https://scholar.google.com/citations?user=24B_5toAAAAJ&hl=en
https://www.ekarousis.net/

We used a human cell-free translation screen (~28 000 compounds) to discover NT-2, a #Fusarium -derived #mycotoxin that blocks human ribosomes.
#Cryo-EM at 1.72 Å reveals a link between chemical inhibition and ribosome dormancy.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

www.nature.com/articles/s41...
A fun collaboration with @beckmannlab.bsky.social @doubleshuang.bsky.social

www.nature.com/articles/s41...
A fun collaboration with @beckmannlab.bsky.social @doubleshuang.bsky.social
“Specialized gas-exchange endothelium of the zebrafish gill” —
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.6...
Amazing to see red blood cells moving through the gills! Don’t forget to check out the supplemental movies ;-)
“Specialized gas-exchange endothelium of the zebrafish gill” —
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.6...
Amazing to see red blood cells moving through the gills! Don’t forget to check out the supplemental movies ;-)
We used a human cell-free translation screen (~28 000 compounds) to discover NT-2, a #Fusarium -derived #mycotoxin that blocks human ribosomes.
#Cryo-EM at 1.72 Å reveals a link between chemical inhibition and ribosome dormancy.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

We used a human cell-free translation screen (~28 000 compounds) to discover NT-2, a #Fusarium -derived #mycotoxin that blocks human ribosomes.
#Cryo-EM at 1.72 Å reveals a link between chemical inhibition and ribosome dormancy.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...


https://paradisiresearch.com/research-highlights/nature-reviews-methods-primers-2025-flow-biocatalysis/
https://paradisiresearch.com/research-highlights/nature-reviews-methods-primers-2025-flow-biocatalysis/

What to do (and what not to do 😅) guide based on our work on Nsp1 published in @cp-cellreports.bsky.social.
www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti...
@unibe.ch @mcid-unibe.bsky.social @nccr-rna-disease.bsky.social @snf-fns.ch

What to do (and what not to do 😅) guide based on our work on Nsp1 published in @cp-cellreports.bsky.social.
www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti...
@unibe.ch @mcid-unibe.bsky.social @nccr-rna-disease.bsky.social @snf-fns.ch



