
When we started Adaptyv a few years ago, our core belief was: AI models for biology are only as good as the lab data they're trained on and the hypotheses they can test in the real world.
When we started Adaptyv a few years ago, our core belief was: AI models for biology are only as good as the lab data they're trained on and the hypotheses they can test in the real world.
No method excels across all scenarios, and uncertainty-based strategies for optimization often did not outperform methods without uncertainty.
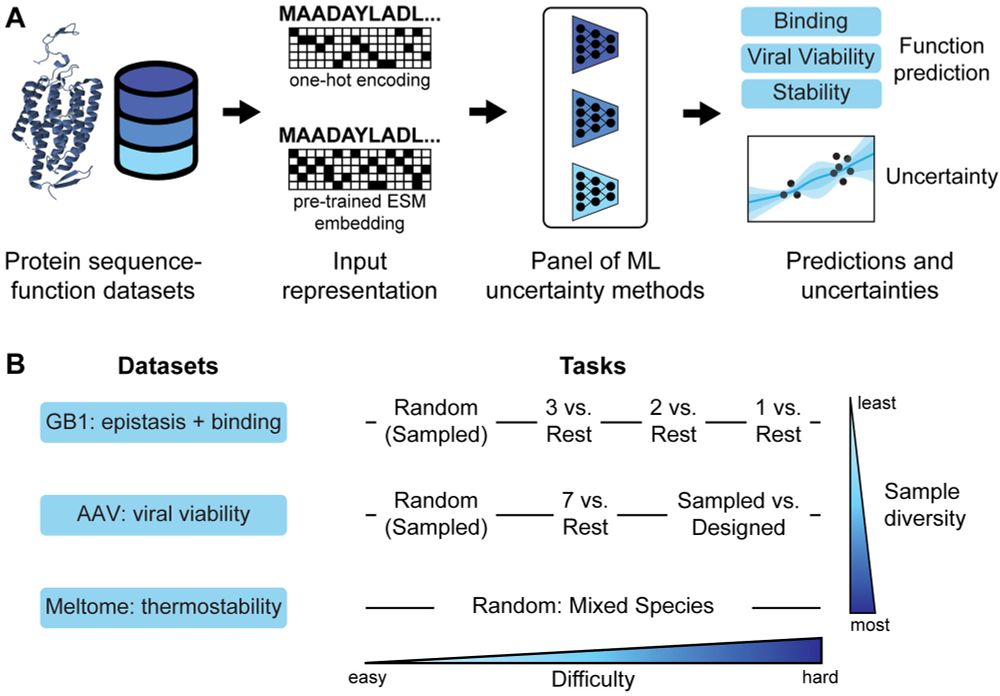
