
Rajiv McCoy
@rajivmccoy.bsky.social
Associate Professor at Johns Hopkins studying human evolutionary and reproductive genetics https://mccoy-lab.org
Pinned
Rajiv McCoy
@rajivmccoy.bsky.social
· Apr 7
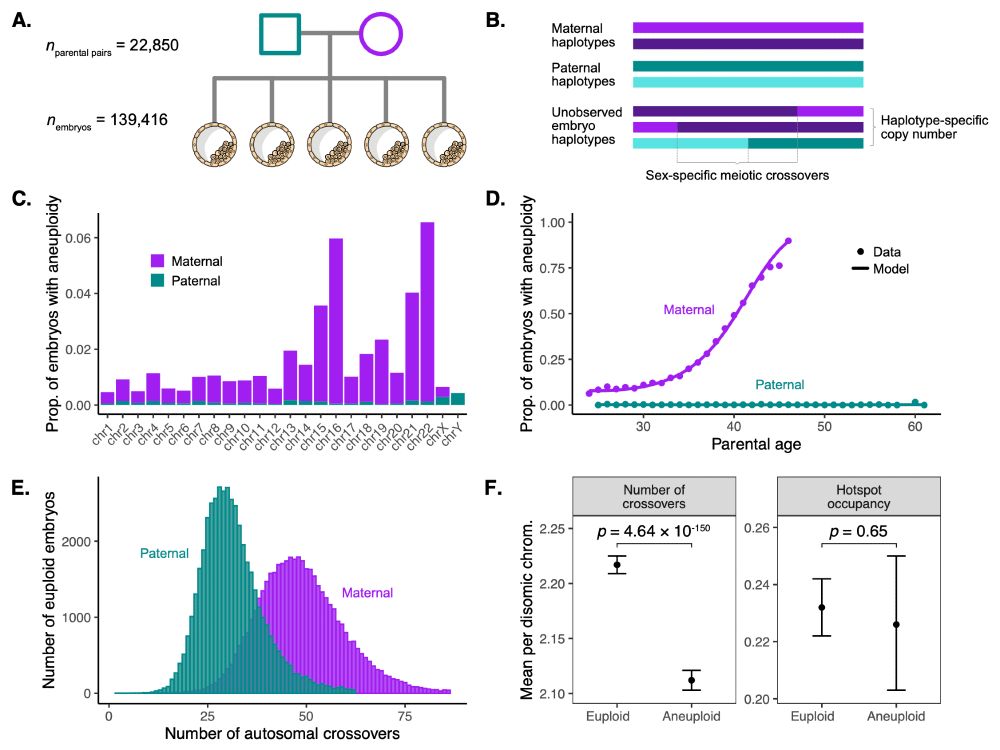
Aneuploidy is the leading cause of pregnancy loss. In work led by @saracarioscia.bsky.social and @aabiddanda.bsky.social, we reanalyzed genetic testing data from 139,416 IVF embryos to discover variants associated with recombination phenotypes and aneuploidy risk. www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1...
Reposted by Rajiv McCoy
How is functional variation at large-effect loci maintained in natural populations, even as environments change? In a paper led by @mkarag.bsky.social, we tracked known pesticide resistant alleles in outdoor 𝘋. 𝘮𝘦𝘭𝘢𝘯𝘰𝘨𝘢𝘴𝘵𝘦𝘳 cages & inferred selection and dominance from temporal sequencing data.

November 6, 2025 at 9:51 PM
How is functional variation at large-effect loci maintained in natural populations, even as environments change? In a paper led by @mkarag.bsky.social, we tracked known pesticide resistant alleles in outdoor 𝘋. 𝘮𝘦𝘭𝘢𝘯𝘰𝘨𝘢𝘴𝘵𝘦𝘳 cages & inferred selection and dominance from temporal sequencing data.
Reposted by Rajiv McCoy
Interesting story in this preprint.
A male infant was diagnosed with Fanconi anemia due to an X-linked frameshift mutation.
Three years later, his hematopoiesis became normal (without intervention). How?
www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1...
A male infant was diagnosed with Fanconi anemia due to an X-linked frameshift mutation.
Three years later, his hematopoiesis became normal (without intervention). How?
www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1...

