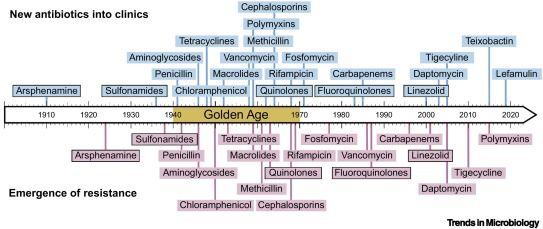
www.microbiologyresearch.org/content/jour...
www.microbiologyresearch.org/content/jour...
🧵 (1/14)
www.doi.org/10.1038/s414...
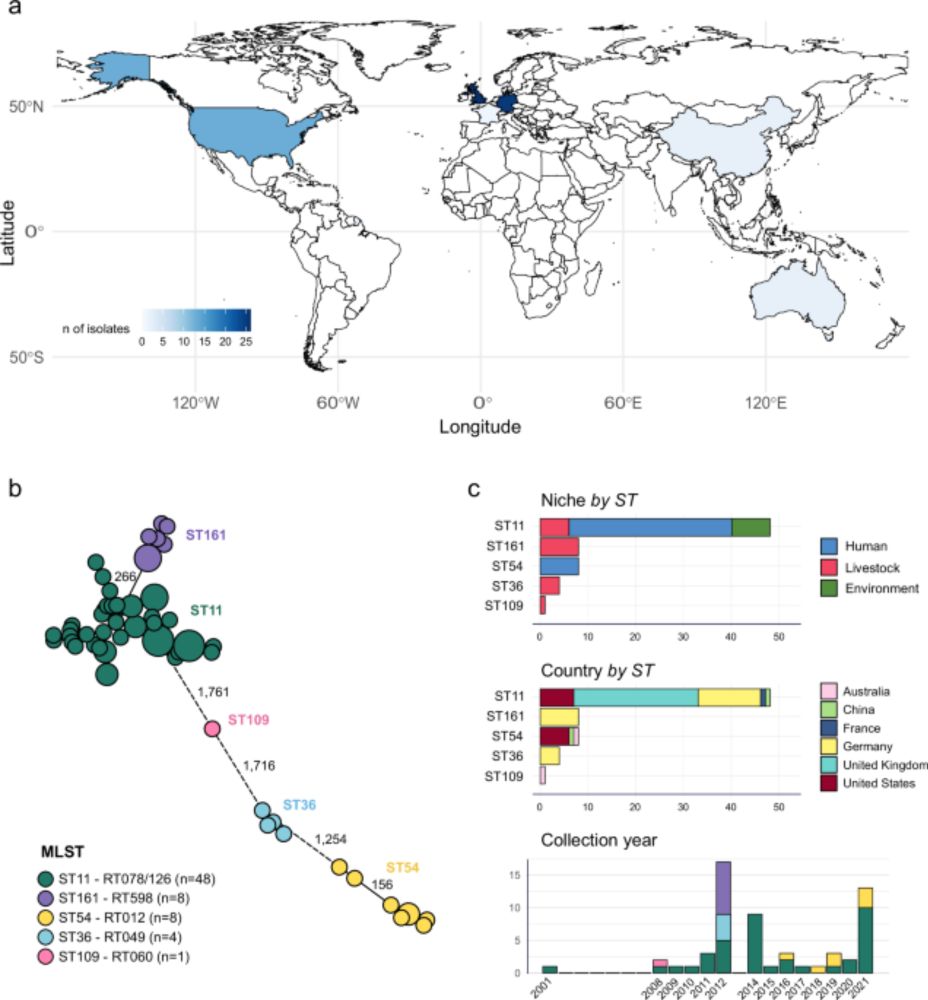
🧵 (1/14)
www.doi.org/10.1038/s414...


www.microbiologyresearch.org/content/jour...

www.microbiologyresearch.org/content/jour...
We organize webinars, write newsletters, promote European research on AMS, participate in the AMS certificate and more
Visit www.escmid.org/esgap/ to find more
Also on www.linkedin.com/groups/90724...


We organize webinars, write newsletters, promote European research on AMS, participate in the AMS certificate and more
Visit www.escmid.org/esgap/ to find more
Also on www.linkedin.com/groups/90724...
Special congratulations to MERMAN PhD student Matt @mattjago.bsky.social for his 1st first author paper & supervisor Mato Lagator!
#MicroSky 🦠🧫
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

Special congratulations to MERMAN PhD student Matt @mattjago.bsky.social for his 1st first author paper & supervisor Mato Lagator!
#MicroSky 🦠🧫
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
https://buff.ly/4grpj97

https://buff.ly/4grpj97