🧵 (1/14)
www.doi.org/10.1038/s414...
a) correcting errors in 4.5 million genomes & their phylogeny
b) improving representation of the Global South in public data
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
(thread 1/n)

a) correcting errors in 4.5 million genomes & their phylogeny
b) improving representation of the Global South in public data
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
(thread 1/n)
We represent plasmids as circles and mutations as dots, resembling an eye, because in this paper we literally 𝑤𝑎𝑡𝑐ℎ plasmids evolve.
‼️Check Paula’s 🧵 and the paper👇
𝗣𝗹𝗮𝘀𝗺𝗶𝗱 𝗺𝘂𝘁𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻 𝗿𝗮𝘁𝗲𝘀 𝘀𝗰𝗮𝗹𝗲 𝘄𝗶𝘁𝗵 𝗰𝗼𝗽𝘆 𝗻𝘂𝗺𝗯𝗲𝗿
www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/...

We represent plasmids as circles and mutations as dots, resembling an eye, because in this paper we literally 𝑤𝑎𝑡𝑐ℎ plasmids evolve.
‼️Check Paula’s 🧵 and the paper👇
𝗣𝗹𝗮𝘀𝗺𝗶𝗱 𝗺𝘂𝘁𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻 𝗿𝗮𝘁𝗲𝘀 𝘀𝗰𝗮𝗹𝗲 𝘄𝗶𝘁𝗵 𝗰𝗼𝗽𝘆 𝗻𝘂𝗺𝗯𝗲𝗿
www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/...
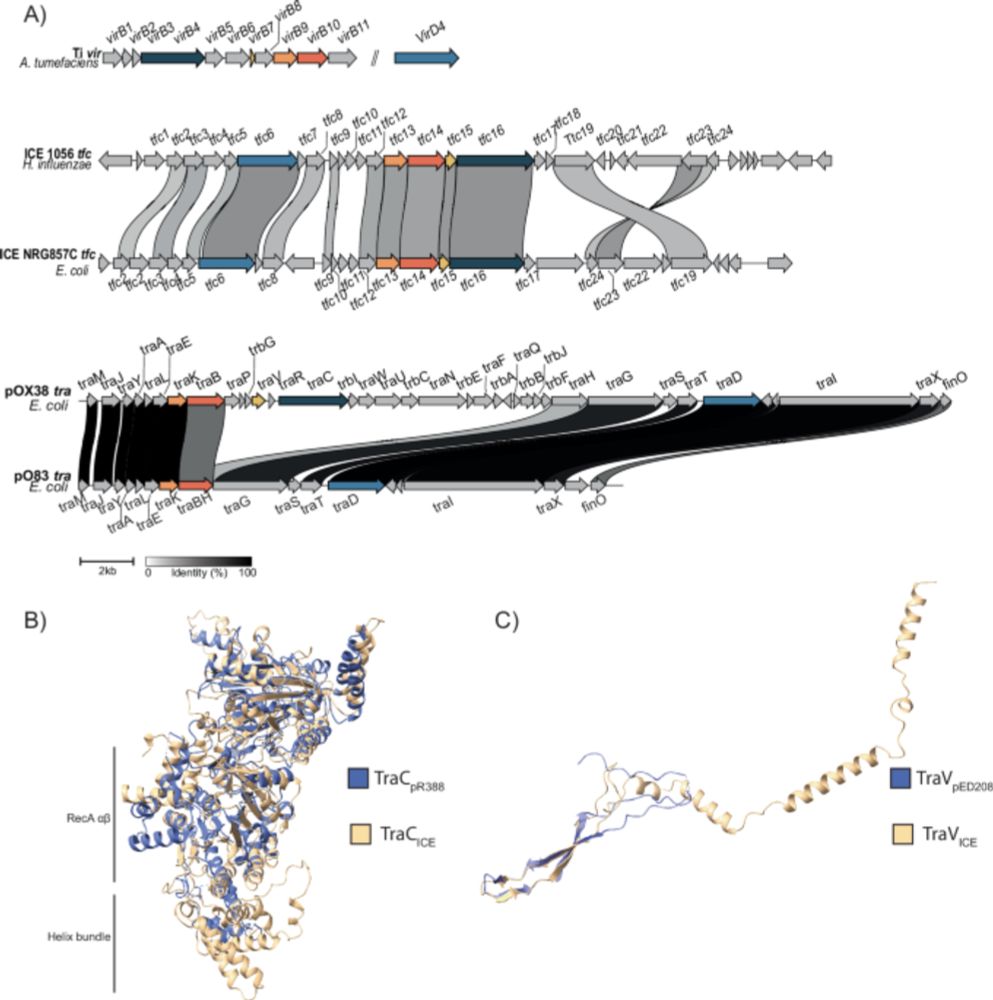
Here we explore the conjugative capacity of these mysterious Genomic Islands.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.6...
Here we explore the conjugative capacity of these mysterious Genomic Islands.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.6...