Multi-lineage natural gene therapy mediated by embryonic triploid mosaicism in the context of Fanconi anaemia
Fanconi anemia is a rare inherited bone marrow failure syndrome caused by inactivation of genes in the Fanconi anemia/BRCA DNA repair pathway. We report a patient with X-linked Fanconi anemia, and aty...
www.medrxiv.org
November 5, 2025 at 8:04 AM
Interesting story in this preprint.
A male infant was diagnosed with Fanconi anemia due to an X-linked frameshift mutation.
Three years later, his hematopoiesis became normal (without intervention). How?
www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1...
A male infant was diagnosed with Fanconi anemia due to an X-linked frameshift mutation.
Three years later, his hematopoiesis became normal (without intervention). How?
www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1...
Reposted by Rajiv McCoy
Our paper on clonal expansions in Sperm is out in Nature www.nature.com/articles/s41...
If you are interested in working at an intersection of Mendelian genomics/Population genetics/Clonal expansions +Cancer genetics/ and of course mutagenesis, please rich out about postdoc in my lab
If you are interested in working at an intersection of Mendelian genomics/Population genetics/Clonal expansions +Cancer genetics/ and of course mutagenesis, please rich out about postdoc in my lab
October 8, 2025 at 4:52 PM
Our paper on clonal expansions in Sperm is out in Nature www.nature.com/articles/s41...
If you are interested in working at an intersection of Mendelian genomics/Population genetics/Clonal expansions +Cancer genetics/ and of course mutagenesis, please rich out about postdoc in my lab
If you are interested in working at an intersection of Mendelian genomics/Population genetics/Clonal expansions +Cancer genetics/ and of course mutagenesis, please rich out about postdoc in my lab
Reposted by Rajiv McCoy
Now published! Our paper on:
(1) Accurate sequencing of sperm at scale
(2) Positive selection of spermatogenesis driver mutations across the exome
(3) Offspring disease risks from male reproductive aging
[1/n]
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
(1) Accurate sequencing of sperm at scale
(2) Positive selection of spermatogenesis driver mutations across the exome
(3) Offspring disease risks from male reproductive aging
[1/n]
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

Sperm sequencing reveals extensive positive selection in the male germline - Nature
A combination of whole-genome NanoSeq with deep whole-exome and targeted NanoSeq is used to accurately characterize mutation rates and genes under positive selection in sperm cells.
www.nature.com
October 8, 2025 at 3:51 PM
Now published! Our paper on:
(1) Accurate sequencing of sperm at scale
(2) Positive selection of spermatogenesis driver mutations across the exome
(3) Offspring disease risks from male reproductive aging
[1/n]
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
(1) Accurate sequencing of sperm at scale
(2) Positive selection of spermatogenesis driver mutations across the exome
(3) Offspring disease risks from male reproductive aging
[1/n]
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Reposted by Rajiv McCoy
How do oocytes prepare for life before life begins? 🧬
Our new review in Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology @annualreview explores how oocytes store proteins to support development and fertility. (1/5)
🔗 go.shr.lc/4o9hsk8
Our new review in Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology @annualreview explores how oocytes store proteins to support development and fertility. (1/5)
🔗 go.shr.lc/4o9hsk8
October 8, 2025 at 12:50 PM
How do oocytes prepare for life before life begins? 🧬
Our new review in Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology @annualreview explores how oocytes store proteins to support development and fertility. (1/5)
🔗 go.shr.lc/4o9hsk8
Our new review in Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology @annualreview explores how oocytes store proteins to support development and fertility. (1/5)
🔗 go.shr.lc/4o9hsk8
Reposted by Rajiv McCoy
🚀 We’re hiring a Postdoc!
Join our group in Poznan, Poland to study meiotic crossover recombination in plants 🌱 Highly motivated & enthusiastic candidates are welcome!
📅 Deadline: Nov 1, 2025
🔗 ibmib.web.amu.edu.pl/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/Postdoc_position-2025-Ziolkowskis-Lab.pdf
Join our group in Poznan, Poland to study meiotic crossover recombination in plants 🌱 Highly motivated & enthusiastic candidates are welcome!
📅 Deadline: Nov 1, 2025
🔗 ibmib.web.amu.edu.pl/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/Postdoc_position-2025-Ziolkowskis-Lab.pdf