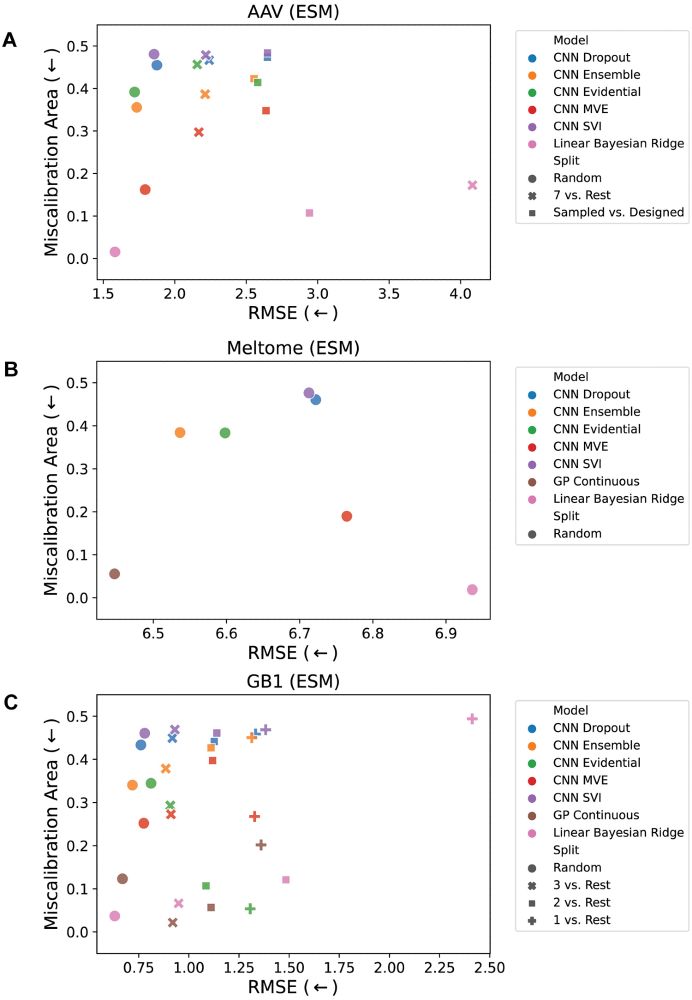
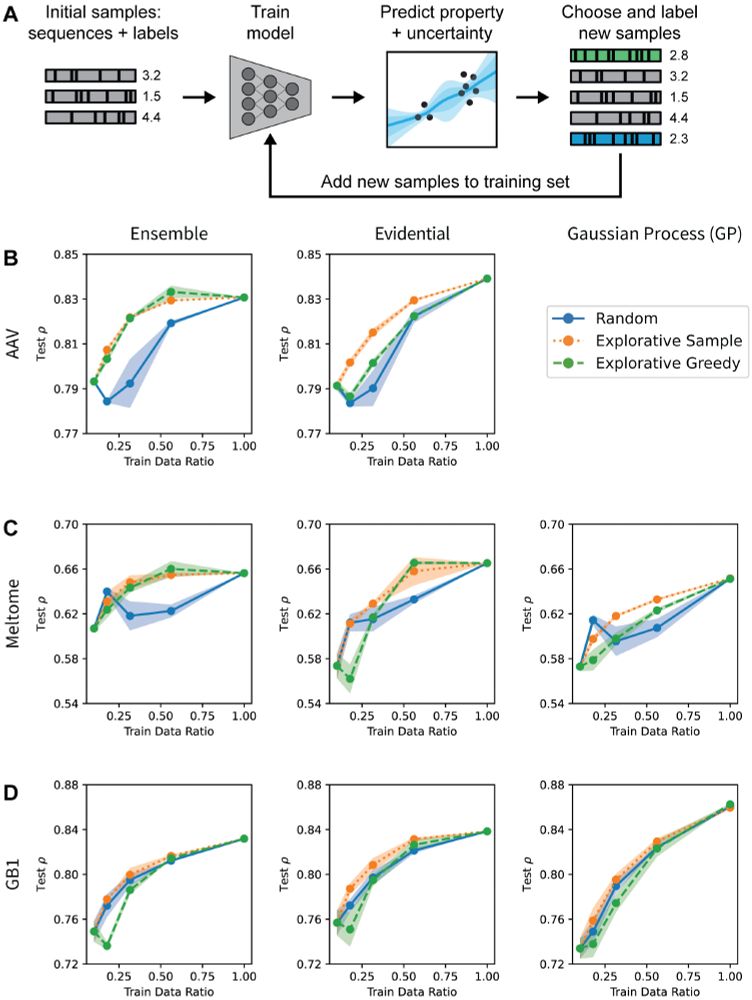
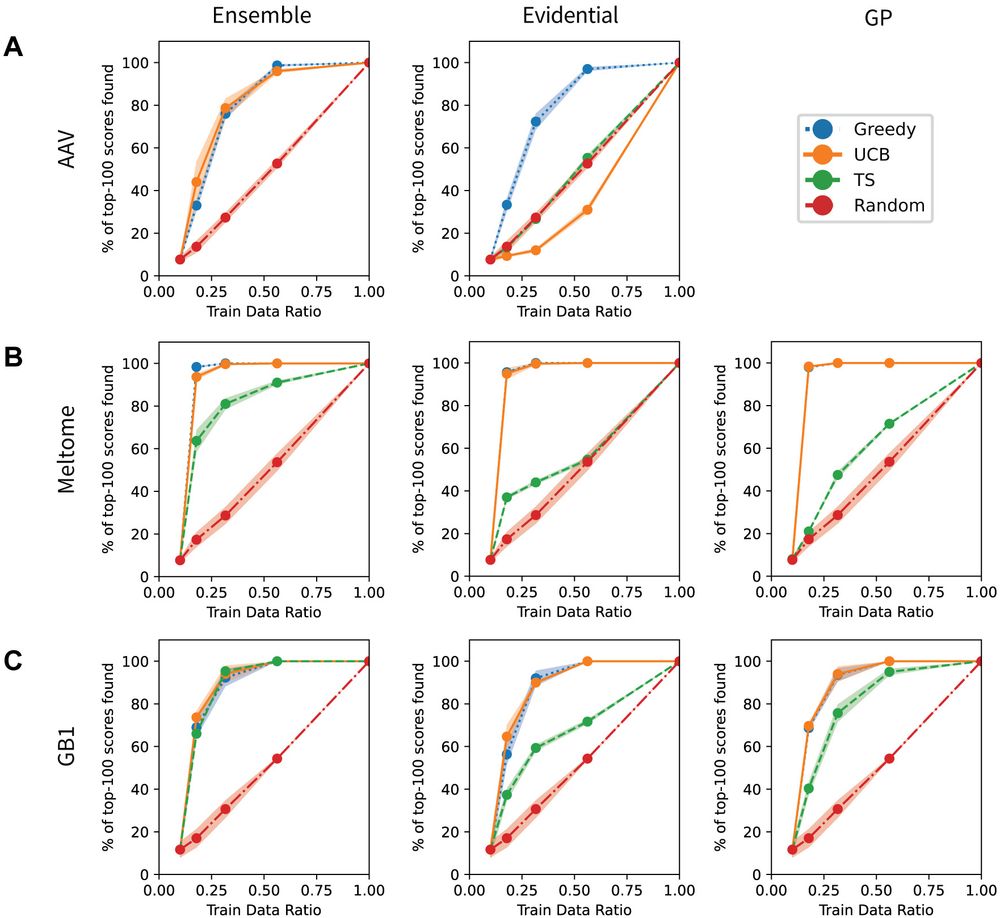
No method excels across all scenarios, and uncertainty-based strategies for optimization often did not outperform methods without uncertainty.
Here, Bemelmans et al. review how scientists use computer algorithms to detect them.
www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti...
🧪 #CompChem

Here, Bemelmans et al. review how scientists use computer algorithms to detect them.