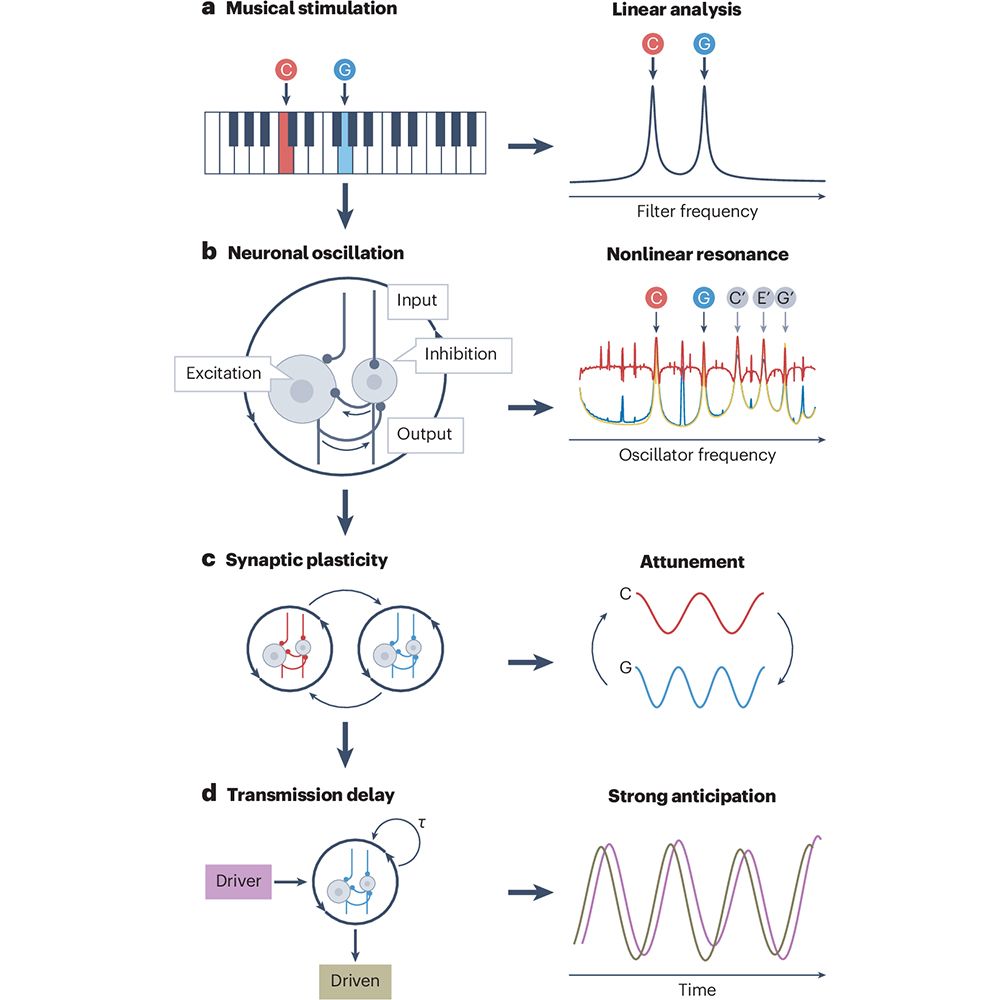
Paper 1 -- an AI model trained to predict translation rates from mRNA sequences: rdcu.be/exN1l
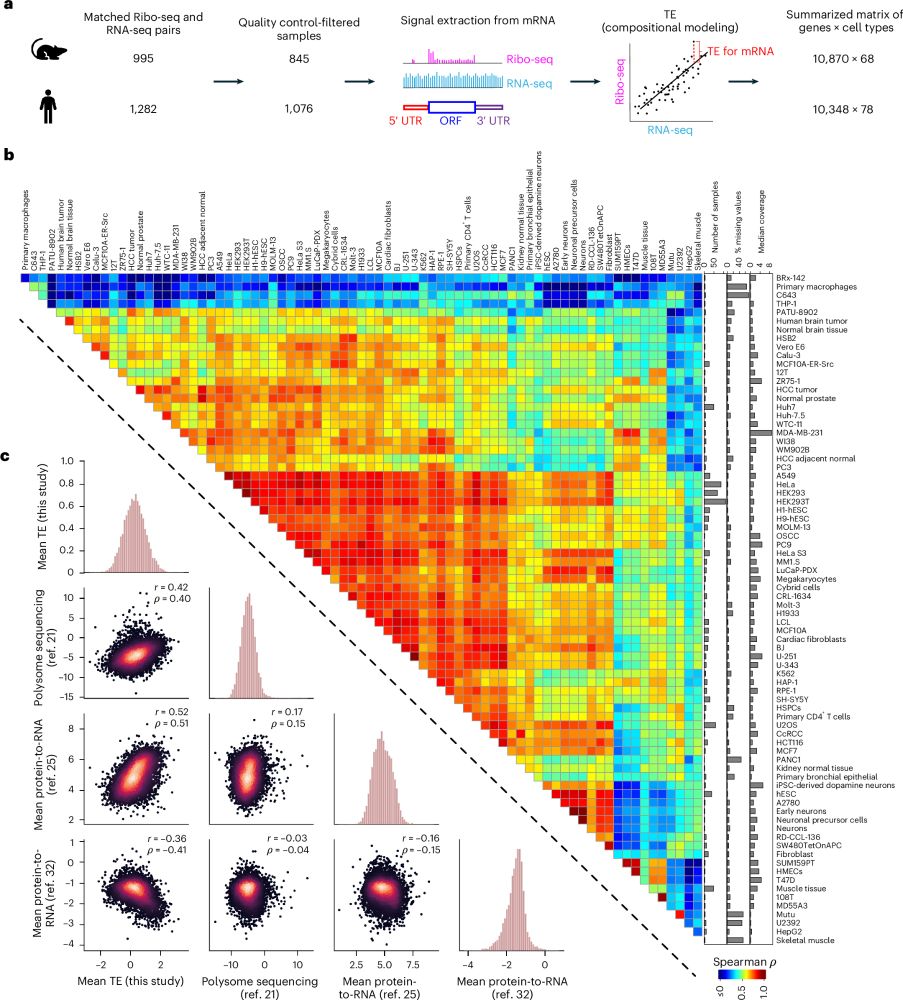
