
• Clinical trials and #FOAMed believer •
Now on @shorten2trial.bsky.social
#AMSsky #IDSky #AMR
Hospital Virgen del Rocío • Seville, Spain 🇪🇸



Happy to share our systematic review in @eclinicalmed.bsky.social which we hope will support AB stewardship implementation in SOT units and future research steps #AMSsky #TxID #IDsky
kwnsfk27.r.eu-west-1.awstrack.me/L0/https:%2F...
#IDsky #AntimicrobialResistance #antimicrobialstewardship #rxsky #pharmacy #FOAMed #NPs #PAs

#IDsky #AntimicrobialResistance #antimicrobialstewardship #rxsky #pharmacy #FOAMed #NPs #PAs

#IDSky #AMSSky
www.clinicalmicrobiologyandinfection.org/article/S119...

#IDSky #AMSSky
www.clinicalmicrobiologyandinfection.org/article/S119...
Nuestro hilo sobre diagnóstico y tratamiento de la infección urinaria.
☝🏻 Bacteriuria asintomática
#EAAD #WAAW #AMSsky #MedSky #UTIsky
(🧵1/2)
bsky.app/profile/hosp...
#EAAD #WAAW @guiaprioam.bsky.social
Learn more:
AMS: https://ow.ly/kYz550Xu6iW
EUCIC: https://ow.ly/zlsl50Xu6iU
#IDSky #clinmicro

Learn more:
AMS: https://ow.ly/kYz550Xu6iW
EUCIC: https://ow.ly/zlsl50Xu6iU
#IDSky #clinmicro
Un hilo con nuestras recomendaciones para acertar con tus tratamientos de consulta para las infecciones respiratorias.
☝🏻 Neumonías y EPOC reagudizado
#EAAD #WAAW #AMSsky #MedSky #PharmSky
(🧵1/4)
bsky.app/profile/hosp...
Un hilo con nuestras recomendaciones para acertar con tus tratamientos de consulta para las infecciones respiratorias.
☝🏻 Neumonías y EPOC reagudizado
#EAAD #WAAW #AMSsky #MedSky #PharmSky
(🧵1/4)
bsky.app/profile/hosp...
¡Te necesitamos!
El uso prudente de los antibióticos es responsabilidad de todos. Durante toda esta semana, no te pierdas nuestros vídeos para hacer un uso prudente de los antibióticos.
💪🏻 ¡La lucha contra las resistencias empieza en tu consulta!
#EAAD #WAAW #AMSsky
¡Te necesitamos!
Durante toda esta semana, no te pierdas nuestra serie de vídeos prácticos para hacer un uso prudente de los antibióticos en tus pacientes ambulatorios
👊🏻 La lucha contra las resistencias, empieza en tu consulta
#EAAD #WAAW #AMSsky #MedSky #PharmSky #SomosHUVR

Mantente atento a las redes de @hospitaluvrocio.bsky.social y @guiaprioam.bsky.social durante la semana que viene.
Tenemos un mensaje para ti… 😉
#EAAD #WAAW #AMSsky #SomosHUVR

Mantente atento a las redes de @hospitaluvrocio.bsky.social y @guiaprioam.bsky.social durante la semana que viene.
Tenemos un mensaje para ti… 😉
#EAAD #WAAW #AMSsky #SomosHUVR
The latest video in our partnership with @glaucomflecken.bsky.social summarizes a recent trial investigating whether a single dose or multiple doses of benzathine penicillin G is needed for early syphilis. 👉 nej.md/DrG28
This will be a most needed and important study. clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT060...
#IDweek2025 #IDsky

This will be a most needed and important study. clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT060...
#IDweek2025 #IDsky
- vax 2 weeks before or 3-6 months after immunocompromise expected
- expect blunted response if given within that window
- defer during acute rejection, illness
- adjust for viral circulation
#IDSky #IDWeek

Cloxacillin versus cefazolin for MSSA Bacteraemia
Cefazolin has a non-inferior efficacy regarding mortality, microbiological or clinical endpoints and was associated with a lower rate of serious adverse events #IDSky
www.thelancet.com/journals/lan...




Cloxacillin versus cefazolin for MSSA Bacteraemia
Cefazolin has a non-inferior efficacy regarding mortality, microbiological or clinical endpoints and was associated with a lower rate of serious adverse events #IDSky
www.thelancet.com/journals/lan...
Our centre already mostly does 7 days (and my prediction is that this will be non-inferior) but it's RCT like these that will shift dial across the board with persuasive evidence.
#IDSky #AMR
Our team is now wrapping up follow-up and polishing databases. Hope to have results ready in the first half of 2026!
Hats off to this awesome research team! 🥳
#AMSsky #IDsky @seimc.bsky.social @ciberisciii.bsky.social @ibis-investigacion.bsky.social

Our team is now wrapping up follow-up and polishing databases. Hope to have results ready in the first half of 2026!
Hats off to this awesome research team! 🥳
#AMSsky #IDsky @seimc.bsky.social @ciberisciii.bsky.social @ibis-investigacion.bsky.social

Our team is now wrapping up follow-up and polishing databases. Hope to have results ready in the first half of 2026!
Hats off to this awesome research team! 🥳
#AMSsky #IDsky @seimc.bsky.social @ciberisciii.bsky.social @ibis-investigacion.bsky.social
Dr. Jonathan Ryder and Dr. Aditi Ramakrishnan discuss the intersection of sexually transmitted infections and antimicrobial stewardship.
Listen now: bit.ly/488Ar9I

Dr. Jonathan Ryder and Dr. Aditi Ramakrishnan discuss the intersection of sexually transmitted infections and antimicrobial stewardship.
Listen now: bit.ly/488Ar9I
doi.org/10.1016/j.cm...
@steventong.bsky.social #IDSky

doi.org/10.1016/j.cm...
@steventong.bsky.social #IDSky
#IDSky #clinmicro

#IDSky #clinmicro
👏🏽👏🏽👏🏽
“The revolutionary HIV prevention tool, injectable lenacapavir, will be available at a cost of US$40 a year in 120 low- and middle-income countries starting in 2027”
@unitaid.bsky.social CHAI Wits RHI
unitaid.org/news-blog/le...

