

Every $ donated to ALK Positive Australia goes towards research.

We report the existence of a previously uncharacterized signaling pathway that is responsible for activating cell death upon loss of gene expression.
1/n 🧪
www.cell.com/cell/fulltex...

We report the existence of a previously uncharacterized signaling pathway that is responsible for activating cell death upon loss of gene expression.
1/n 🧪
www.cell.com/cell/fulltex...
Sept 18-21 in Sant Feliu, Girona, Spain.
Registration OPEN!!!!!
Tons of opportunities for talks (including some full length ones).
You don’t want to miss it!
meetings.embo.org/event/25-lin...

Sept 18-21 in Sant Feliu, Girona, Spain.
Registration OPEN!!!!!
Tons of opportunities for talks (including some full length ones).
You don’t want to miss it!
meetings.embo.org/event/25-lin...
See below for event details. Our colleague Ruqian will also present her spatial work on lung fibrosis: events.unimelb.edu.au/MIG/event/44...
See below for event details. Our colleague Ruqian will also present her spatial work on lung fibrosis: events.unimelb.edu.au/MIG/event/44...
Dr. Jiadong Mao extends Φ-Space for spatial transcriptomics. Φ-Space ST is fast, platform-agnostic, and segmentation-free—uncovering niche-specific cell states with high accuracy.
Read it here: www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
#SpatialTranscriptomics #singlecell

Dr. Jiadong Mao extends Φ-Space for spatial transcriptomics. Φ-Space ST is fast, platform-agnostic, and segmentation-free—uncovering niche-specific cell states with high accuracy.
Read it here: www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
#SpatialTranscriptomics #singlecell
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

