
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
1/n
#GABA #Neuroscience #scATACseq #scRNAseq
www.cell.com/cell/fulltex...
Key findings in a thread (1/6):

www.cell.com/cell/fulltex...
Key findings in a thread (1/6):
Fill out this form to be considered for a talk in our Jan-June 2026 schedule! forms.gle/TBi38UgYxPAB...
Please repost and share!

Fill out this form to be considered for a talk in our Jan-June 2026 schedule! forms.gle/TBi38UgYxPAB...
Please repost and share!
popEVE (pop.evemodel.org) finds the needles in the haystacks of human genetic variation:

popEVE (pop.evemodel.org) finds the needles in the haystacks of human genetic variation:
The cis-regulatory logic integrating spatial and temporal patterning in the vertebrate neural tube
A global temporal chromatin program operates across the vertebrate nervous system to control neural cell diversity
www.cell.com/developmenta...

The cis-regulatory logic integrating spatial and temporal patterning in the vertebrate neural tube
A global temporal chromatin program operates across the vertebrate nervous system to control neural cell diversity
www.cell.com/developmenta...
doi.org/10.1016/j.ce...
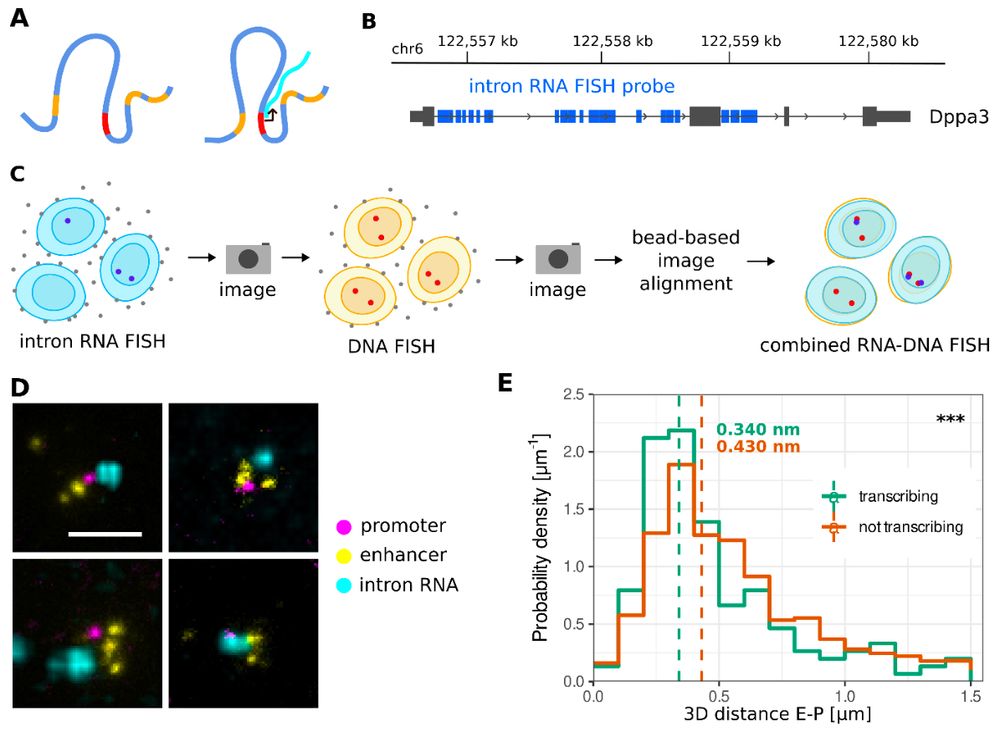
We developed a new method called MCC ultra, which allows 3D chromatin structure to be visualised with a 1 base pair pixel size.

doi.org/10.1016/j.ce...
We developed a new method called MCC ultra, which allows 3D chromatin structure to be visualised with a 1 base pair pixel size.
We show that active learning + transcriptomic perturbations can guide which exps to run next, boosting phenotypic hit rates >13x. AI not just predicting bio, but designing it. 🔁