September 27, 2025 at 5:03 AM
🚀 We’re hiring a Postdoc!
Join our group in Poznan, Poland to study meiotic crossover recombination in plants 🌱 Highly motivated & enthusiastic candidates are welcome!
📅 Deadline: Nov 1, 2025
🔗 ibmib.web.amu.edu.pl/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/Postdoc_position-2025-Ziolkowskis-Lab.pdf
Join our group in Poznan, Poland to study meiotic crossover recombination in plants 🌱 Highly motivated & enthusiastic candidates are welcome!
📅 Deadline: Nov 1, 2025
🔗 ibmib.web.amu.edu.pl/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/Postdoc_position-2025-Ziolkowskis-Lab.pdf
Reposted by Rajiv McCoy
We are excited to share GPN-Star, a cost-effective, biologically grounded genomic language modeling framework that achieves state-of-the-art performance across a wide range of variant effect prediction tasks relevant to human genetics.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
(1/n)
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
(1/n)

September 22, 2025 at 5:29 AM
We are excited to share GPN-Star, a cost-effective, biologically grounded genomic language modeling framework that achieves state-of-the-art performance across a wide range of variant effect prediction tasks relevant to human genetics.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
(1/n)
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
(1/n)
Reposted by Rajiv McCoy
A project many years in the process, we’re pleased to present our work on multi-ancestry meta-analysis across a boatload of traits in the UK Biobank: www.nature.com/articles/s41...

Pan-UK Biobank genome-wide association analyses enhance discovery and resolution of ancestry-enriched effects - Nature Genetics
Genome-wide analyses for 7,266 traits leveraging data from several genetic ancestry groups in UK Biobank identify new associations and enhance resources for interpreting risk variants across diverse p...
www.nature.com
September 18, 2025 at 5:25 PM
A project many years in the process, we’re pleased to present our work on multi-ancestry meta-analysis across a boatload of traits in the UK Biobank: www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Reposted by Rajiv McCoy
Are you interested in doing a PhD in Copenhagen? Interested in studying Neanderthals and Denisovans which live on in our genomes?
Than you are more than welcome to apply to join my group starting Jan 2026 :)
candidate.hr-manager.net/ApplicationI...
Please reach out if you have any questions!
Than you are more than welcome to apply to join my group starting Jan 2026 :)
candidate.hr-manager.net/ApplicationI...
Please reach out if you have any questions!

August 28, 2025 at 12:35 PM
Are you interested in doing a PhD in Copenhagen? Interested in studying Neanderthals and Denisovans which live on in our genomes?
Than you are more than welcome to apply to join my group starting Jan 2026 :)
candidate.hr-manager.net/ApplicationI...
Please reach out if you have any questions!
Than you are more than welcome to apply to join my group starting Jan 2026 :)
candidate.hr-manager.net/ApplicationI...
Please reach out if you have any questions!
Reposted by Rajiv McCoy
Our paper on the evolution of MUC19 in humans, Neanderthals, and Denisovans is finally out today in Science!
This has been a six-year effort by 13 authors to weave together 3 separate but related evolutionary stories around this one gene (more on thread 🧵).
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
This has been a six-year effort by 13 authors to weave together 3 separate but related evolutionary stories around this one gene (more on thread 🧵).
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...

The MUC19 gene: An evolutionary history of recurrent introgression and natural selection
We study the gene MUC19, for which some modern humans carry a Denisovan-like haplotype. MUC19 is a mucin, a glycoprotein that forms gels with various biological functions. We find diagnostic variants ...
www.science.org
August 21, 2025 at 7:36 PM
Our paper on the evolution of MUC19 in humans, Neanderthals, and Denisovans is finally out today in Science!
This has been a six-year effort by 13 authors to weave together 3 separate but related evolutionary stories around this one gene (more on thread 🧵).
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
This has been a six-year effort by 13 authors to weave together 3 separate but related evolutionary stories around this one gene (more on thread 🧵).
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
Reposted by Rajiv McCoy
I built a Gradio app to illustrate how selective sweeps can be detected from population genetic data: ryangutenkunst-sweep-detection-dpi.hf.space . It can help with your first submissions to the GHIST sweep detection challenges! ghi.st #GHIST

