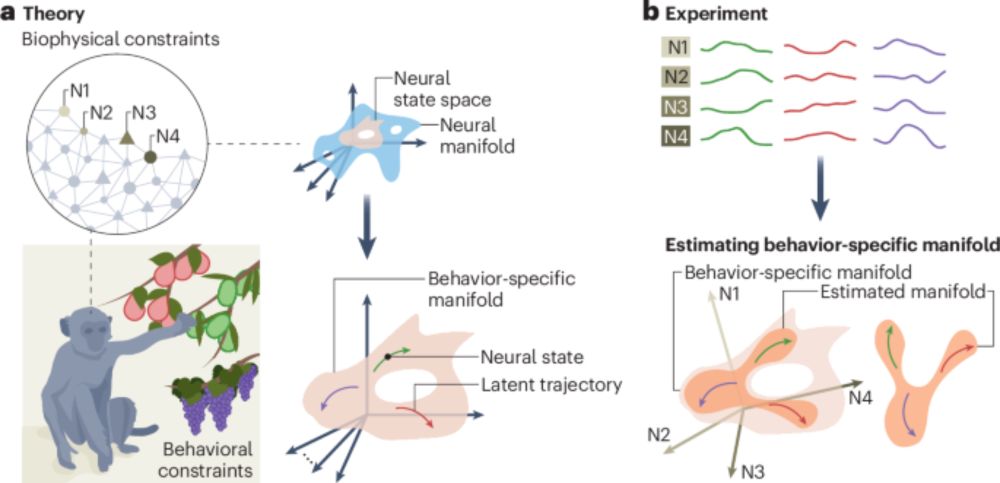
@david-g-clark.bsky.social and Ashok Litwin-Kumar! Timely too, as “low-D manifold” has been trending again. (If you read thru the end, we escape Flatland and return to the glorious high-D world we deserve.) www.biorxiv.org/content/10.6...

@david-g-clark.bsky.social and Ashok Litwin-Kumar! Timely too, as “low-D manifold” has been trending again. (If you read thru the end, we escape Flatland and return to the glorious high-D world we deserve.) www.biorxiv.org/content/10.6...

www.nature.com/articles/s41...
#neuroAI

www.nature.com/articles/s41...
#neuroAI
New preprint of work with Christian Machens: www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

New preprint of work with Christian Machens: www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
![What do representations tell us about a system? Image of a mouse with a scope showing a vector of activity patterns, and a neural network with a vector of unit activity patterns
Common analyses of neural representations: Encoding models (relating activity to task features) drawing of an arrow from a trace saying [on_____on____] to a neuron and spike train. Comparing models via neural predictivity: comparing two neural networks by their R^2 to mouse brain activity. RSA: assessing brain-brain or model-brain correspondence using representational dissimilarity matrices](https://cdn.bsky.app/img/feed_thumbnail/plain/did:plc:e6ewzleebkdi2y2bxhjxoknt/bafkreiav2io2ska33o4kizf57co5bboqyyfdpnozo2gxsicrfr5l7qzjcq@jpeg)
It's a pleasure to share our paper at @cp-cell.bsky.social, showing how mice learning over long timescales display key hallmarks of gradient descent (GD).
The culmination of my PhD supervised by @laklab.bsky.social, @saxelab.bsky.social and Rafal Bogacz!
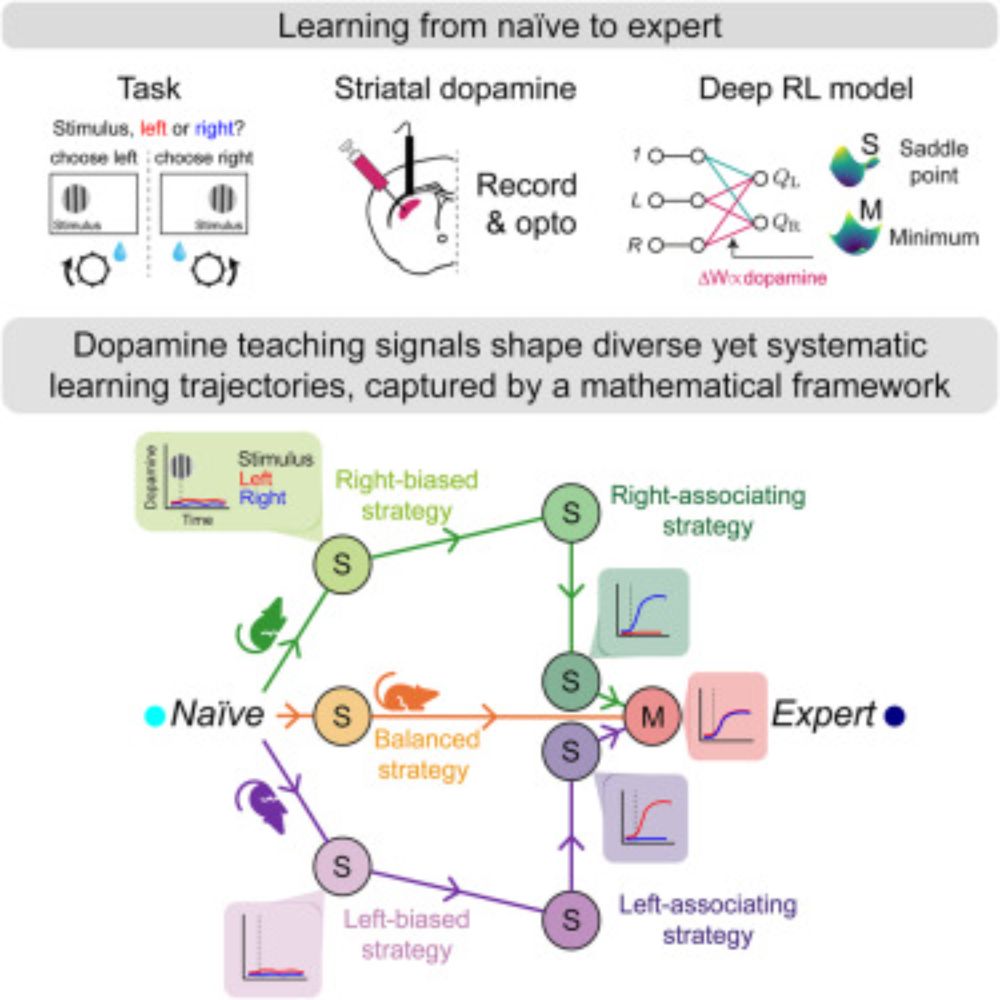
It's a pleasure to share our paper at @cp-cell.bsky.social, showing how mice learning over long timescales display key hallmarks of gradient descent (GD).
The culmination of my PhD supervised by @laklab.bsky.social, @saxelab.bsky.social and Rafal Bogacz!

Most people can understand it.
No PhD-level intelligence needed.

We show how to exactly map recurrent spiking networks into recurrent rate networks, with the same number of neurons. No temporal or spatial averaging needed!
Presented at Gatsby Neural Dynamics Workshop, London.

We show how to exactly map recurrent spiking networks into recurrent rate networks, with the same number of neurons. No temporal or spatial averaging needed!
Presented at Gatsby Neural Dynamics Workshop, London.
🔗: www.nature.com/articles/s41...
📄: rdcu.be/ex8hW
🔗: www.nature.com/articles/s41...
📄: rdcu.be/ex8hW