www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
(Zoom registration link and more information in thread!)
🧵
(Zoom registration link and more information in thread!)
🧵
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
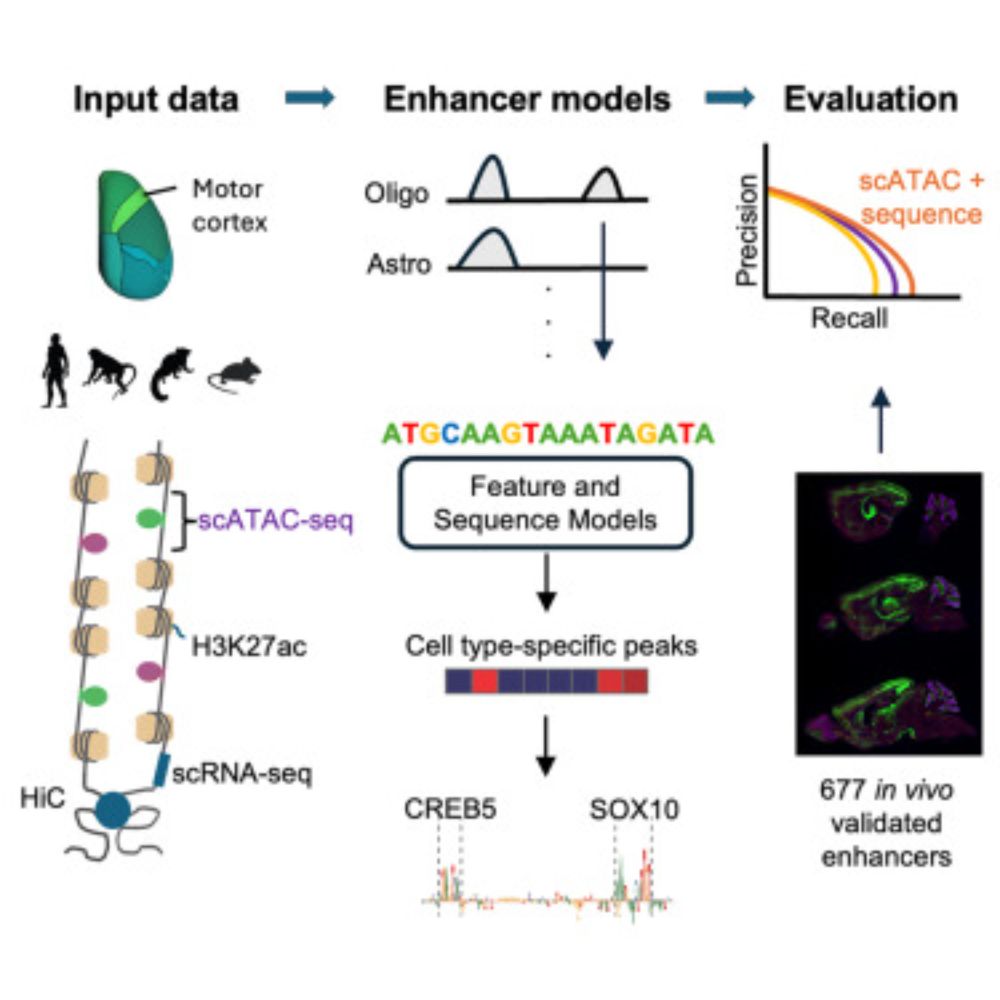

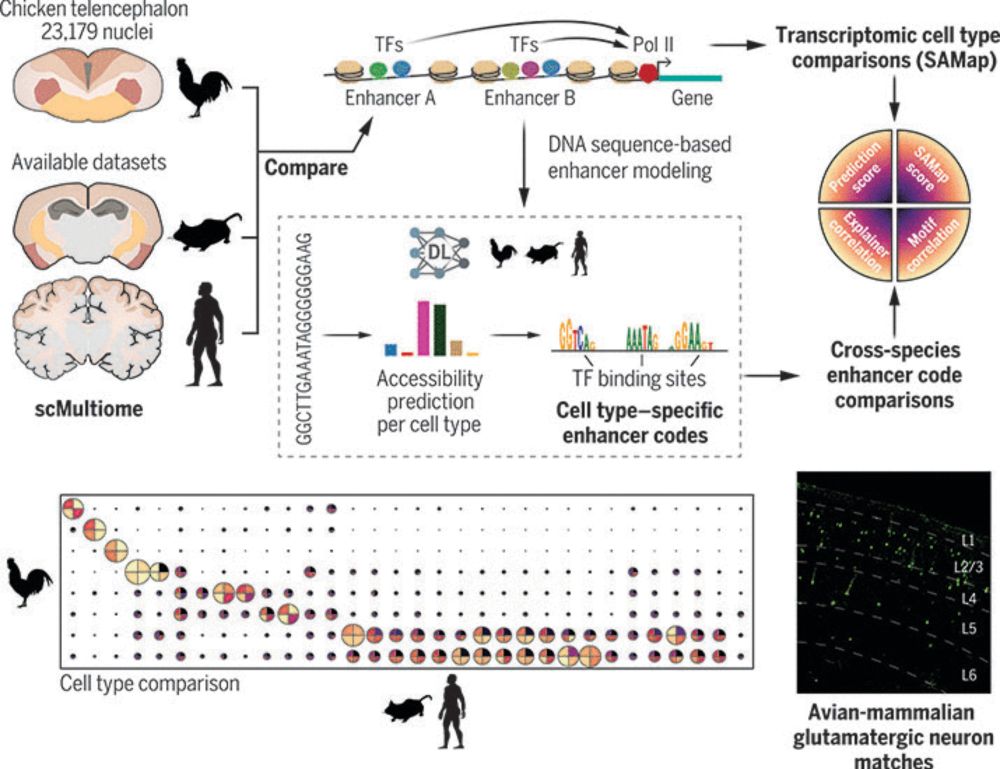
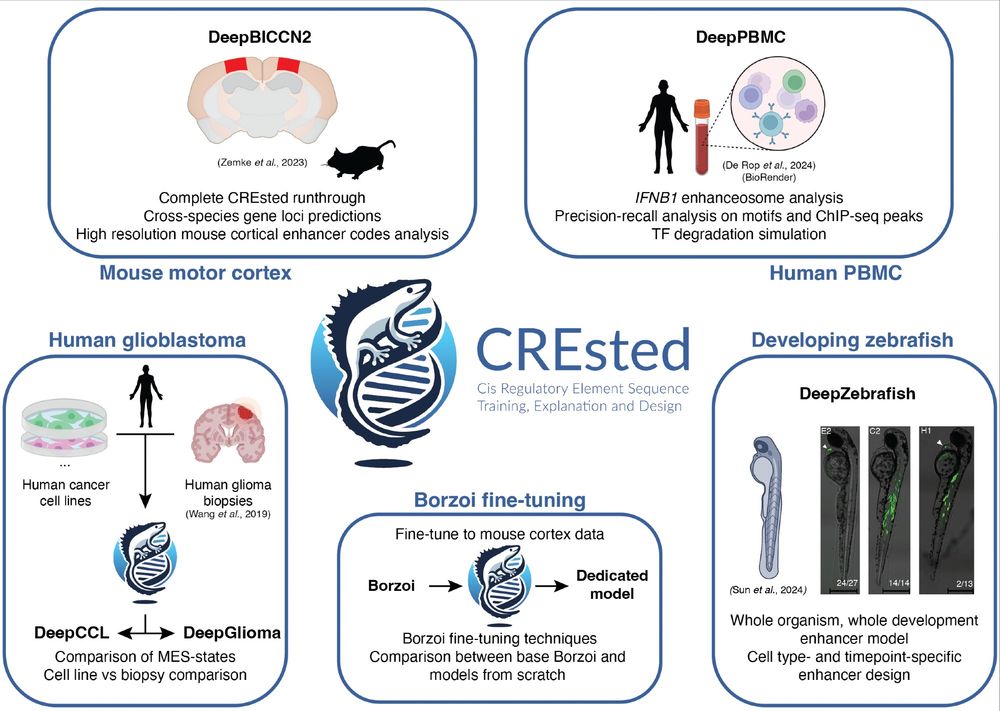
1) CREsted: to train sequence-to-function deep learning models on scATAC-seq atlases, and use them to