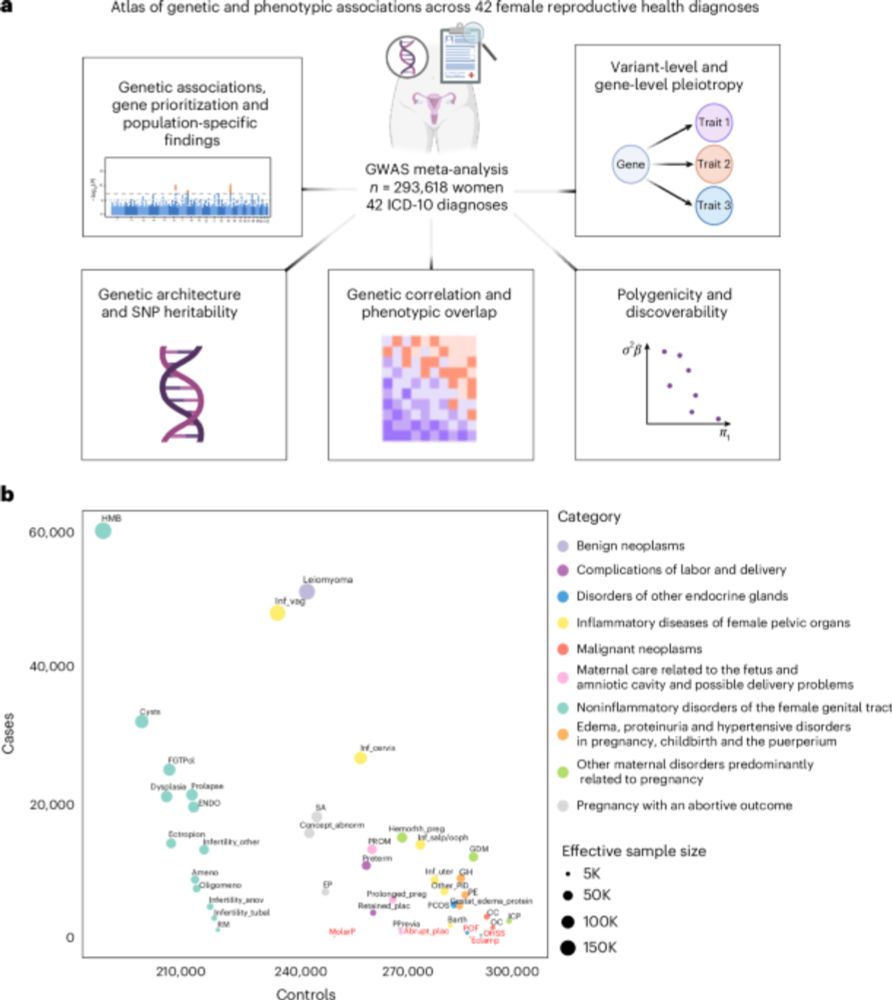
👉 www.nature.com/articles/s41...
We mapped & characterized genetic risk factors for 42 female reproductive health diagnoses. What we found & why it matters? 👇🧵
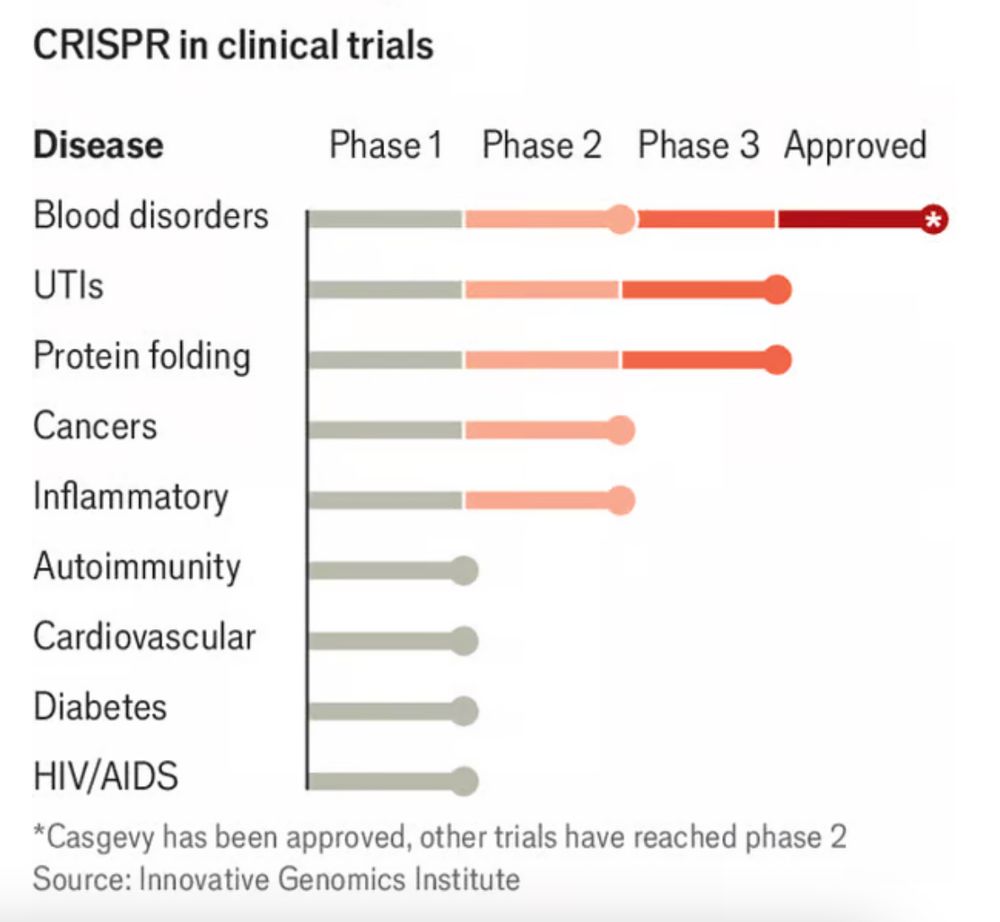
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
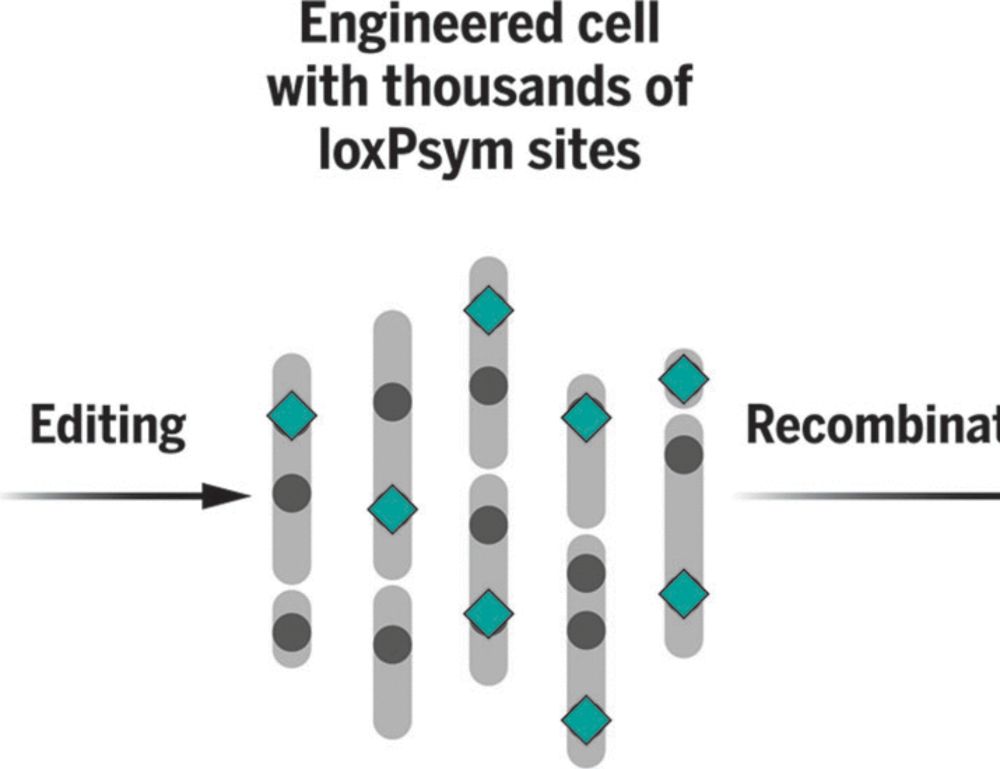
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
This prestigious summer school brings together leaders in human genetics with PhD students
📅 July 27-31, 2025
📍 Wellcome Genome Campus, UK
📝 Apply by March 7 at www.lpshg.com
This prestigious summer school brings together leaders in human genetics with PhD students
📅 July 27-31, 2025
📍 Wellcome Genome Campus, UK
📝 Apply by March 7 at www.lpshg.com
✅ The 2nd most googled “How to…?” question in Estonia 2024: “How to become a biobank participant?”
✅ "Estonian Biobank" among Top 10 search terms.
Huge thanks to the entire UniTartu & EstBB teams! ✨

✅ The 2nd most googled “How to…?” question in Estonia 2024: “How to become a biobank participant?”
✅ "Estonian Biobank" among Top 10 search terms.
Huge thanks to the entire UniTartu & EstBB teams! ✨

Pre-print: doi.org/10.1101/2024...
Repo: github.com/PacificBiosc...

With our novel method, we inferred the parental origin of alleles for >220,000 individuals, uncovering novel insights into genetics, evolution, and health.
👉 Read here: www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1...
👇 Highlights below!

With our novel method, we inferred the parental origin of alleles for >220,000 individuals, uncovering novel insights into genetics, evolution, and health.
👉 Read here: www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1...
👇 Highlights below!
I am very proud to be part of the @ebi.embl.org community delivering on this
🌍 101 million requests to our data resource websites on an average day
💻 36 million unique IP addresses annually
Which of our resources have you used recently? 👀
www.ebi.ac.uk/about/our-im...

I am very proud to be part of the @ebi.embl.org community delivering on this

