
We uncover an unexpected role for endogenous Xist RNA in regulating X-linked genes that escape X-inactivation.

We uncover an unexpected role for endogenous Xist RNA in regulating X-linked genes that escape X-inactivation.
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
If you work in human genetics or transcriptomics, do not miss our tweetorial!👇
@guigolab.bsky.social @bsc-cns.bsky.social @crg.eu
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
If you work in human genetics or transcriptomics, do not miss our tweetorial!👇
@guigolab.bsky.social @bsc-cns.bsky.social @crg.eu

Next X-inactivation meeting in Sapporo, Japan, 19-23 October 2026. Visit x-inactivation-meeting.org to join our mailing list. 🧬 speakers @dandergassen.bsky.social @marnieblewitt.bsky.social @heard65.bsky.social @crougeulle.bsky.social @sexchrlab.bsky.social @zhouqi1982.bsky.social

Next X-inactivation meeting in Sapporo, Japan, 19-23 October 2026. Visit x-inactivation-meeting.org to join our mailing list. 🧬 speakers @dandergassen.bsky.social @marnieblewitt.bsky.social @heard65.bsky.social @crougeulle.bsky.social @sexchrlab.bsky.social @zhouqi1982.bsky.social
Here, we combine the PacBio Iso-Seq workflow with the established WhatsHap phasing approach to assign long reads to the correct allele in polymorphic F1 mouse hybrids.
Here, we combine the PacBio Iso-Seq workflow with the established WhatsHap phasing approach to assign long reads to the correct allele in polymorphic F1 mouse hybrids.
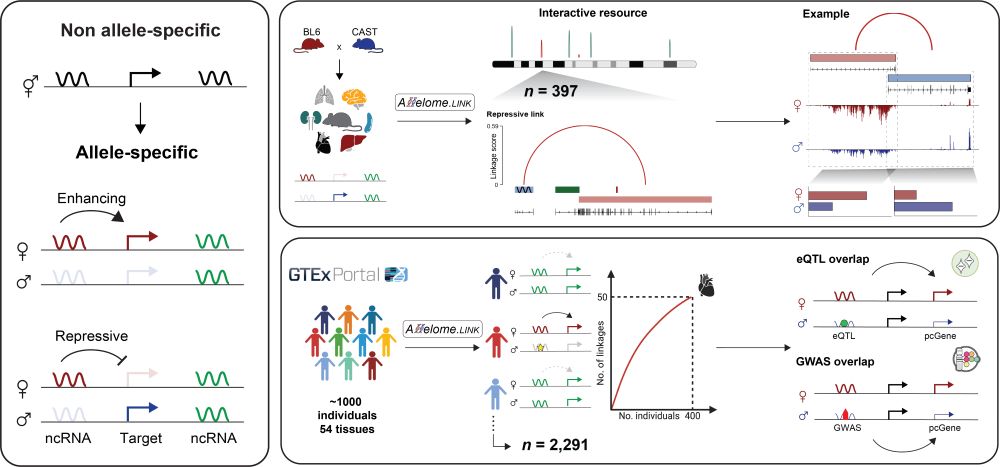
Can we link non-coding elements—like lncRNAs and enhancers—to their protein-coding target genes, and in doing so, connect overlapping non-coding disease variants to their protein-coding counterparts?

Can we link non-coding elements—like lncRNAs and enhancers—to their protein-coding target genes, and in doing so, connect overlapping non-coding disease variants to their protein-coding counterparts?
codon-biased genes in inter-chromosomal proximity. tROLs bridge the non-coding
and coding genomes. @sickkidsto.bsky.social @uoftpress.bsky.social