We show that active learning + transcriptomic perturbations can guide which exps to run next, boosting phenotypic hit rates >13x. AI not just predicting bio, but designing it. 🔁
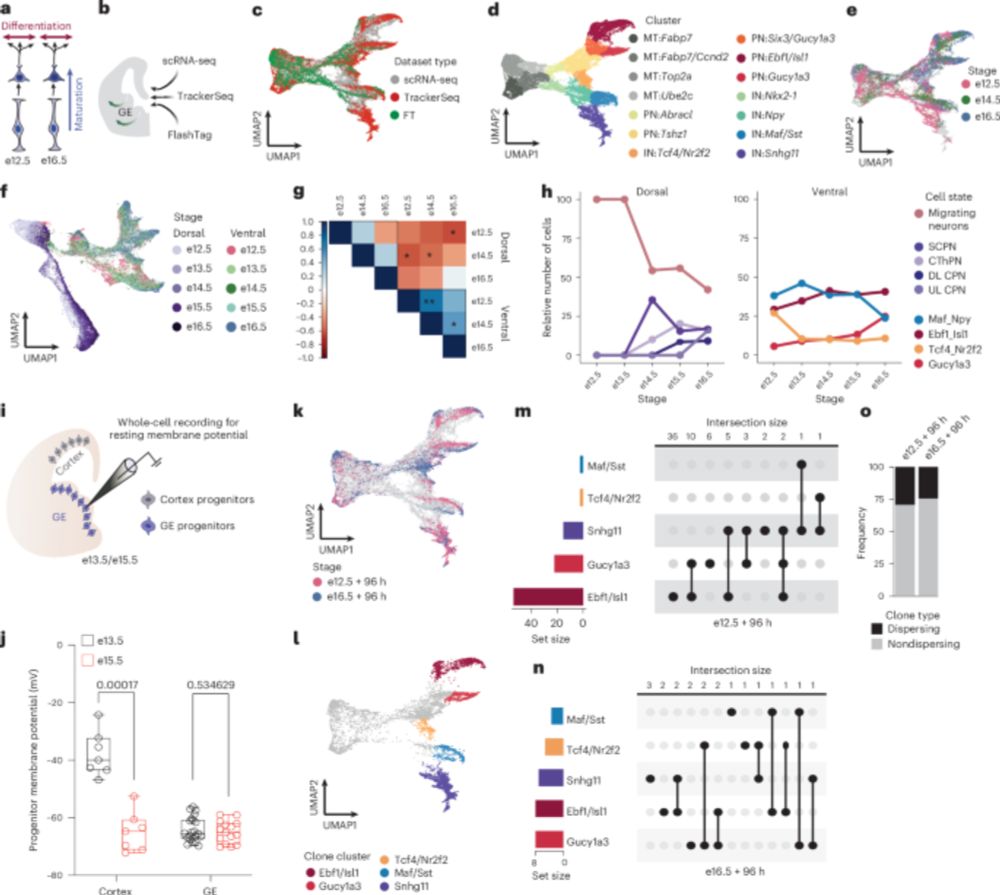
We used genomic barcoding + scRNAseq in chick & human embryos to reveal a lineage architecture that reshapes how we understand neural tube development & cell fate decisions
🧵👇
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

We used genomic barcoding + scRNAseq in chick & human embryos to reveal a lineage architecture that reshapes how we understand neural tube development & cell fate decisions
🧵👇
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

Special thanks to the reviewers whose comments improved our manuscript a lot! rdcu.be/eI3tD

Special thanks to the reviewers whose comments improved our manuscript a lot! rdcu.be/eI3tD

The E2G Portal! e2g.stanford.edu
This collates our predictions of enhancer-gene regulatory interactions across >1,600 cell types and tissues.
Uses cases 👇
1/
The E2G Portal! e2g.stanford.edu
This collates our predictions of enhancer-gene regulatory interactions across >1,600 cell types and tissues.
Uses cases 👇
1/

We found a preference for visual objects in the mouse spatial navigation system where they dynamically refine head-direction coding. In short, objects boost our inner compass! 🧭
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
🧵1/

We found a preference for visual objects in the mouse spatial navigation system where they dynamically refine head-direction coding. In short, objects boost our inner compass! 🧭
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
🧵1/
register here for the entire series: us06web.zoom.us/webinar/regi...

register here for the entire series: us06web.zoom.us/webinar/regi...

Our new paper by Mannion et al. takes a systematic look at "hidden enhancers" and why they remain so hard to find. With @mosterwalder.bsky.social, @jlopezrios.bsky.social & many more
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

