
Botond Sipos
@sbotond.bsky.social
EMBL::EBI::EnsEMBL::Compara
GitHub: https://github.com/botond-sipos
Scholar: https://bit.ly/botond-sipos-scholar
Substack: https://substack.com/@sbotond
GitHub: https://github.com/botond-sipos
Scholar: https://bit.ly/botond-sipos-scholar
Substack: https://substack.com/@sbotond
Reposted by Botond Sipos
Great work by Nicola De Maio and Nick Goldman - not just scaleable to "pandemic scale" trees but - if I have got this right - arguably more valid than traditional column based bootstrap in the context of very tight evolution.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, the millions of viral genomes coming in overwhelmed traditional methods for data analysis.
Find out how SPRTA, a new tool, provides a fast, scalable way to measure confidence of phylogenetic trees, helping scientists track outbreaks.
www.ebi.ac.uk/about/news/t...
Find out how SPRTA, a new tool, provides a fast, scalable way to measure confidence of phylogenetic trees, helping scientists track outbreaks.
www.ebi.ac.uk/about/news/t...

SPRTA: a smarter way to measure evolution uncertainty
A new method from EMBL-EBI and collaborators offers fast, easy-to-interpret confidence scores for phylogenetic trees for pandemic preparedness.
www.ebi.ac.uk
November 5, 2025 at 10:33 PM
Great work by Nicola De Maio and Nick Goldman - not just scaleable to "pandemic scale" trees but - if I have got this right - arguably more valid than traditional column based bootstrap in the context of very tight evolution.
Reposted by Botond Sipos
Yes - isometric scaling as a way to understand the benefits and costs of being small versus large. Haldane's Harpers article from 1926 is an amazing example of popular science writing.

October 31, 2025 at 9:53 PM
Yes - isometric scaling as a way to understand the benefits and costs of being small versus large. Haldane's Harpers article from 1926 is an amazing example of popular science writing.
Reposted by Botond Sipos
Can an AI tool help us better understand the origins of cancer?
Researchers from EMBL's Korbel Group have developed a new AI method – MAGIC – which, through a game of molecular laser tag, is shedding light on how chromosomal abnormalities form in cells.
www.embl.org/news/science...
Researchers from EMBL's Korbel Group have developed a new AI method – MAGIC – which, through a game of molecular laser tag, is shedding light on how chromosomal abnormalities form in cells.
www.embl.org/news/science...

October 29, 2025 at 4:11 PM
Can an AI tool help us better understand the origins of cancer?
Researchers from EMBL's Korbel Group have developed a new AI method – MAGIC – which, through a game of molecular laser tag, is shedding light on how chromosomal abnormalities form in cells.
www.embl.org/news/science...
Researchers from EMBL's Korbel Group have developed a new AI method – MAGIC – which, through a game of molecular laser tag, is shedding light on how chromosomal abnormalities form in cells.
www.embl.org/news/science...
#Annotating the genome at single-nucleotide resolution with #DNA foundation models www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Annotating the genome at single-nucleotide resolution with DNA foundation models - Nature Methods
By leveraging the power of pretrained DNA foundation models, SegmentNT achieves performant genome annotation through segmenting different genic and regulatory elements.
www.nature.com
October 29, 2025 at 2:48 PM
#Annotating the genome at single-nucleotide resolution with #DNA foundation models www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Unlocking the regulatory code of #RNA: launching the Human #RNome Project genomebiology.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....

Unlocking the regulatory code of RNA: launching the Human RNome Project | Genome Biology | Full Text
The human RNome, the complete set of RNA molecules in human cells, arises through complex processing and includes diverse molecular species. While research traditionally focuses on four canonical nucleotide residues, the RNome, encompassing over 180 distinct modifications across organisms, with at least 50 in humans, is increasingly recognized. These modifications play critical roles in regulating RNA structure, stability, and function, yet the rules linking their precise locations to biological outcomes remain poorly defined. The Human RNome Project aims to map all RNA modifications, build essential resources, and harness new technologies to transform RNA biology, therapeutic development, agriculture, and even data storage.
genomebiology.biomedcentral.com
October 26, 2025 at 6:11 PM
Unlocking the regulatory code of #RNA: launching the Human #RNome Project genomebiology.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
Reposted by Botond Sipos
I am genuinely impressed by large language models - they can absorb disparate components of text into some consolidated view, they can produce extremely good language and - with the right model - translate pretty well between languages and they are an excellent text based UI for humans to use. But..
October 26, 2025 at 7:48 AM
I am genuinely impressed by large language models - they can absorb disparate components of text into some consolidated view, they can produce extremely good language and - with the right model - translate pretty well between languages and they are an excellent text based UI for humans to use. But..
Reposted by Botond Sipos
Think of AI labs as Cronos, a titan in Greek mythology, trying to devour his children. The question, as with Cronos, is: can the little ones survive and fight back?