decipher enhancer logic and design synthetic enhancers. This has been a wonderful lab-wide collaborative effort. www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

1) CREsted: to train sequence-to-function deep learning models on scATAC-seq atlases, and use them to decipher enhancer logic and design synthetic enhancers. This has been a wonderful lab-wide collaborative effort. www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
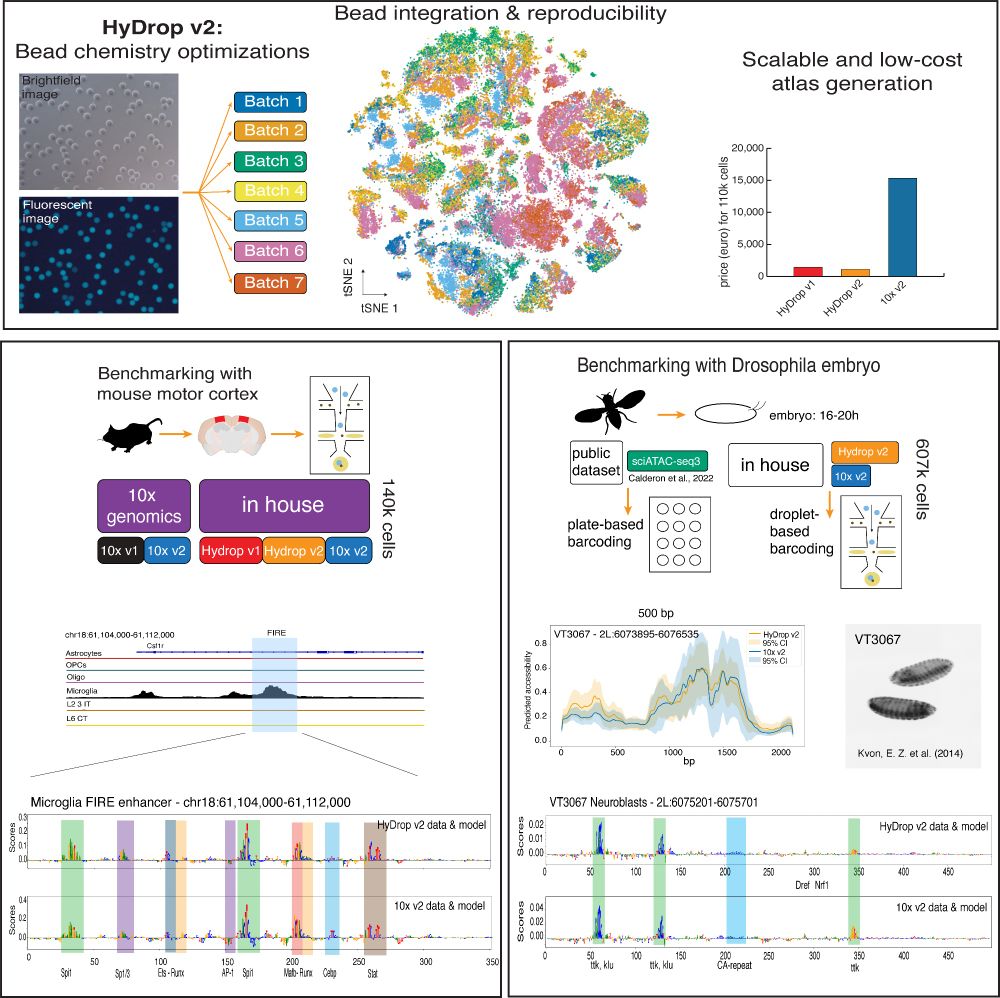
Led by @ioansarr.bsky.social, @marisepp.bsky.social and @tyamadat.bsky.social, in collaboration with @steinaerts.bsky.social
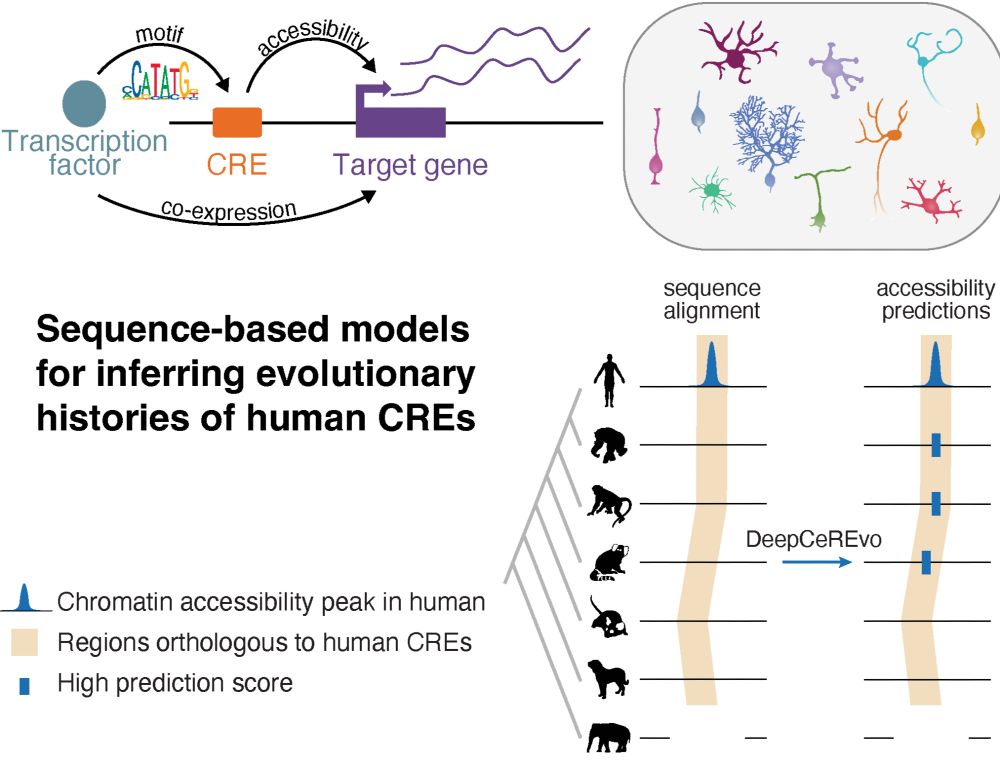
Led by @ioansarr.bsky.social, @marisepp.bsky.social and @tyamadat.bsky.social, in collaboration with @steinaerts.bsky.social
Watch: www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qcms...

Watch: www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qcms...