codon-biased genes in inter-chromosomal proximity. tROLs bridge the non-coding
and coding genomes. @sickkidsto.bsky.social @uoftpress.bsky.social
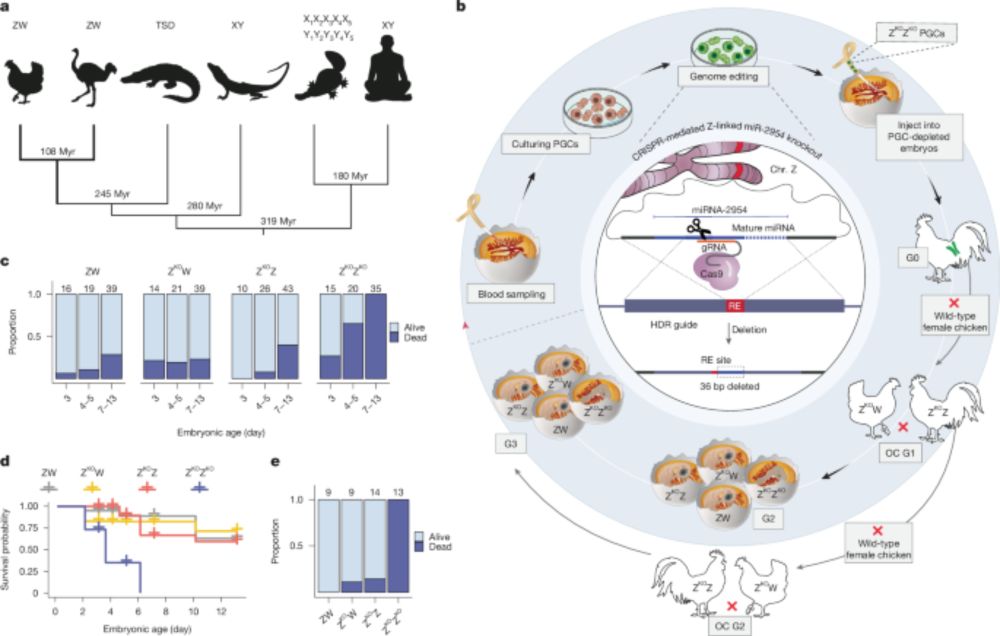


#genetics #aging
📷 @dandergassen.bsky.social

#genetics #aging
📷 @dandergassen.bsky.social
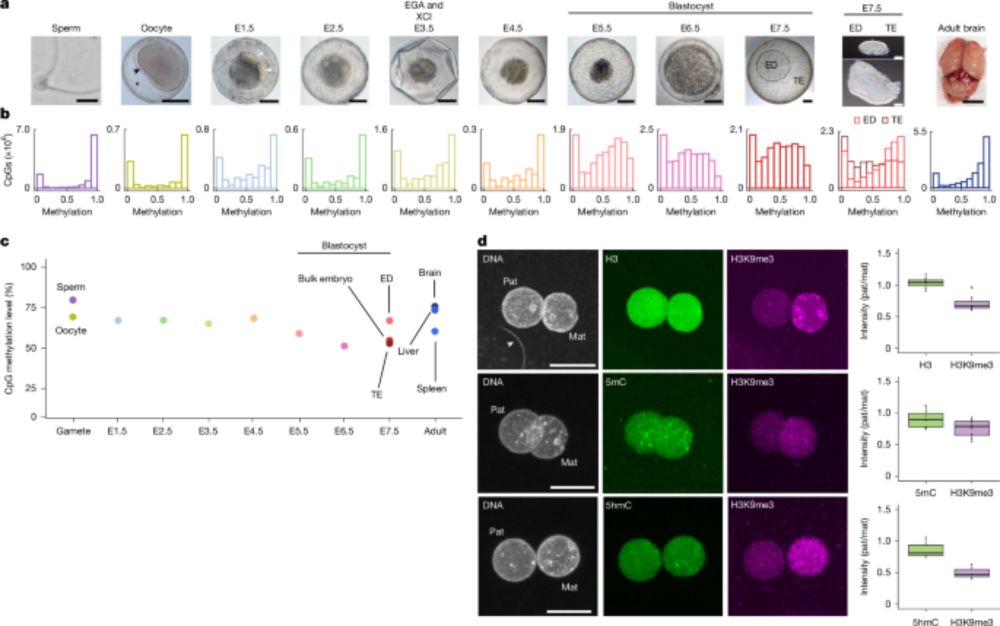
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
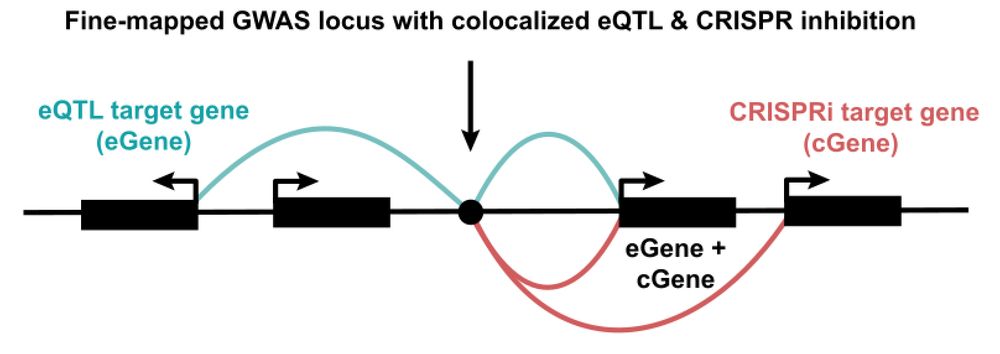
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Have you ever worried about what’s inside your gene annotation GTF⁉️
WELL, YOU SHOULD! 😱
Especially when studying a genetically diverse 🌍 cohort!
🔴We discover that gene annotations are European-biased 👉 impacting downstream analyses!
Don't miss this thread🧵⬇️
1/13