August 15, 2025 at 11:08 AM
I built a Gradio app to illustrate how selective sweeps can be detected from population genetic data: ryangutenkunst-sweep-detection-dpi.hf.space . It can help with your first submissions to the GHIST sweep detection challenges! ghi.st #GHIST
Reposted by Rajiv McCoy
Complete genomes alert! @glennislogsdon.bsky.social, @christinebeck.bsky.social, and I were on @scifri.bsky.social today talking about "Complex genetic variation in nearly complete human genomes"
📄 www.nature.com/articles/s41...
📻 www.sciencefriday.com/segments/65-...
📄 www.nature.com/articles/s41...
📻 www.sciencefriday.com/segments/65-...
65 Genomes Expand Our Picture Of Human Genetics
Researchers closely examined the genomes of 65 individuals to paint a more complex, and more complete, picture of human genetic diversity.
www.sciencefriday.com
August 1, 2025 at 8:49 PM
Complete genomes alert! @glennislogsdon.bsky.social, @christinebeck.bsky.social, and I were on @scifri.bsky.social today talking about "Complex genetic variation in nearly complete human genomes"
📄 www.nature.com/articles/s41...
📻 www.sciencefriday.com/segments/65-...
📄 www.nature.com/articles/s41...
📻 www.sciencefriday.com/segments/65-...
Reposted by Rajiv McCoy
How to get introgressed fragments in genomic data? Everything you always wanted to know you find in our review in @cp-trendsgenetics.bsky.social, led by Xin Huang:
doi.org/10.1016/j.ti...
doi.org/10.1016/j.ti...

July 24, 2025 at 2:04 AM
How to get introgressed fragments in genomic data? Everything you always wanted to know you find in our review in @cp-trendsgenetics.bsky.social, led by Xin Huang:
doi.org/10.1016/j.ti...
doi.org/10.1016/j.ti...
Lab retreat at the JHU Bloomberg Center in DC

July 12, 2025 at 2:27 AM
Lab retreat at the JHU Bloomberg Center in DC
Reposted by Rajiv McCoy
NEW pub: The role of metabolism in shaping #enzyme structures over 400 million years. Now out in @nature.com
Super grateful to have played a small role in this project - congrats to lead/corr authors Oliver, Benjamin, and Markus!
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
#alphafold #evolution #genomics
Super grateful to have played a small role in this project - congrats to lead/corr authors Oliver, Benjamin, and Markus!
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
#alphafold #evolution #genomics

