
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
(1/n)

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
(1/n)
doi.org/10.1038/s415...
It was a long journey – 16 months from initial submission to acceptance. Is it just me, or has peer review gotten more arduous lately? 4+ rounds of review isn't so unusual these days...

doi.org/10.1038/s415...
It was a long journey – 16 months from initial submission to acceptance. Is it just me, or has peer review gotten more arduous lately? 4+ rounds of review isn't so unusual these days...

www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
@science.org

www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
@science.org
> EHR-based risk scores often outperform PGS for several common diseases and add predictive value even when combined with PGS.
> PGS better in predicting cancer.
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

> EHR-based risk scores often outperform PGS for several common diseases and add predictive value even when combined with PGS.
> PGS better in predicting cancer.
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Zhidian Zhang, @milot.bsky.social, @martinsteinegger.bsky.social, and @sokrypton.org
biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
TLDR: We introduce MSA Pairformer, a 111M parameter protein language model that challenges the scaling paradigm in self-supervised protein language modeling🧵

Zhidian Zhang, @milot.bsky.social, @martinsteinegger.bsky.social, and @sokrypton.org
biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
TLDR: We introduce MSA Pairformer, a 111M parameter protein language model that challenges the scaling paradigm in self-supervised protein language modeling🧵
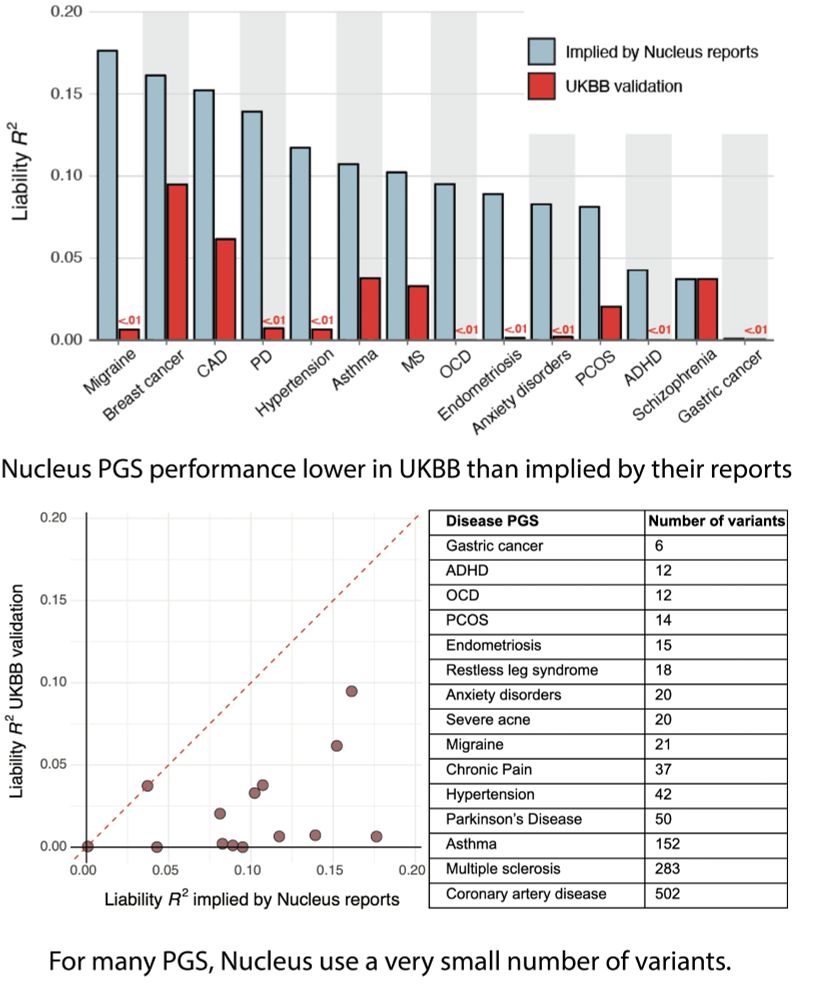


www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
probgen2026.github.io
Please help spread the news.
probgen2026.github.io
Please help spread the news.
www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1...

www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1...
Do these studies find the most IMPORTANT genes? If not, how DO they rank genes?
Here we present a surprising result: these studies actually test for SPECIFICITY! A 🧵on what this means... (🧪🧬)
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

Do these studies find the most IMPORTANT genes? If not, how DO they rank genes?
Here we present a surprising result: these studies actually test for SPECIFICITY! A 🧵on what this means... (🧪🧬)
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
we develop a method to map QTL that change gene coexpression networks. For each genetic marker in an F2 cross, split the data by genotype & build a coexpression network for each genotype

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
we develop a method to map QTL that change gene coexpression networks. For each genetic marker in an F2 cross, split the data by genotype & build a coexpression network for each genotype


authors.elsevier.com/a/1igrbL7PXq...
authors.elsevier.com/a/1igrbL7PXq...
threadreaderapp.com/thread/17633...
threadreaderapp.com/thread/17633...



