
www.embopress.org/doi/full/10....

www.embopress.org/doi/full/10....
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

www.nature.com/articles/s41...
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
www.embopress.org/doi/full/10....

rupress.org/jem/article/...

rupress.org/jem/article/...
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
surprising new cell-intrinsic innate immune function in 𝘕𝘈𝘛𝘜𝘙𝘌
PROTEOSOMES generate antimicrobial peptides that kill bacteria as a first line of defense
bacterial infection alters proteasome function to boost this protective activity
are proteosomes a novel target for antimicrobial therapy?

Melbourne, Australia 🔬🦘💥
Work in a cutting edge research environment in a vibrant world city!
We value research excellence, creativity and diversity.
Join us!
careers.petermac.org/job/MELBOURN...
Melbourne, Australia 🔬🦘💥
Work in a cutting edge research environment in a vibrant world city!
We value research excellence, creativity and diversity.
Join us!
careers.petermac.org/job/MELBOURN...

I've only skimmed so far, but they propose reducing 13 grant schemes to 6, with intent & scope in the table👇
Submissions are being accepted in response until 13 April. Get to it!
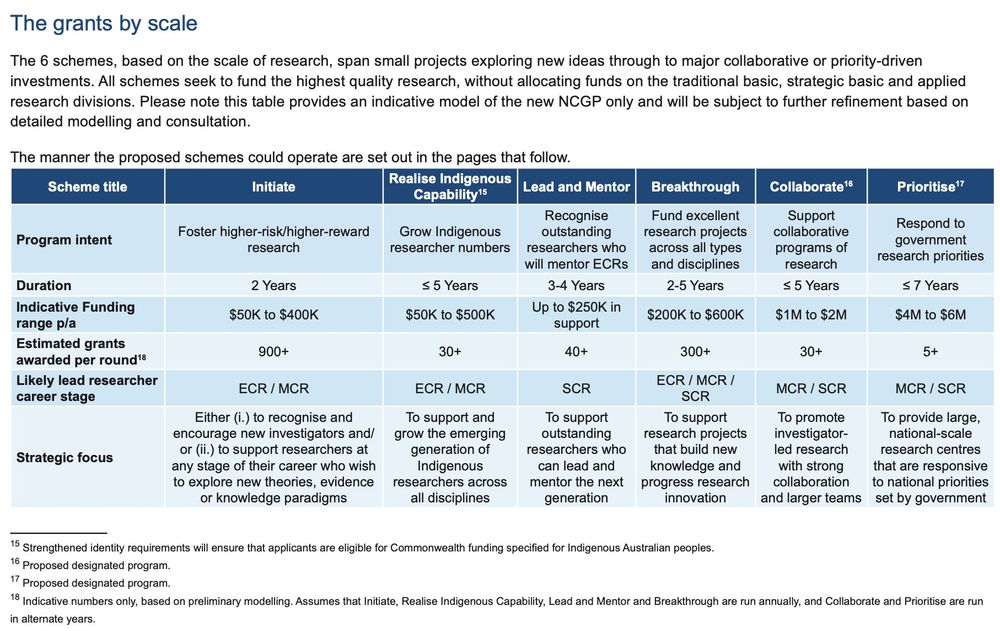
I've only skimmed so far, but they propose reducing 13 grant schemes to 6, with intent & scope in the table👇
Submissions are being accepted in response until 13 April. Get to it!
I’m very excited to share a preprint of the bulk of my thesis work in @sunnyshinlab.bsky.social where we investigate how dendritic cells respond to Legionella pneumophila
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...


A. Ablasser
L. Andreeva
@audeber.bsky.social
@jelenalab.bsky.social
V. Dixit
@v-hornung.bsky.social
B. Lemaitre
O. Majer
@manellab.bsky.social
E. Miao
@oliveiramann.bsky.social
M. Pasparakis
@inflammasomelab.bsky.social
@sparrerlab.bsky.social
R. Vance
@lozanzi.bsky.social