OpenAI and Anthropic v app developers: tech’s Cronos syndrome
Will the labs devour the apps that run on their models?
econ.st
October 25, 2025 at 10:40 AM
Think of AI labs as Cronos, a titan in Greek mythology, trying to devour his children. The question, as with Cronos, is: can the little ones survive and fight back?
Reposted by Botond Sipos
Really exciting that the preprint on Barbell, a new demultiplexer, is finally out!
It's the first tool that builds on Sassy, the approximate-DNA-searching tool that @rickbitloo.bsky.social and myself developed earlier this year, specifically with this application in mind.
It's the first tool that builds on Sassy, the approximate-DNA-searching tool that @rickbitloo.bsky.social and myself developed earlier this year, specifically with this application in mind.
Around 10% of your Nanopore reads (SQK-RBK114) are incorrectly trimmed. Here is why, and how our new tool Barbell solves it:
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Want to get started? github.com/rickbeeloo/b...
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Want to get started? github.com/rickbeeloo/b...
October 23, 2025 at 9:28 PM
Really exciting that the preprint on Barbell, a new demultiplexer, is finally out!
It's the first tool that builds on Sassy, the approximate-DNA-searching tool that @rickbitloo.bsky.social and myself developed earlier this year, specifically with this application in mind.
It's the first tool that builds on Sassy, the approximate-DNA-searching tool that @rickbitloo.bsky.social and myself developed earlier this year, specifically with this application in mind.
AGNES: Adaptive Graph Neural Network and Dynamic Programming Hybrid Framework for Real-Time #Nanopore Seed Chaining arxiv.org/abs/2510.16013

AGNES: Adaptive Graph Neural Network and Dynamic Programming Hybrid Framework for Real-Time Nanopore Seed Chaining
Nanopore sequencing enables real-time long-read DNA sequencing with reads exceeding 10 kilobases, but inherent error rates of 12-15 percent present significant computational challenges for read alignm...
arxiv.org
October 22, 2025 at 6:34 AM
AGNES: Adaptive Graph Neural Network and Dynamic Programming Hybrid Framework for Real-Time #Nanopore Seed Chaining arxiv.org/abs/2510.16013
Reposted by Botond Sipos
Full comic here: www.smbc-comics.com/comic/signal-4 #smbc
October 20, 2025 at 5:16 PM
Full comic here: www.smbc-comics.com/comic/signal-4 #smbc
Reposted by Botond Sipos
Biological life depends on two families of large molecule: nucleic acids and proteins. The first of our collection of primers explains what they are and how they work

Nucleic acids and proteins
Big complex molecules are the unique stuff of life. This is how they work
econ.st
October 11, 2025 at 12:20 PM
Biological life depends on two families of large molecule: nucleic acids and proteins. The first of our collection of primers explains what they are and how they work
Reposted by Botond Sipos
I am looking to get my hands on some #Illumina 5-base methylation data - does anyone have a bam file that I could use for some testing? Please RT for reach!
October 21, 2025 at 9:36 AM
I am looking to get my hands on some #Illumina 5-base methylation data - does anyone have a bam file that I could use for some testing? Please RT for reach!
Reposted by Botond Sipos
Bayesian probability, like frequentist probability, is a model-based activity that is mathematically anchored by physical randomization at one end and calibration to a reference set at the other
statmodeling.stat.columbia.edu/2025/10/20/b...
statmodeling.stat.columbia.edu/2025/10/20/b...
Bayesian probability, like frequentist probability, is a model-based activity that is mathematically anchored by physical randomization at one end and calibration to a reference set at the other | St...
statmodeling.stat.columbia.edu
October 20, 2025 at 1:59 PM
Bayesian probability, like frequentist probability, is a model-based activity that is mathematically anchored by physical randomization at one end and calibration to a reference set at the other
statmodeling.stat.columbia.edu/2025/10/20/b...
statmodeling.stat.columbia.edu/2025/10/20/b...
Reposted by Botond Sipos
New tool "bwt-svg" for making illustrations of the BWT and the many auxiliary arrays and other structures related to it. Pyodide-based no-installation-necessary interface here: benlangmead.github.io/bwt-svg/. (H/t to @robert.bio for pointing me to pyodide!) Full repo: github.com/benlangmead/....