Paper 1 -- an AI model trained to predict translation rates from mRNA sequences: rdcu.be/exN1l
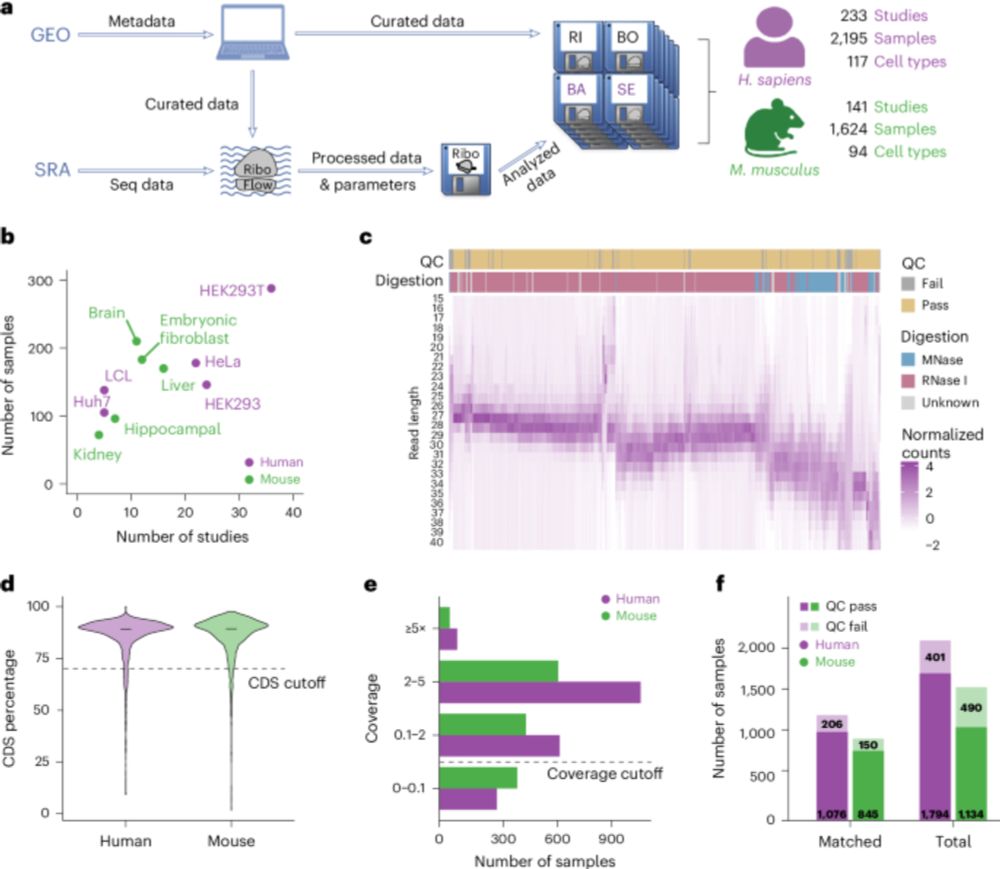