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.6...

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.6...
A new approach for detecting mutation-driven antimicrobial resistance directly from metagenomic reads.
Fills a major gap in current resistome profiling by capturing chromosomal AMR mutations that metagenome tools miss.
github.com/aldertzomer/...
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

www.nature.com/articles/s41...
📖 shorturl.at/vkQuS
✍️ @sylvainbrisse.bsky.social & coll.
@pasteur.fr @ox.ac.uk @monashuniversity.bsky.social @lshtm.bsky.social

📖 shorturl.at/vkQuS
✍️ @sylvainbrisse.bsky.social & coll.
@pasteur.fr @ox.ac.uk @monashuniversity.bsky.social @lshtm.bsky.social
We show how interactions within gut microbiomes allow certain antibiotic-resistant E. coli strains to persist even without antibiotics, helping explain how resistance is maintained in the human gut.
Now published in @natcomms.nature.com rdcu.be/eOf63

We show how interactions within gut microbiomes allow certain antibiotic-resistant E. coli strains to persist even without antibiotics, helping explain how resistance is maintained in the human gut.
Now published in @natcomms.nature.com rdcu.be/eOf63


'Antimicrobial resistance among Gram-positive agents of bacteraemia in the UK and Ireland: trends from 2001 to 2019'
TL;DR:
- dramatic falls in MRSA
- pneumococcal resistance rates low
- E. faecium more prevalent (and more vanR) than E. faecalis
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/41140273/

'Antimicrobial resistance among Gram-positive agents of bacteraemia in the UK and Ireland: trends from 2001 to 2019'
TL;DR:
- dramatic falls in MRSA
- pneumococcal resistance rates low
- E. faecium more prevalent (and more vanR) than E. faecalis
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/41140273/
Really looking forward to see what plasmid aficionados think of this one!!
With @asantoslopez.bsky.social @wfigueroac3.bsky.social Akshay Sabins and others
www.cell.com/cell-reports...

Really looking forward to see what plasmid aficionados think of this one!!
With @asantoslopez.bsky.social @wfigueroac3.bsky.social Akshay Sabins and others
www.cell.com/cell-reports...
Bacterial Strain Taxonomy for Genomic Surveillance
📅 22–23.10, 09:00–12:00 (CEST)
Learn how bacterial pathogens are classified & named in genomic surveillance – from #MLST & #cgMLST to SNP-based & k-mer clustering.
Info: bit.ly/48qT5df
#ECDCTraining #IDsky #EpiSky