www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti...
🧪 #CompChem


www.nature.com/articles/s41...

www.nature.com/articles/s41...
- toxin/antitoxin pairs
- anti-CRISPR proteins
+ a database of 120B synthetic base pairs
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
@brianhie.bsky.social
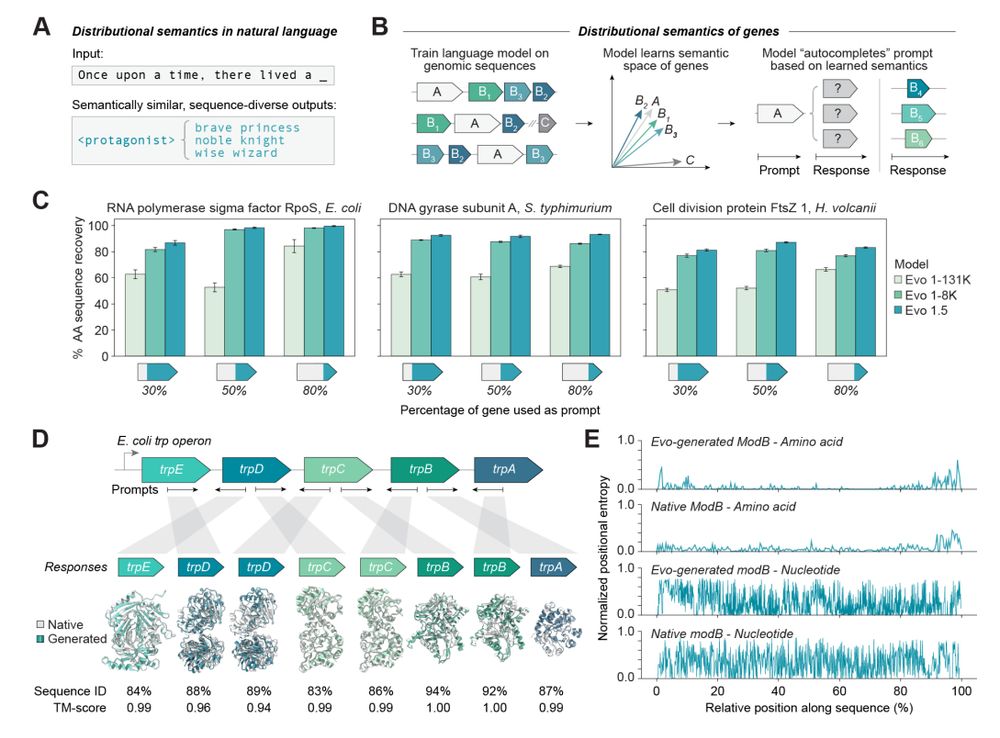
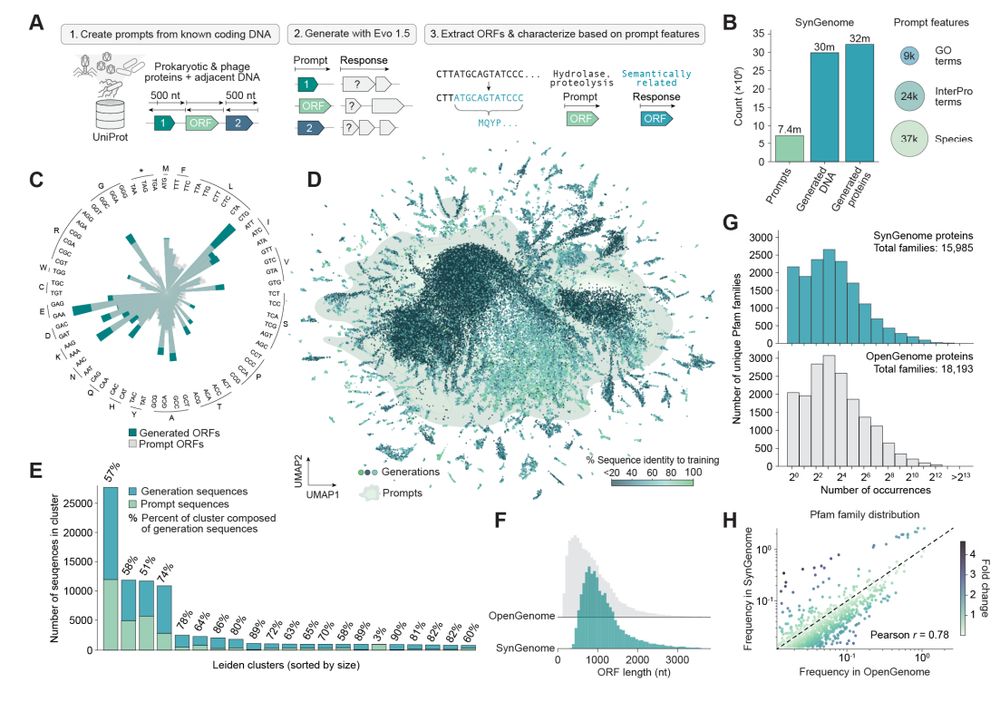
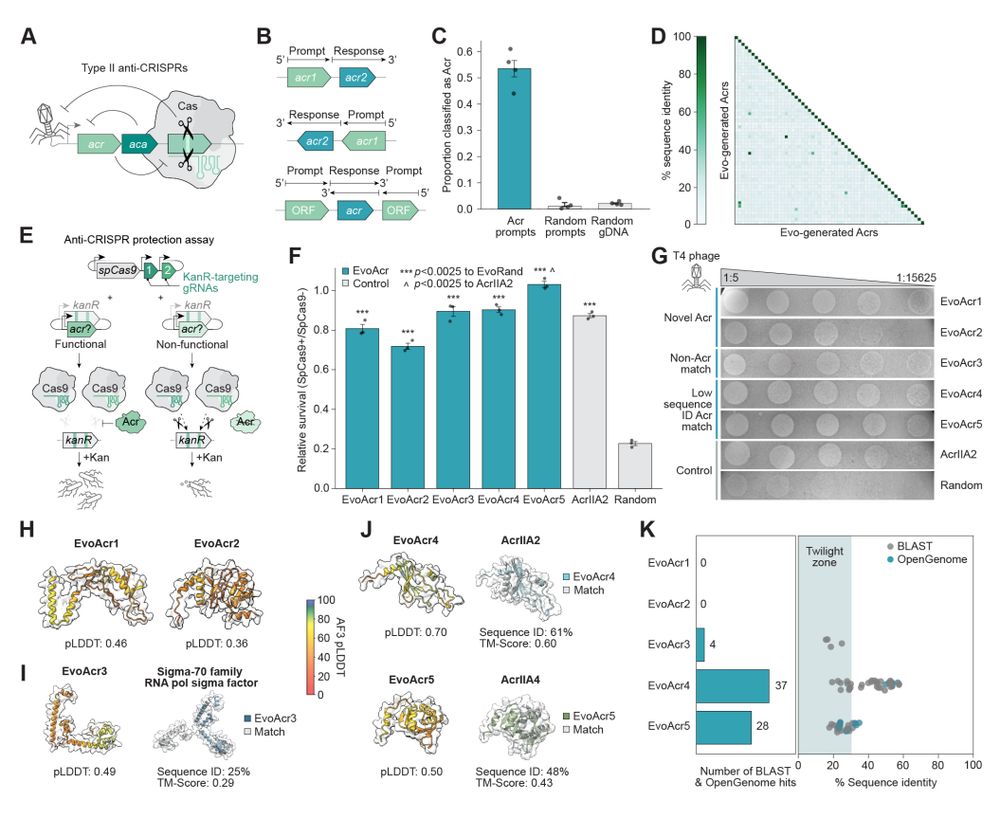
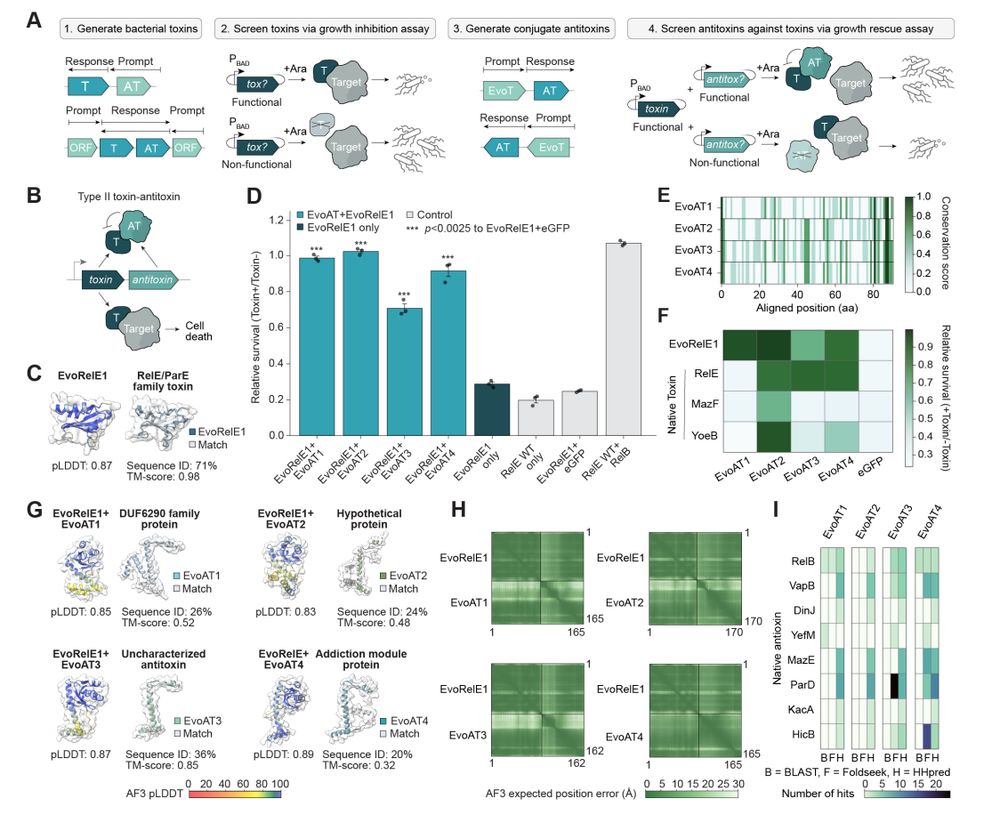
- toxin/antitoxin pairs
- anti-CRISPR proteins
+ a database of 120B synthetic base pairs