Continuing our successful collaboration with DeuerlingLab @uni-konstanz.de & Shu-ou Chan @caltech.edu
@snsf.ch @ethz.ch
www.cell.com/molecular-ce...
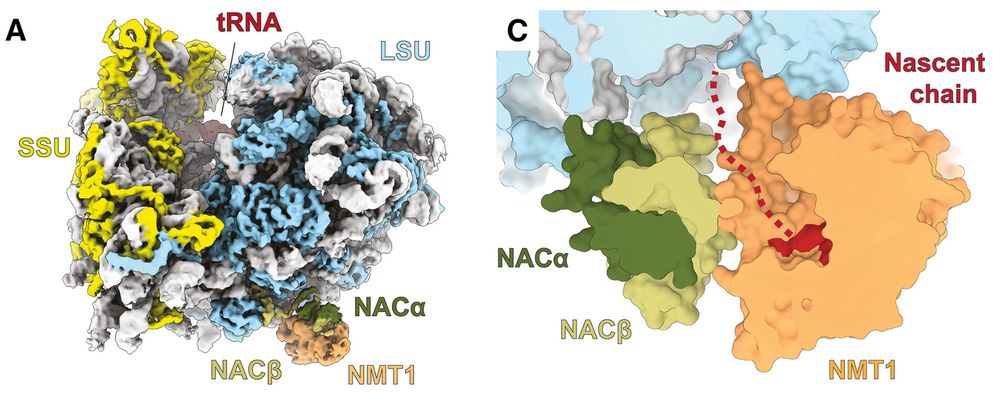
Continuing our successful collaboration with DeuerlingLab @uni-konstanz.de & Shu-ou Chan @caltech.edu
@snsf.ch @ethz.ch
www.cell.com/molecular-ce...
www.nature.com/articles/s41... Intracellular pathogen effector reprograms host gene expression by inhibiting mRNA decay | Nature Communications
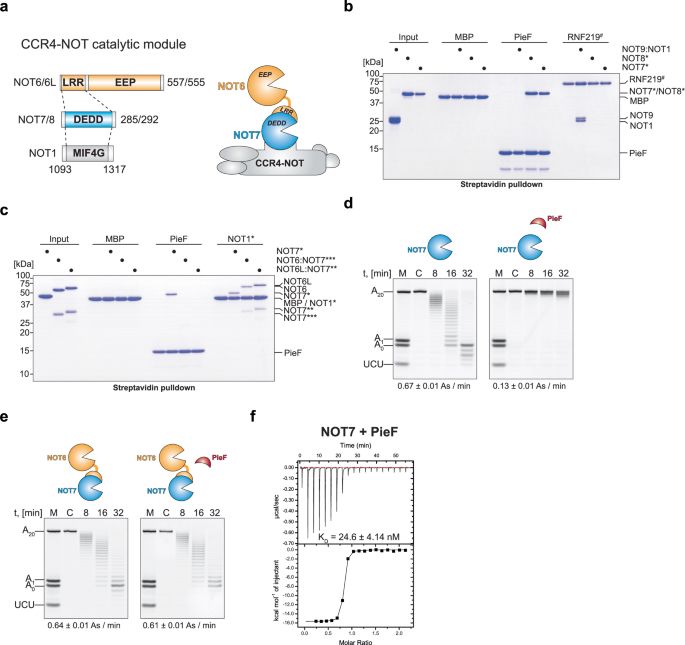
www.nature.com/articles/s41... Intracellular pathogen effector reprograms host gene expression by inhibiting mRNA decay | Nature Communications



@muehlemann.bsky.social @nickkouvelas.bsky.social

@muehlemann.bsky.social @nickkouvelas.bsky.social
He’ll be talking about “Decoding viral secrets using cell-free translation” 🧬
📅 May 12 🕐 1:15 PM ➡️Lynen Lecture Hall
Don’t miss it! 🤗✨
@karousislab.bsky.social @jonathanbohlen.bsky.social
@unibe.ch



@karousislab.bsky.social @nccr-rna-disease.bsky.social @mcid-unibe.bsky.social
Image: © Adrian Bothe

@karousislab.bsky.social @nccr-rna-disease.bsky.social @mcid-unibe.bsky.social
Image: © Adrian Bothe
Gluconeogenesis feat. Greek language lessons 🍭

Gluconeogenesis feat. Greek language lessons 🍭