Bacterial Strain Taxonomy for Genomic Surveillance
📅 22–23.10, 09:00–12:00 (CEST)
Learn how bacterial pathogens are classified & named in genomic surveillance – from #MLST & #cgMLST to SNP-based & k-mer clustering.
Info: bit.ly/48qT5df
#ECDCTraining #IDsky #EpiSky
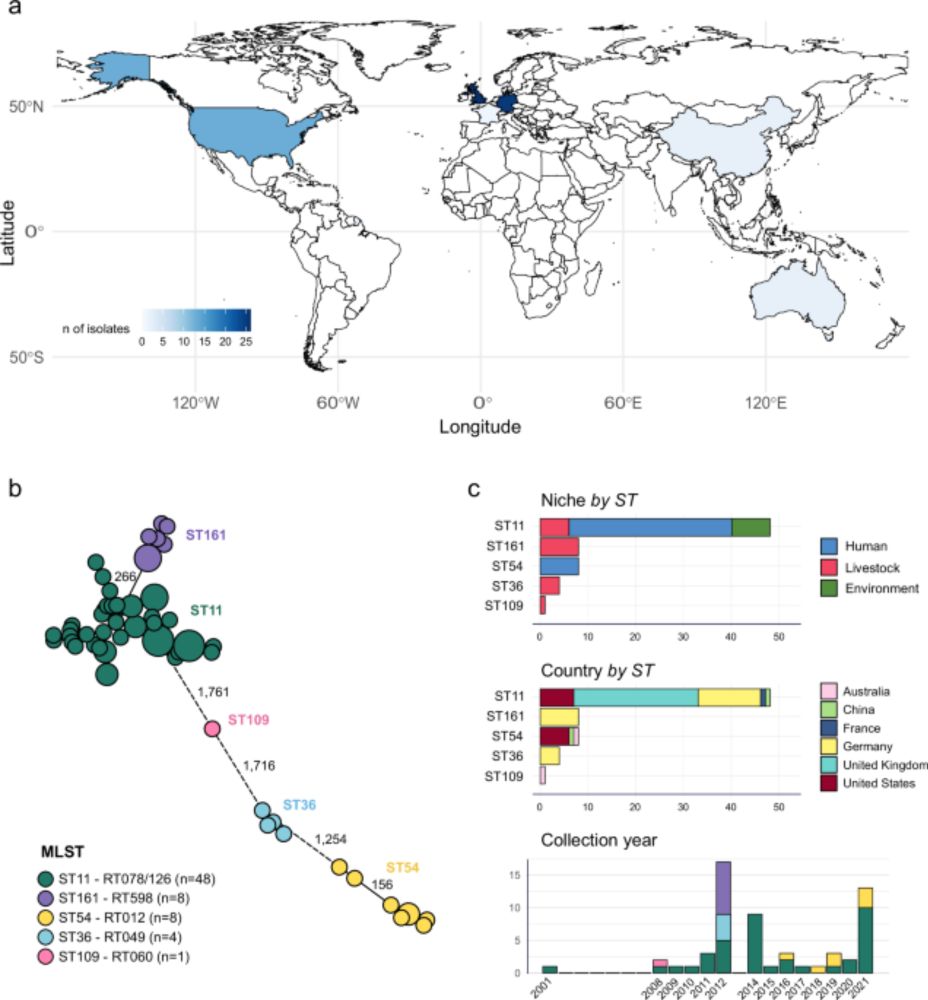
We just did that to study the history of #AMR spread @science.org
doi.org/10.1126/scie...
If you like time travel & biology, this 🧵is for you👇

We just did that to study the history of #AMR spread @science.org
doi.org/10.1126/scie...
If you like time travel & biology, this 🧵is for you👇
To further improve the functional annotation of "hypothetical" CDS, me and @gbouras13.bsky.social, we are looking for the worst Bakta-annotated bacterial genomes ;-)
(1/2)
To further improve the functional annotation of "hypothetical" CDS, me and @gbouras13.bsky.social, we are looking for the worst Bakta-annotated bacterial genomes ;-)
(1/2)
Paper: academic.oup.com/bioinformati...
Website: biomodels.bacpop.org
Code: github.com/bacpop/SBMLt...
Paper: academic.oup.com/bioinformati...
Website: biomodels.bacpop.org
Code: github.com/bacpop/SBMLt...

"Autocycler circularised the most chromosomes (87/92). .. Flye performed worse than other assemblers on almost all metrics. Autocycler + Medaka... was the most accurate long-read only assembler/polisher "
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

"Autocycler circularised the most chromosomes (87/92). .. Flye performed worse than other assemblers on almost all metrics. Autocycler + Medaka... was the most accurate long-read only assembler/polisher "
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Thread 1/n

Thread 1/n
www.embl.org/about/info/e...
We have three positions in microbial genomics at EMBL-EBI, including one in my group. Please do apply, or if you know anyone that would be interested pass on to them
www.embl.org/about/info/e...
We have three positions in microbial genomics at EMBL-EBI, including one in my group. Please do apply, or if you know anyone that would be interested pass on to them
And especially co-organisers @leonielorenz.bsky.social @sonjalehtinen.bsky.social Joel Hellewell
Join us for 2026's EMBO Practical Course. Sign up for 'Causality in biomedicine' alerts and hear as this new course develops: www.ebi.ac.uk/training/eve...
🧬🧫

And especially co-organisers @leonielorenz.bsky.social @sonjalehtinen.bsky.social Joel Hellewell