July 10, 2025 at 7:57 PM
NEW pub: The role of metabolism in shaping #enzyme structures over 400 million years. Now out in @nature.com
Super grateful to have played a small role in this project - congrats to lead/corr authors Oliver, Benjamin, and Markus!
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
#alphafold #evolution #genomics
Super grateful to have played a small role in this project - congrats to lead/corr authors Oliver, Benjamin, and Markus!
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
#alphafold #evolution #genomics
Reposted by Rajiv McCoy
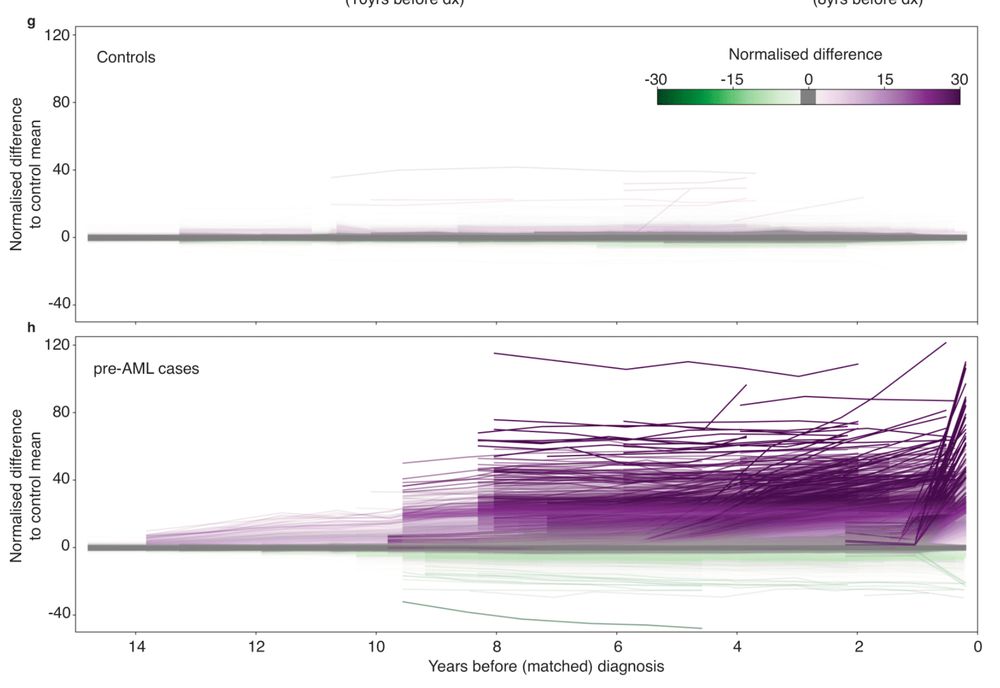
Delighted to share our latest on longitudinal methylation dynamics preceding cancer. Epigenetic signs of AML appear in blood DECADES before Dx.
👉 Early cancer detection
👉 Methylation drivers
👉 Epimutation rates
👉 CpG lineage tracing
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
👉 Early cancer detection
👉 Methylation drivers
👉 Epimutation rates
👉 CpG lineage tracing
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
July 3, 2025 at 8:47 PM
Delighted to share our latest on longitudinal methylation dynamics preceding cancer. Epigenetic signs of AML appear in blood DECADES before Dx.
👉 Early cancer detection
👉 Methylation drivers
👉 Epimutation rates
👉 CpG lineage tracing
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
👉 Early cancer detection
👉 Methylation drivers
👉 Epimutation rates
👉 CpG lineage tracing
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Reposted by Rajiv McCoy
Caiti Smukowski Heil @caitismuheil.bsky.social tells us about th domestication of yeast in bread 🍞
Humans have made a profound impact on the genome of S. cerevisiae
And commercial baking strains are super weird!
#Evol2025 #Evol25
Humans have made a profound impact on the genome of S. cerevisiae
And commercial baking strains are super weird!
#Evol2025 #Evol25

June 22, 2025 at 9:23 PM
Caiti Smukowski Heil @caitismuheil.bsky.social tells us about th domestication of yeast in bread 🍞
Humans have made a profound impact on the genome of S. cerevisiae
And commercial baking strains are super weird!
#Evol2025 #Evol25
Humans have made a profound impact on the genome of S. cerevisiae
And commercial baking strains are super weird!
#Evol2025 #Evol25
Reposted by Rajiv McCoy
Finally! Denisovans are officially Homo longi, the Harbin skull is the holotype.
Dragon Man was a Denisovan! DNA and proteins both confirm it, giving this mysterious human lineage a face at long last. Here’s my story. [Gift link] nyti.ms/44nQq1i