Have you ever worried about what’s inside your gene annotation GTF⁉️
WELL, YOU SHOULD! 😱
Especially when studying a genetically diverse 🌍 cohort!
🔴We discover that gene annotations are European-biased 👉 impacting downstream analyses!
Don't miss this thread🧵⬇️
1/13
🔗 tinyurl.com/3jkzzy7d
🔗 tinyurl.com/3jkzzy7d
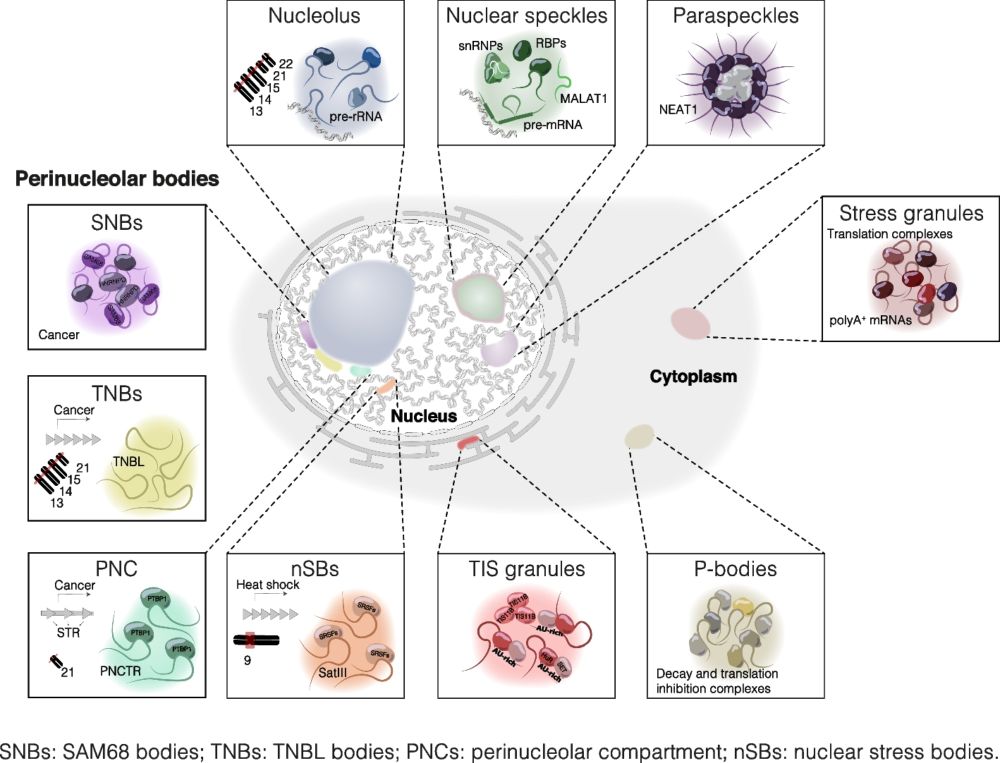
@hasenbeint.bsky.social and co-authors Sarah Hölzl, Stefan Engelhardt @tum.de👇🧵
@hasenbeint.bsky.social and co-authors Sarah Hölzl, Stefan Engelhardt @tum.de👇🧵