www.nature.com/articles/s41...
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
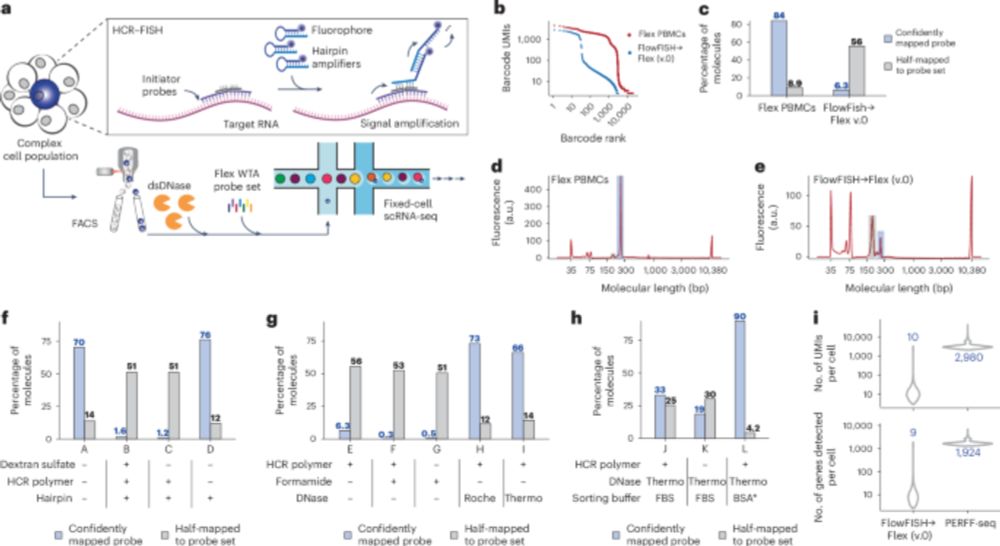
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
www.encodeproject.org/single-cell/...
www.encodeproject.org/single-cell/...
bsky.app/profile/marc...
bsky.app/profile/marc...
🧬 Discover how a pioneer transcription factor-like complex infiltrates repressive heterochromatin, producing transcripts with hidden introns that kickstart RNAi-mediated heterochromatin formation www.nature.com/articles/s41...
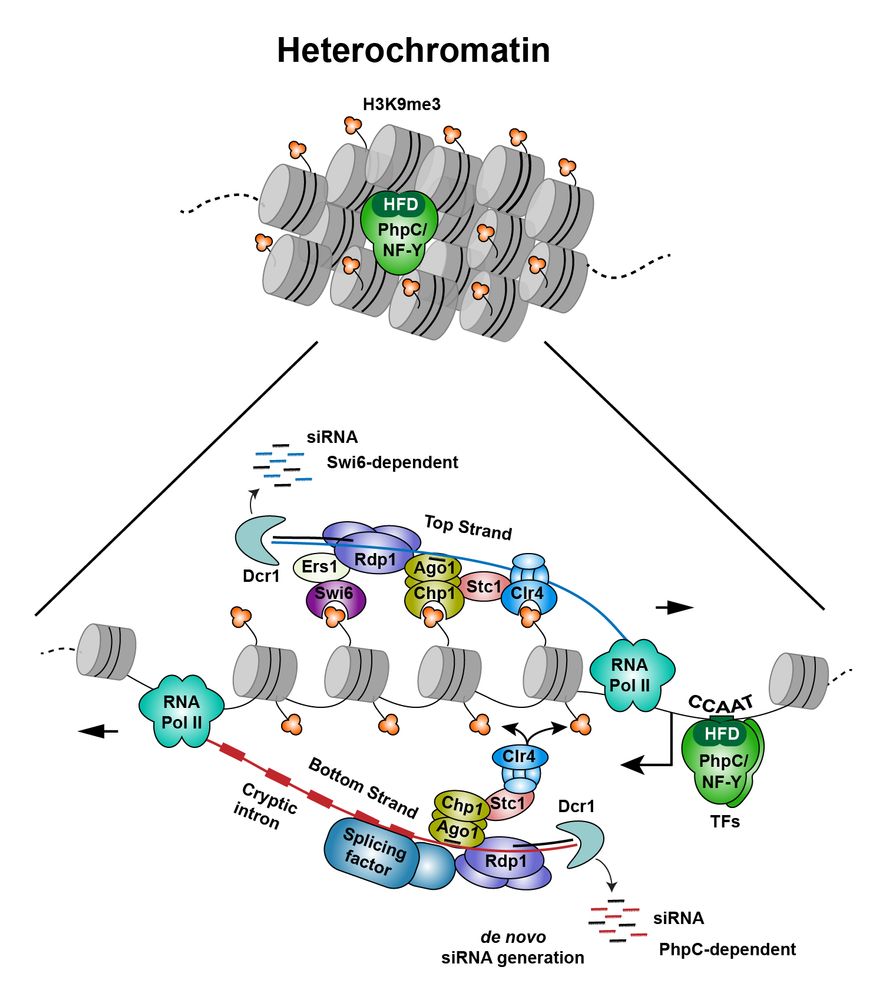
🧬 Discover how a pioneer transcription factor-like complex infiltrates repressive heterochromatin, producing transcripts with hidden introns that kickstart RNAi-mediated heterochromatin formation www.nature.com/articles/s41...
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
LEMUR is a tool to analyze multi-condition single-cell data and model differential expression as a continuous function of the cell-state space.
Some highlights⬇️
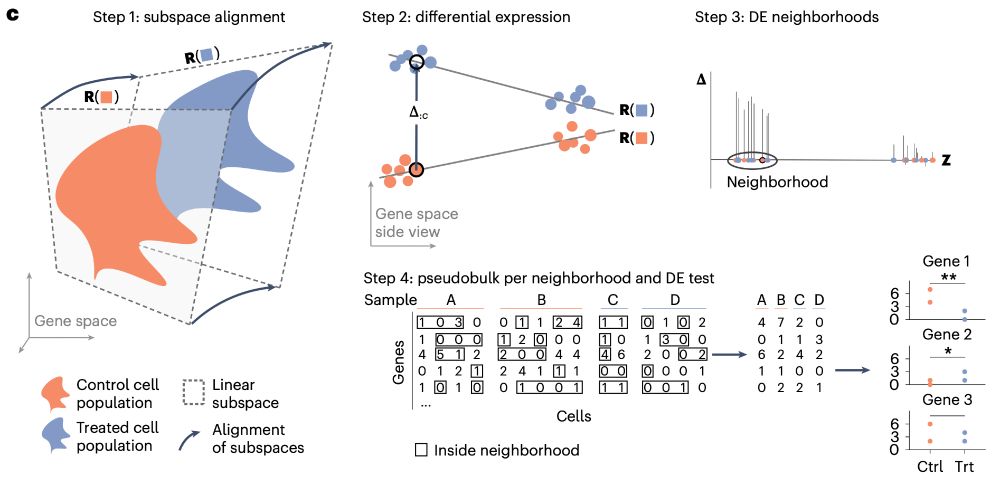
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
LEMUR is a tool to analyze multi-condition single-cell data and model differential expression as a continuous function of the cell-state space.
Some highlights⬇️

-> go.nature.com/4gCYtuL
A huge thank to the @fendtlab.bsky.social and all our collaborators for the terrific team work 🙏
A brief 🧵
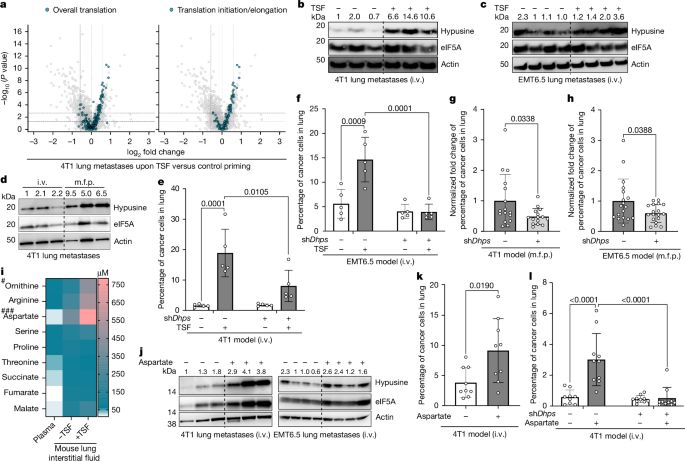
doi.org/10.1186/s130...