October 14, 2025 at 8:48 PM
New tool "bwt-svg" for making illustrations of the BWT and the many auxiliary arrays and other structures related to it. Pyodide-based no-installation-necessary interface here: benlangmead.github.io/bwt-svg/. (H/t to @robert.bio for pointing me to pyodide!) Full repo: github.com/benlangmead/....
Reposted by Botond Sipos
🚨 New preprint alert 🚨
We systematically benchmarked @nanoporetech.com 's modification-aware basecalling models released for RNA on sets of in vitro and in vivo sequences and made some curious observations 🧬🔍.
bit.ly/4lXqNul
Follow along for a little recap (1/12)
We systematically benchmarked @nanoporetech.com 's modification-aware basecalling models released for RNA on sets of in vitro and in vivo sequences and made some curious observations 🧬🔍.
bit.ly/4lXqNul
Follow along for a little recap (1/12)

Systematic benchmarking of basecalling models for RNA modification detection with highly multiplexed nanopore sequencing
Nanopore direct RNA sequencing (DRS) holds promise for advancing our understanding of the epitranscriptome by detecting RNA modifications in native RNA molecules. Recently, Oxford Nanopore Technologie...
bit.ly
July 14, 2025 at 4:00 PM
🚨 New preprint alert 🚨
We systematically benchmarked @nanoporetech.com 's modification-aware basecalling models released for RNA on sets of in vitro and in vivo sequences and made some curious observations 🧬🔍.
bit.ly/4lXqNul
Follow along for a little recap (1/12)
We systematically benchmarked @nanoporetech.com 's modification-aware basecalling models released for RNA on sets of in vitro and in vivo sequences and made some curious observations 🧬🔍.
bit.ly/4lXqNul
Follow along for a little recap (1/12)
Reposted by Botond Sipos
Go 1.25 interactive tour
Go 1.25 is scheduled for release in August, so it's a good time to explore what's new.
#golang
antonz.org/go-1-25/
Go 1.25 is scheduled for release in August, so it's a good time to explore what's new.
#golang
antonz.org/go-1-25/

Go 1.25 interactive tour
Fake clock, new GC, flight recorder and more.
antonz.org
June 28, 2025 at 3:15 AM
Go 1.25 interactive tour
Go 1.25 is scheduled for release in August, so it's a good time to explore what's new.
#golang
antonz.org/go-1-25/
Go 1.25 is scheduled for release in August, so it's a good time to explore what's new.
#golang
antonz.org/go-1-25/
Reposted by Botond Sipos
Excited to launch our AlphaGenome API goo.gle/3ZPUeFX along with the preprint goo.gle/45AkUyc describing and evaluating our latest DNA sequence model powering the API. Looking forward to seeing how scientists use it! @googledeepmind
June 25, 2025 at 2:29 PM
Excited to launch our AlphaGenome API goo.gle/3ZPUeFX along with the preprint goo.gle/45AkUyc describing and evaluating our latest DNA sequence model powering the API. Looking forward to seeing how scientists use it! @googledeepmind
Reposted by Botond Sipos
New paper from the lab from Sriram Garg in my group. We introduce a general substitution matrix for structural phylogenetics. I think this is a big deal, so read on below if you think deep history is important. academic.oup.com/mbe/advance-...