A. Ablasser
L. Andreeva
@audeber.bsky.social
@jelenalab.bsky.social
V. Dixit
@v-hornung.bsky.social
B. Lemaitre
O. Majer
@manellab.bsky.social
E. Miao
@oliveiramann.bsky.social
M. Pasparakis
@inflammasomelab.bsky.social
@sparrerlab.bsky.social
R. Vance
@lozanzi.bsky.social
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Great work led by postdoc Ales Drobek showing for the first time the critical role in vivo of the SLC15A4/TASL/IRF5 pathway that we discovered few years ago.
#ImmunoSky #InterferoSky
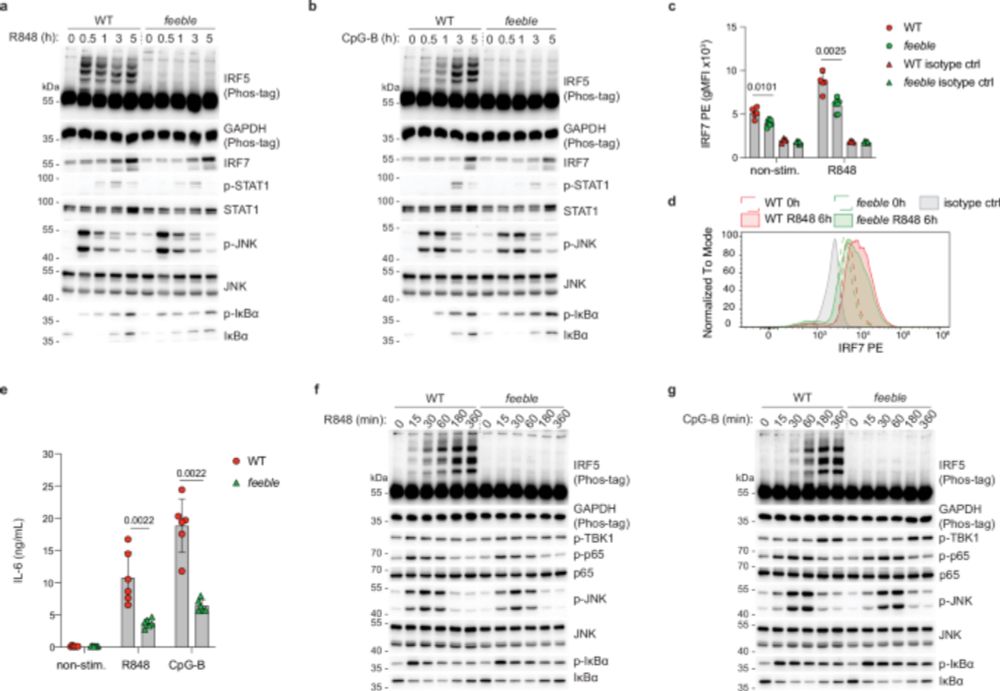
Great work led by postdoc Ales Drobek showing for the first time the critical role in vivo of the SLC15A4/TASL/IRF5 pathway that we discovered few years ago.
#ImmunoSky #InterferoSky

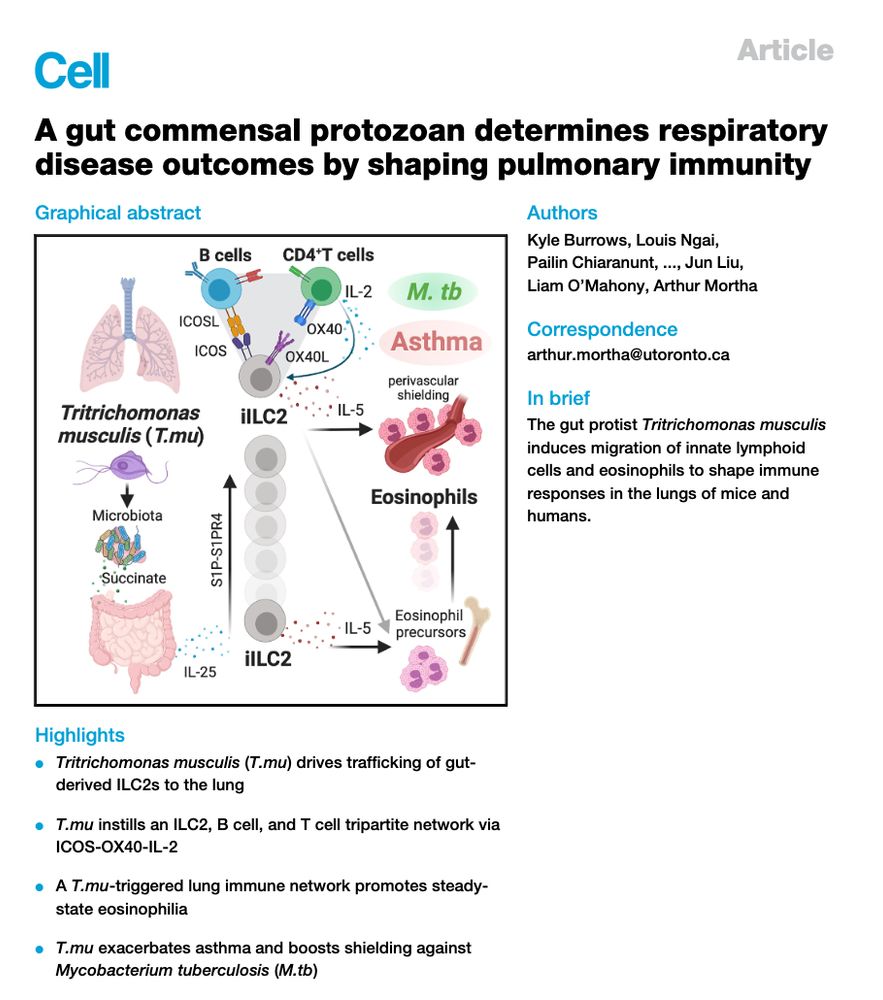
Here #theonlylabever reports how a gut protozoan commensal shapes pulmonary immunity to exacerbate asthma and limit the dissemination of mycobacteria.
@cellpress.bsky.social ⬇️(1/x)
www.cell.com/cell/fulltex...
Here #theonlylabever reports how a gut protozoan commensal shapes pulmonary immunity to exacerbate asthma and limit the dissemination of mycobacteria.
@cellpress.bsky.social ⬇️(1/x)
www.cell.com/cell/fulltex...
#CancerResearch #Anticancer
#CancerResearch #Anticancer