From conventional machine learning methods to CNNs and using models as oracles/generative AI for synthetic enhancer design!
@natrevbioeng.bsky.social
www.nature.com/articles/s44...
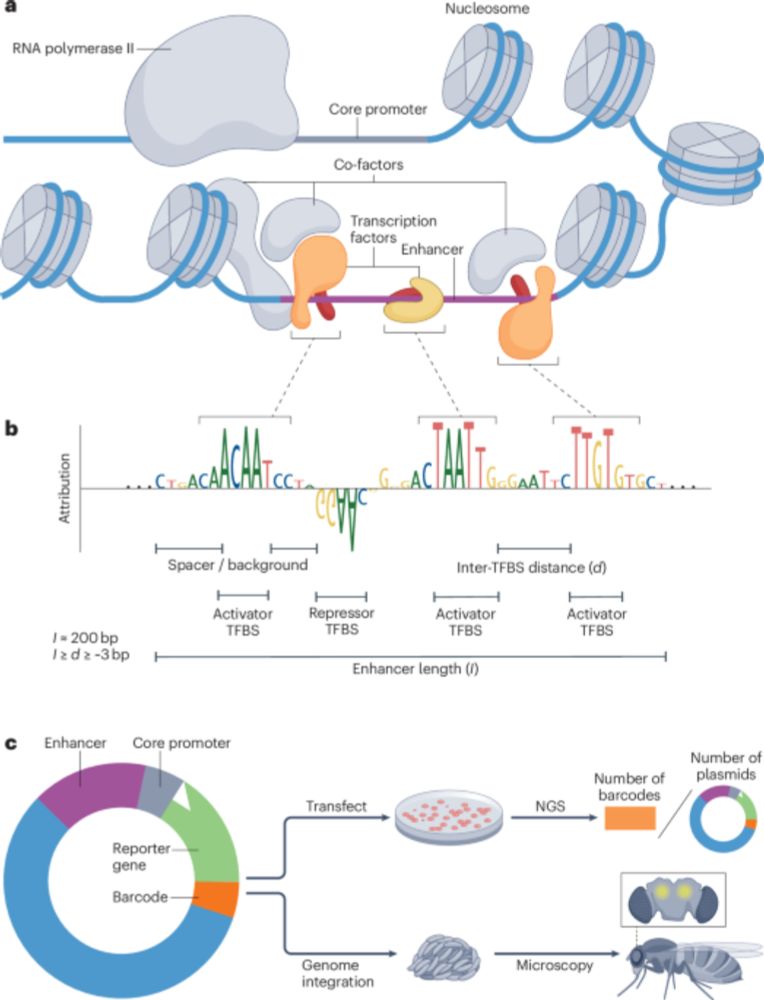
From conventional machine learning methods to CNNs and using models as oracles/generative AI for synthetic enhancer design!
@natrevbioeng.bsky.social
www.nature.com/articles/s44...
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...