doi.org/10.1186/s130...
A big thanks to collaborators, especially to Ewa Michalak, Vi Wickramasinghe, Jeff Chao and Mark Dawson @mafdawson.bsky.social. @fmiscience.bsky.social
So incredibly proud of @tobiaswilliams.bsky.social & Ewa Michalak who led the work!
www.cell.com/molecular-ce...
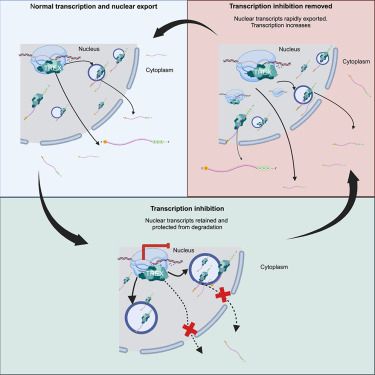
A big thanks to collaborators, especially to Ewa Michalak, Vi Wickramasinghe, Jeff Chao and Mark Dawson @mafdawson.bsky.social. @fmiscience.bsky.social
So incredibly proud of @tobiaswilliams.bsky.social & Ewa Michalak who led the work!
www.cell.com/molecular-ce...

So incredibly proud of @tobiaswilliams.bsky.social & Ewa Michalak who led the work!
www.cell.com/molecular-ce...
-> go.nature.com/4gCYtuL
A huge thank to the @fendtlab.bsky.social and all our collaborators for the terrific team work 🙏
A brief 🧵

-> go.nature.com/4gCYtuL
A huge thank to the @fendtlab.bsky.social and all our collaborators for the terrific team work 🙏
A brief 🧵
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
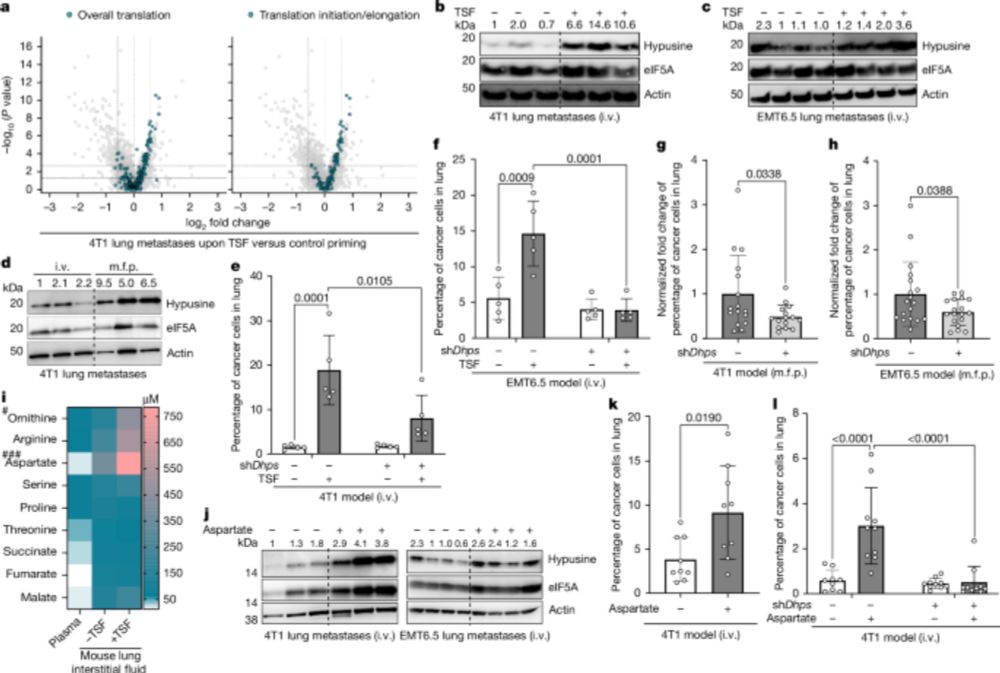

For the first time, we present a systematic exploration of Archaea—a major yet underexplored branch of the tree of life—as a source of novel antimicrobial compounds. www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

For the first time, we present a systematic exploration of Archaea—a major yet underexplored branch of the tree of life—as a source of novel antimicrobial compounds. www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