June 18, 2025 at 3:22 PM
Finally! Denisovans are officially Homo longi, the Harbin skull is the holotype.
Reposted by Rajiv McCoy
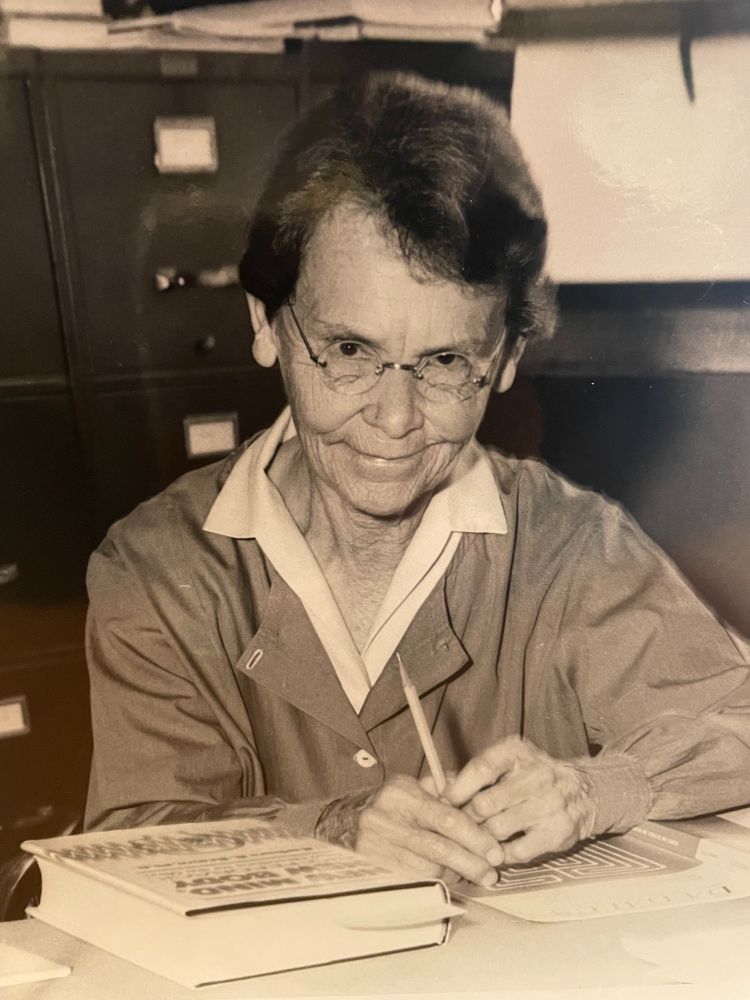
🧬🌽 Happy Transposon Day! 🌽🧬
Today we celebrate the birthday of Barbara McClintock - scientist extraordinaire and discoverer of jumping genes. Still the only woman to have an unshared Nobel Prize in the biomedical sciences #TransposonDay2025
Today we celebrate the birthday of Barbara McClintock - scientist extraordinaire and discoverer of jumping genes. Still the only woman to have an unshared Nobel Prize in the biomedical sciences #TransposonDay2025

June 16, 2025 at 3:14 PM
🧬🌽 Happy Transposon Day! 🌽🧬
Today we celebrate the birthday of Barbara McClintock - scientist extraordinaire and discoverer of jumping genes. Still the only woman to have an unshared Nobel Prize in the biomedical sciences #TransposonDay2025
Today we celebrate the birthday of Barbara McClintock - scientist extraordinaire and discoverer of jumping genes. Still the only woman to have an unshared Nobel Prize in the biomedical sciences #TransposonDay2025
Reposted by Rajiv McCoy
📣 Latest from the lab: Performance of deep-learning-based approaches to improve polygenic scores www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Its thought deep learning will substantially improve PGS but the reality is MANY have tried but no/little gain has been seen so far. Here we report our negative results.
Its thought deep learning will substantially improve PGS but the reality is MANY have tried but no/little gain has been seen so far. Here we report our negative results.
June 5, 2025 at 1:37 PM
📣 Latest from the lab: Performance of deep-learning-based approaches to improve polygenic scores www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Its thought deep learning will substantially improve PGS but the reality is MANY have tried but no/little gain has been seen so far. Here we report our negative results.
Its thought deep learning will substantially improve PGS but the reality is MANY have tried but no/little gain has been seen so far. Here we report our negative results.
Reposted by Rajiv McCoy
90% of doing science is being open to new ideas.

May 31, 2025 at 6:14 PM
90% of doing science is being open to new ideas.
Reposted by Rajiv McCoy
Industry friends, now is the time for MUCH more speaking out on behalf of academic colleagues under duress. Here are core open source methods that many of your products doubtlessly depend on either directly or indirectly (see en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HMMER) being abruptly defunded. Make noise.
May 29, 2025 at 2:39 PM
Industry friends, now is the time for MUCH more speaking out on behalf of academic colleagues under duress. Here are core open source methods that many of your products doubtlessly depend on either directly or indirectly (see en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HMMER) being abruptly defunded. Make noise.
Reposted by Rajiv McCoy
HMMER is crucial to our modern understanding of protein biochemistry and has almost certainly generated at least a 10-fold return on investment for every dollar the US government has spent on funding it.
NIH funding supporting the HMMER and Infernal software projects has been terminated. NIH states that our work, as well as all other federally funded research at Harvard, is of no benefit to the US.
May 28, 2025 at 4:26 PM
HMMER is crucial to our modern understanding of protein biochemistry and has almost certainly generated at least a 10-fold return on investment for every dollar the US government has spent on funding it.