👏🏽👏🏽👏🏽
“The revolutionary HIV prevention tool, injectable lenacapavir, will be available at a cost of US$40 a year in 120 low- and middle-income countries starting in 2027”
@unitaid.bsky.social CHAI Wits RHI
unitaid.org/news-blog/le...
#AMS is climate action
doi.org/10.1093/jaca...
#JACAMRNews #Stewardship #Sustainability #IDSky @saiedali.bsky.social
#AMS is climate action
doi.org/10.1093/jaca...
#JACAMRNews #Stewardship #Sustainability #IDSky @saiedali.bsky.social
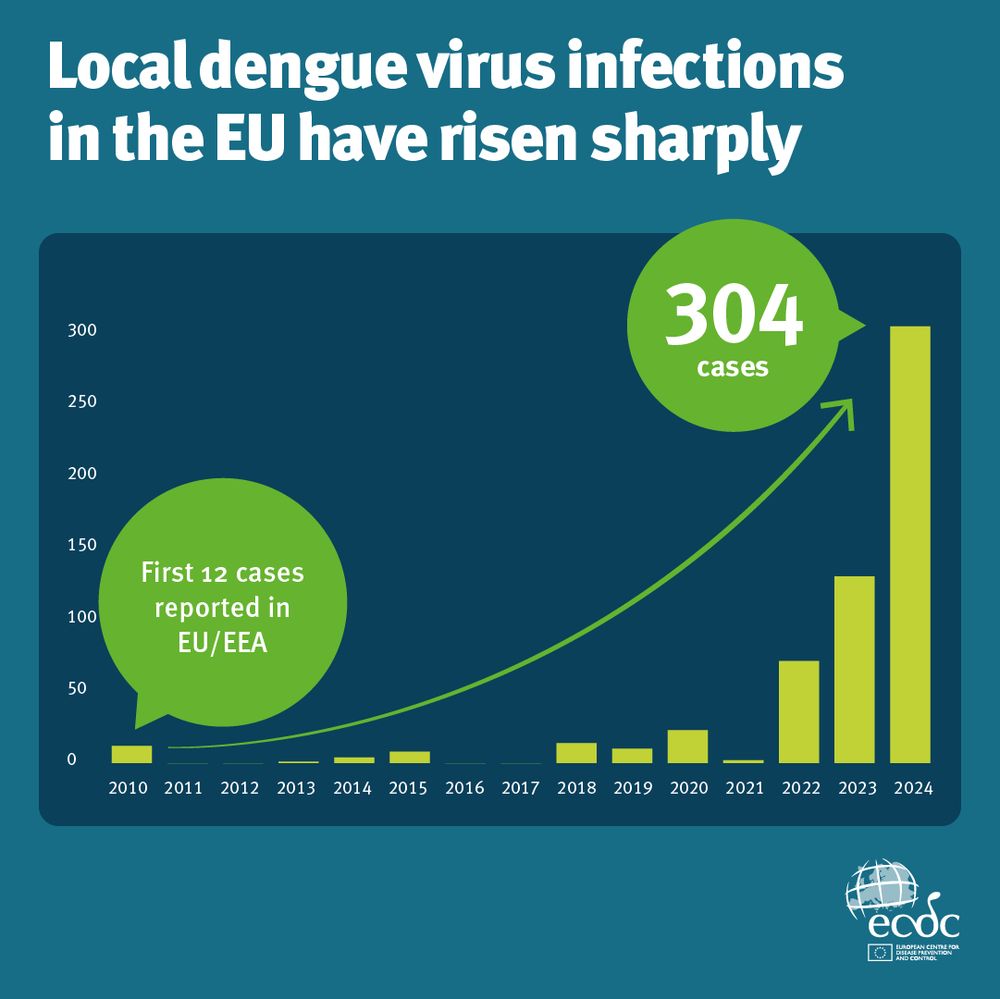
1,700 in 2015 → 5,100 in 2023
Now we’re also seeing more local transmission.
👩⚕️ ECDC is running weekly enhanced surveillance across the EU/EEA - tracking cases and supporting public health action, including for substances of human origin (#SoHO).
#IDsky #EpiSky
www.clinicalmicrobiologyandinfection.com/article/S119... #UTIsky #AMSsky #IDsky
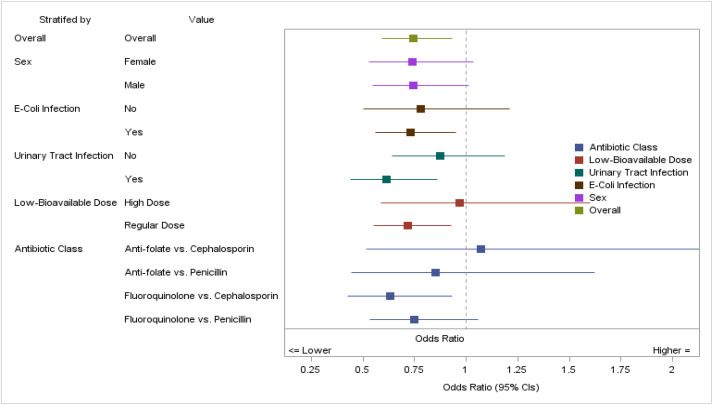
www.clinicalmicrobiologyandinfection.com/article/S119... #UTIsky #AMSsky #IDsky

