Peer was a giant of bioinformatics and computational biology and an inspiring mentor to everyone who had been in his group. I find myself repeating things he said all the time and will probably keep doing so for the rest of my life
www.embl.org/news/embl-an...

Peer was a giant of bioinformatics and computational biology and an inspiring mentor to everyone who had been in his group. I find myself repeating things he said all the time and will probably keep doing so for the rest of my life
www.embl.org/news/embl-an...

@quadraminstitute.bsky.social
rdcu.be/eMmcT

@quadraminstitute.bsky.social
rdcu.be/eMmcT

www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10....

www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10....
🔗 www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti...

🔗 www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti...


www.nature.com/articles/s41...
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
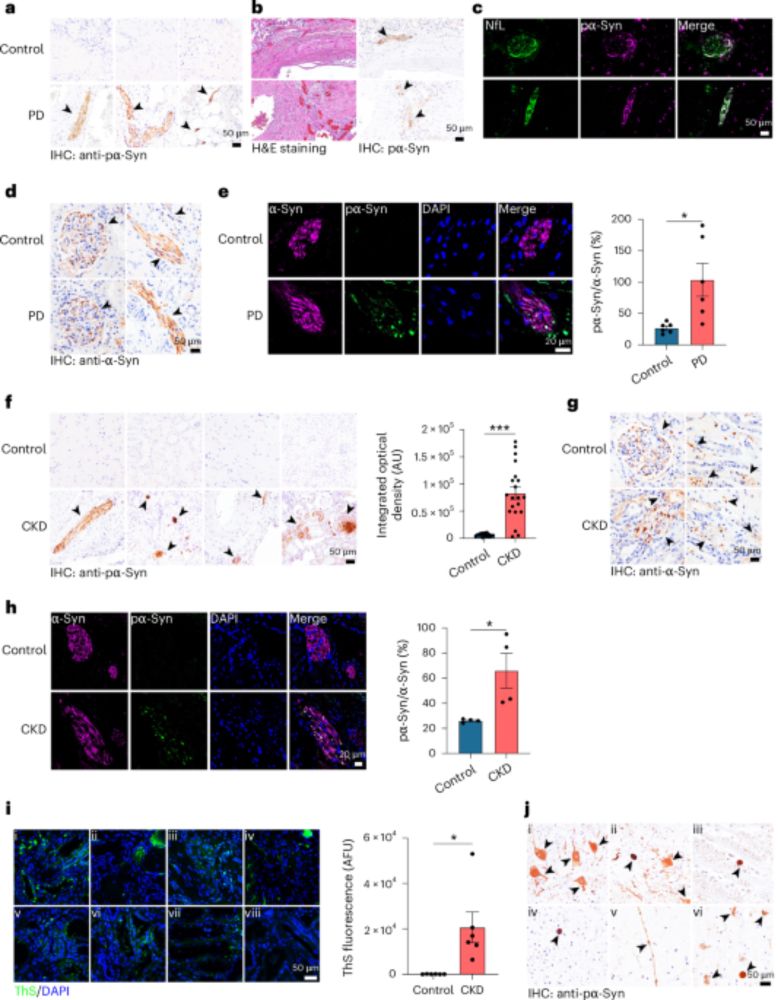
The majority of them (3,088) are enriched at the protein but not RNA level.
The brain hosts the largest number of proteins that are only enriched at the protein level but not RNA level.

The majority of them (3,088) are enriched at the protein but not RNA level.
The brain hosts the largest number of proteins that are only enriched at the protein level but not RNA level.
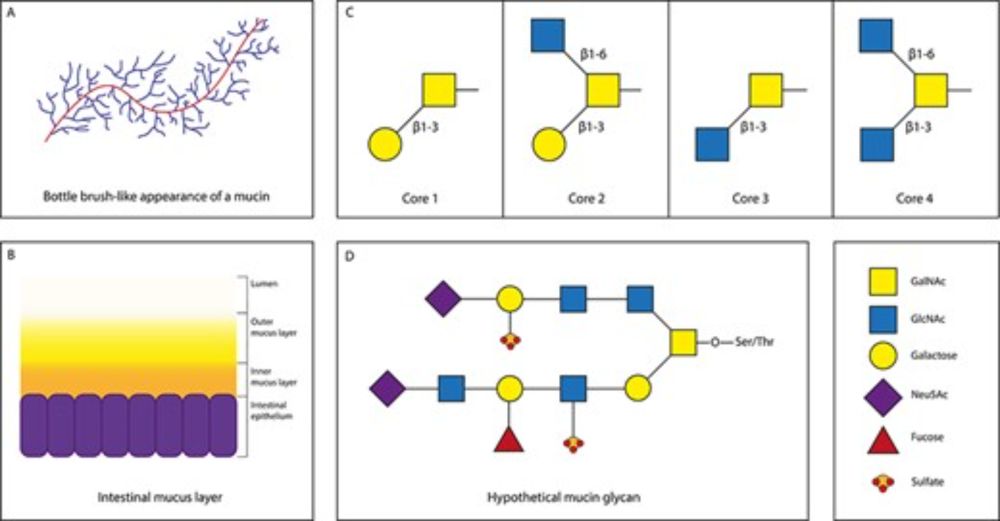
✂️ What enzymes do they use to degrade mucin glycans and how does that lead to cross-feeding?
#glycotime
#microbiology
academic.oup.com/glycob/artic...
✂️ What enzymes do they use to degrade mucin glycans and how does that lead to cross-feeding?
#glycotime
#microbiology
academic.oup.com/glycob/artic...


doi.org/10.1101/2024...
@wwood @rhysnewell @CMR_QUT
🧵1/6

doi.org/10.1101/2024...
@wwood @rhysnewell @CMR_QUT
🧵1/6
#microbiome #metaproteomics
pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/...

#microbiome #metaproteomics
pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/...