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
@brianhie.bsky.social
Aligning autoregressive pLM's to generate EGFR binders via Direct Policy Optimization (DPO) from the incredible @noeliaferruz.bsky.social who gave a great talk as part of the MLSB workshop

Aligning autoregressive pLM's to generate EGFR binders via Direct Policy Optimization (DPO) from the incredible @noeliaferruz.bsky.social who gave a great talk as part of the MLSB workshop

For the first time, we present a systematic exploration of Archaea—a major yet underexplored branch of the tree of life—as a source of novel antimicrobial compounds. www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

For the first time, we present a systematic exploration of Archaea—a major yet underexplored branch of the tree of life—as a source of novel antimicrobial compounds. www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
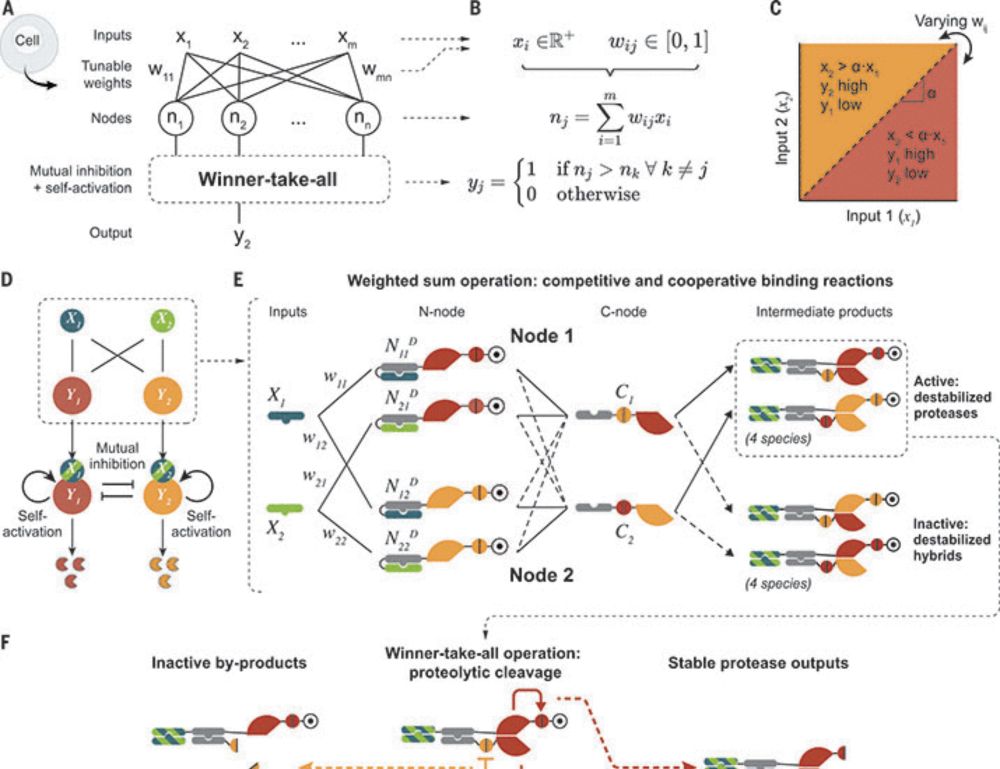


www.nature.com/articles/s43...
www.nature.com/articles/s43...
- showing how to combine multiple models in a principled way
- modern Transformers + GNN to featurize chemical reaction:
- new insights in where the models shine
+ bonus: find the quirky named reaction!
Feedback welcome!
arxiv.org/abs/2412.05269

doi: doi.org/10.1101/2024...
doi: doi.org/10.1101/2024...
foundry.adaptyvbio.com/competition
foundry.adaptyvbio.com/competition
It’s refreshing as most of us are always set on doing things only one way.
You always think back at the end and wonder if you only had tackled it differently from the start www.adaptyvbio.com/blog/po103

It’s refreshing as most of us are always set on doing things only one way.