Our new paper by Mannion et al. takes a systematic look at "hidden enhancers" and why they remain so hard to find. With @mosterwalder.bsky.social, @jlopezrios.bsky.social & many more
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
We show that astrocytes in the cortex arise from not one, but two distinct progenitor lineages, each giving rise to specialized subtypes with distinct roles.
Here the story📖 doi.org/10.1038/s414...
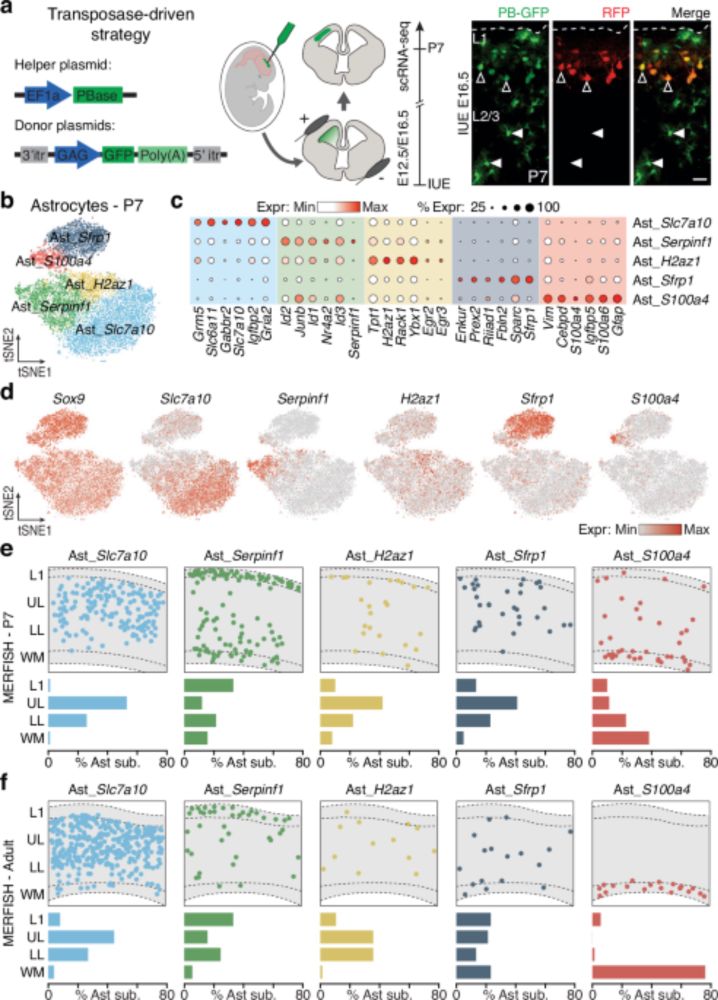
We show that astrocytes in the cortex arise from not one, but two distinct progenitor lineages, each giving rise to specialized subtypes with distinct roles.
Here the story📖 doi.org/10.1038/s414...
A global #cis-regulatory temporal program guides how spatial cues are interpreted in neural progenitors. We show how #space and #time can be integrated to generate cell type diversity in the #spinalcord.
Congrats to all authors.
www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti...

A global #cis-regulatory temporal program guides how spatial cues are interpreted in neural progenitors. We show how #space and #time can be integrated to generate cell type diversity in the #spinalcord.
Congrats to all authors.
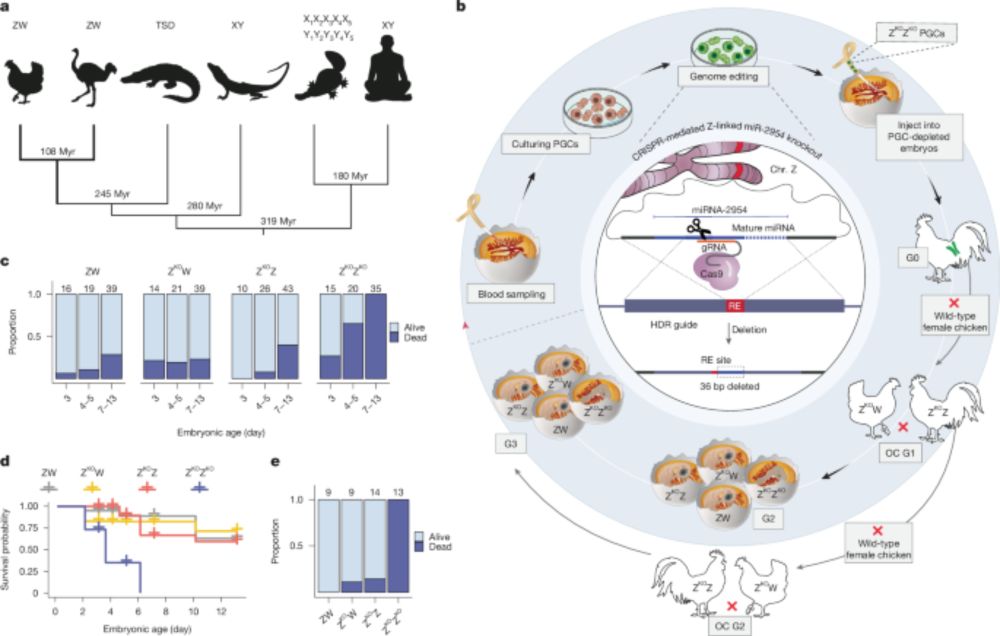
A global temporal chromatin program, operating across the CNS, directs binding of specific spatial TFs & hence when/where neurons & glia are born
authors.elsevier.com/sd/article/S...
A global temporal chromatin program, operating across the CNS, directs binding of specific spatial TFs & hence when/where neurons & glia are born
authors.elsevier.com/sd/article/S...