A general substitution matrix for structural phylogenetics.
Abstract. Sequence-based maximum likelihood (ML) phylogenetics is a widely used method for inferring evolutionary relationships, which has illuminated the
academic.oup.com
June 11, 2025 at 2:01 PM
New paper from the lab from Sriram Garg in my group. We introduce a general substitution matrix for structural phylogenetics. I think this is a big deal, so read on below if you think deep history is important. academic.oup.com/mbe/advance-...
Reposted by Botond Sipos
Vaughan & @tanjastadler.bsky.social develop a method to infer multitype population trajectories and apply it to MERS-CoV, revealing transmission patterns between camels and humans.
🔗 doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msaf130
#evobio #molbio #virus
🔗 doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msaf130
#evobio #molbio #virus
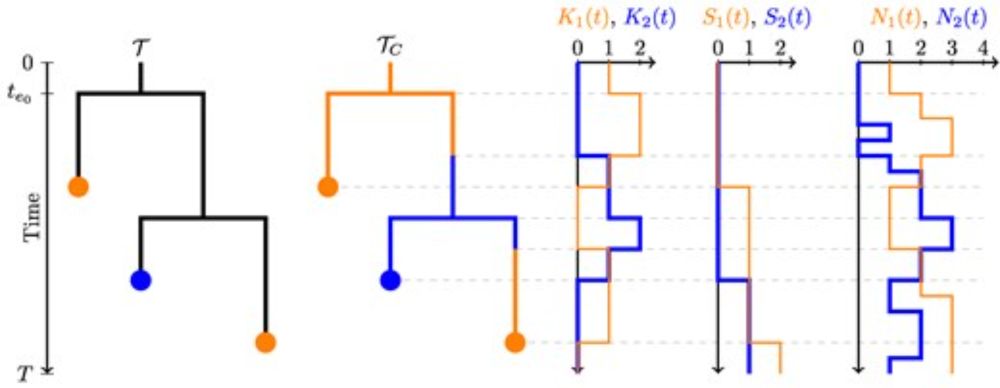
Bayesian Phylodynamic Inference of Multitype Population Trajectories Using Genomic Data
Abstract. Phylodynamic methods provide a coherent framework for the inference of population parameters directly from genetic data. They are an important to
doi.org
June 17, 2025 at 2:29 PM
Vaughan & @tanjastadler.bsky.social develop a method to infer multitype population trajectories and apply it to MERS-CoV, revealing transmission patterns between camels and humans.
🔗 doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msaf130
#evobio #molbio #virus
🔗 doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msaf130