You always think back at the end and wonder if you only had tackled it differently from the start www.adaptyvbio.com/blog/po103

bit.ly/plaid-proteins
🧵
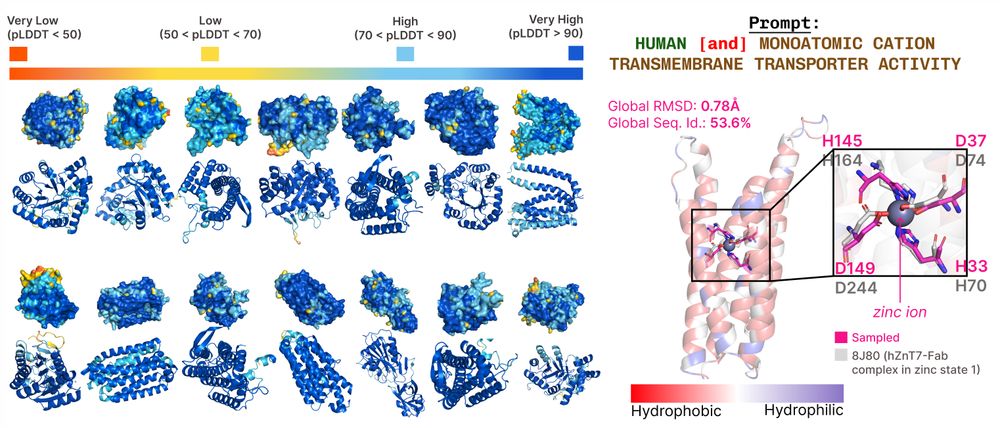
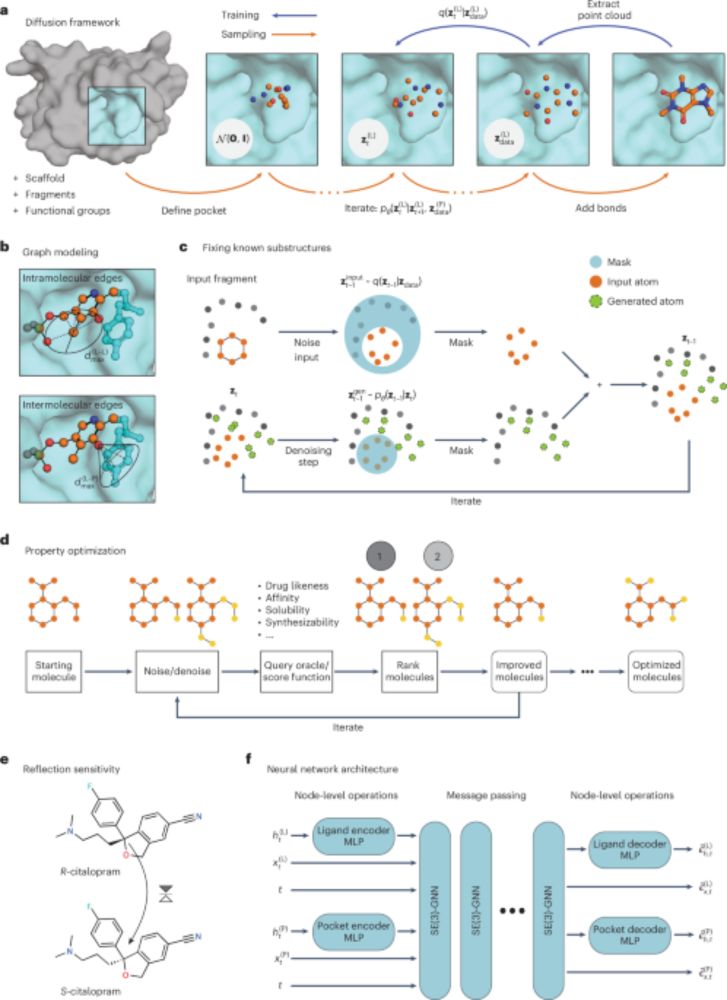
bit.ly/plaid-proteins
🧵
www.adaptyvbio.com/blog/po103

www.adaptyvbio.com/blog/po103
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
• "What [DiffDock] appears to be doing cannot be considered" docking
• "Results are ... contaminated with near neighbors to test cases"
• "Results for DiffDock were artifactual"
• "Results for other methods were incorrectly done"
arxiv.org/abs/2412.02889

• "What [DiffDock] appears to be doing cannot be considered" docking
• "Results are ... contaminated with near neighbors to test cases"
• "Results for DiffDock were artifactual"
• "Results for other methods were incorrectly done"
arxiv.org/abs/2412.02889