#evobio #molbio #virus
Reposted by Botond Sipos
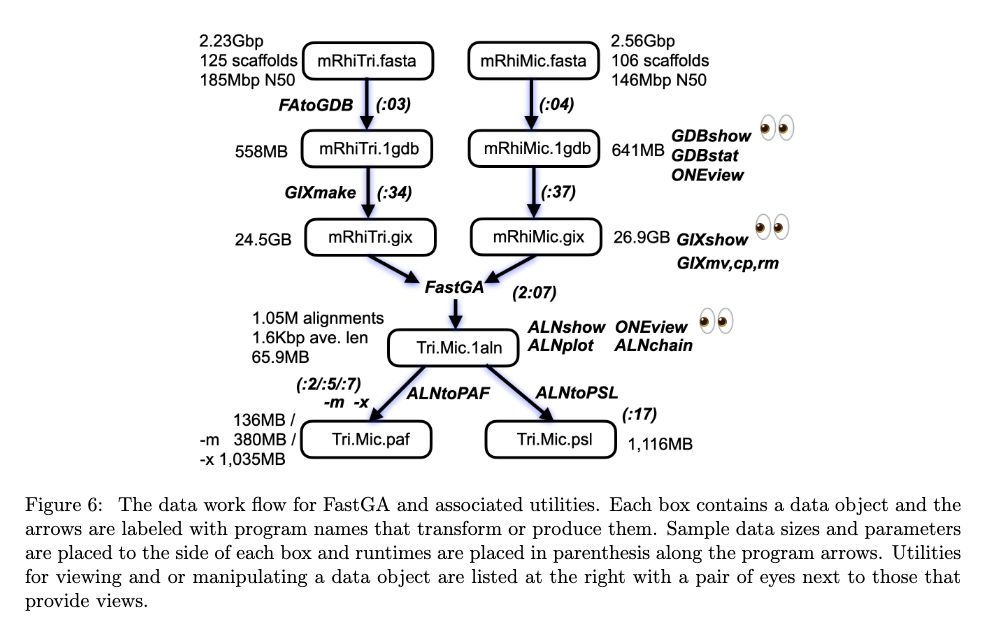
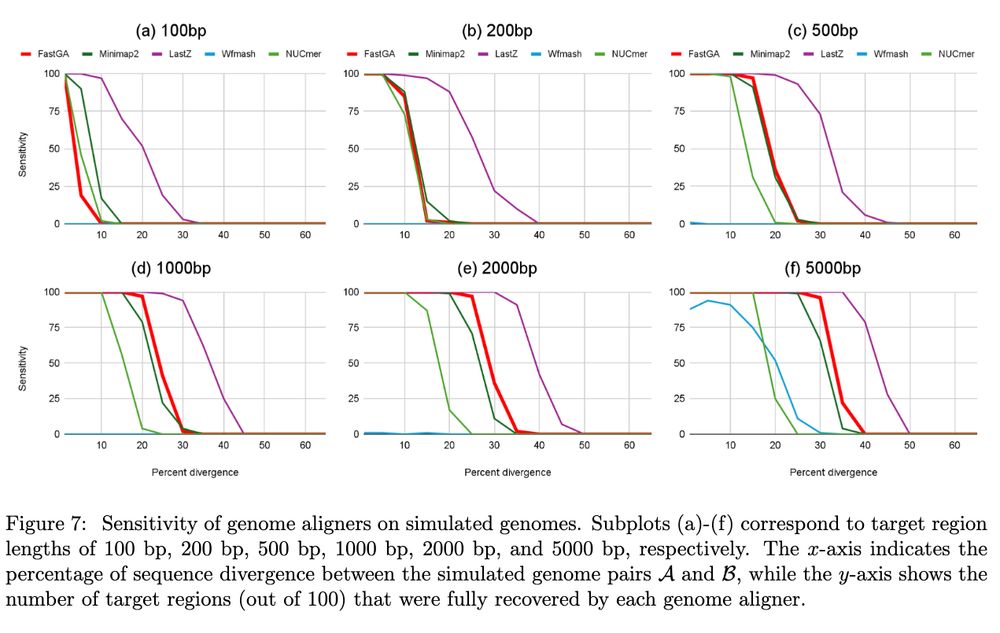
FastGA: Fast Genome Alignment www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1... 🧬🖥️🧪 www.github.com/thegenemyers...
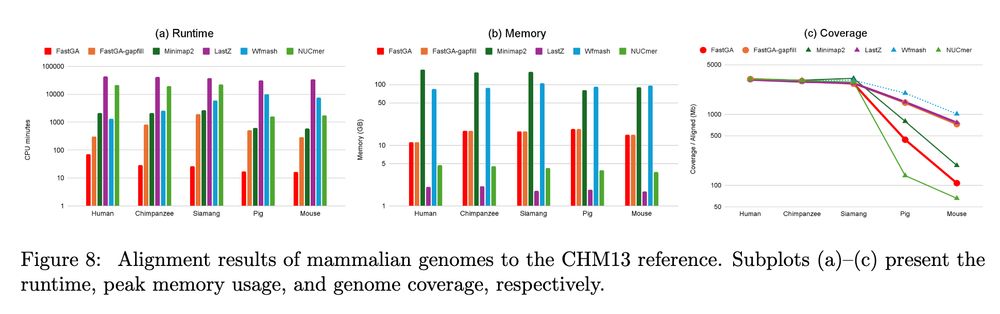
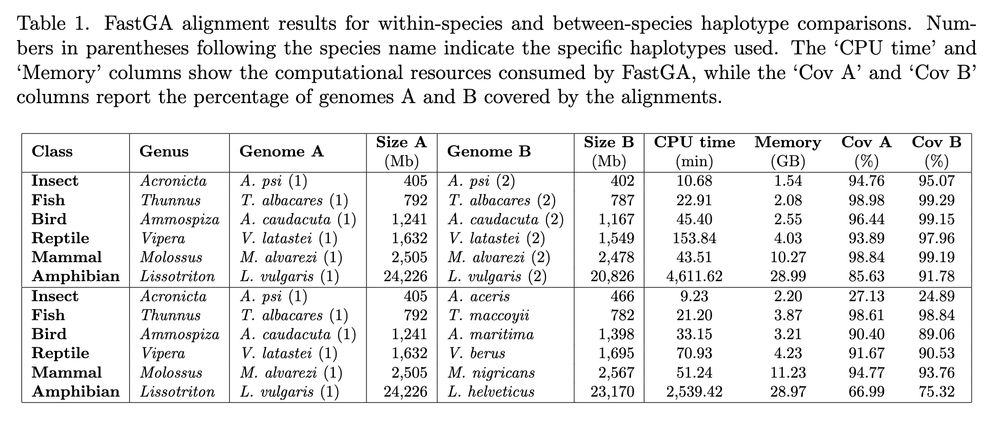
June 20, 2025 at 9:39 AM
FastGA: Fast Genome Alignment www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1... 🧬🖥️🧪 www.github.com/thegenemyers...
Reposted by Botond Sipos
Powerful stuff from @juliosaezrod.bsky.social who found himself on the other end of the process - as a patient not a computational biology researcher - giving him insight into both research and patient perspectives. Huge credit to Julio for talking about his experiences here
June 20, 2025 at 8:06 AM
Powerful stuff from @juliosaezrod.bsky.social who found himself on the other end of the process - as a patient not a computational biology researcher - giving him insight into both research and patient perspectives. Huge credit to Julio for talking about his experiences here
Reposted by Botond Sipos
Michael Ashburner FRS was an influential figure in the fields of Drosophila genomics and early sequencing database initiatives such as @ebi.embl.org.
Read about their contributions across genetics and bioinformatics in the new biographical memoir: buff.ly/f01zNat
@geneticscam.bsky.social
Read about their contributions across genetics and bioinformatics in the new biographical memoir: buff.ly/f01zNat
@geneticscam.bsky.social

June 17, 2025 at 10:44 AM
Michael Ashburner FRS was an influential figure in the fields of Drosophila genomics and early sequencing database initiatives such as @ebi.embl.org.
Read about their contributions across genetics and bioinformatics in the new biographical memoir: buff.ly/f01zNat
@geneticscam.bsky.social
Read about their contributions across genetics and bioinformatics in the new biographical memoir: buff.ly/f01zNat
@geneticscam.bsky.social
Reposted by Botond Sipos
Preprint on "Improving spliced alignment by modeling splice sites with deep learning". It describes minisplice for modeling splice signals. Minimap2 and miniprot now optionally use the predicted scores to improve spliced alignment.
arxiv.org/abs/2506.12986
arxiv.org/abs/2506.12986
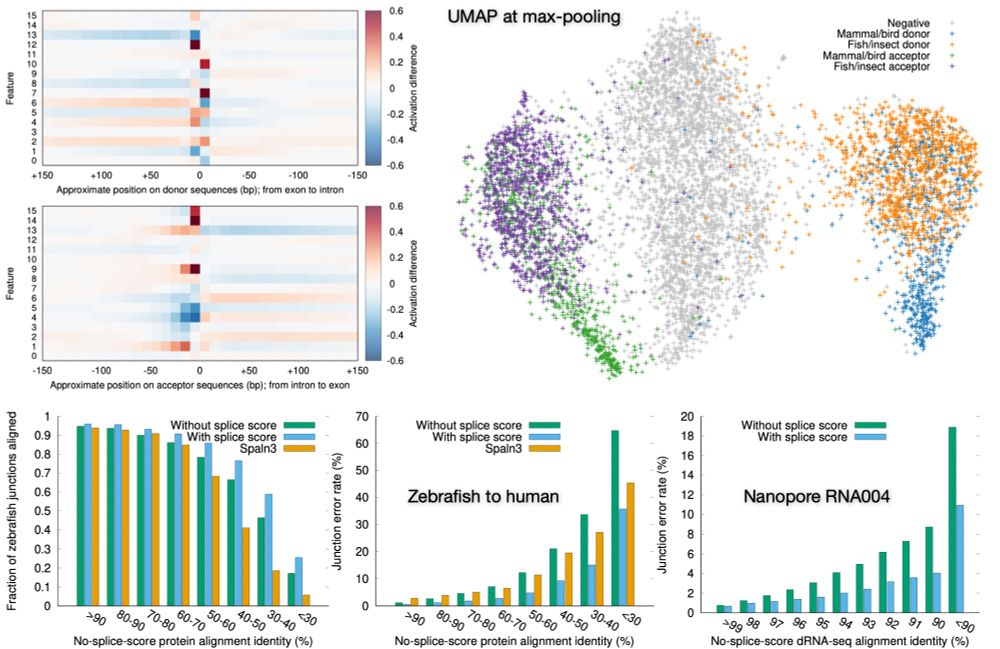
June 17, 2025 at 1:49 AM
Preprint on "Improving spliced alignment by modeling splice sites with deep learning". It describes minisplice for modeling splice signals. Minimap2 and miniprot now optionally use the predicted scores to improve spliced alignment.
arxiv.org/abs/2506.12986
arxiv.org/abs/2506.12986


