
@natsmb.nature.com
1/7
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Read our paper @cp-cell.bsky.social!
❕Publication: doi.org/10.1016/j.ce...
❕Press Release: www.biochem.mpg.de/en/pressroom
@uoftmedicine.bsky.social
@erc.europa.eu #UPSmeetMet
Read our paper @cp-cell.bsky.social!
❕Publication: doi.org/10.1016/j.ce...
❕Press Release: www.biochem.mpg.de/en/pressroom
@uoftmedicine.bsky.social
@erc.europa.eu #UPSmeetMet
Using cryo-electron tomography, we show it forms amyloid structures inside lysosomes that mechanically rupture membranes – revealing a new paradigm for lysosomal failure.
🔗 doi.org/10.64898/202...
#CryoET

Using cryo-electron tomography, we show it forms amyloid structures inside lysosomes that mechanically rupture membranes – revealing a new paradigm for lysosomal failure.
🔗 doi.org/10.64898/202...
#CryoET
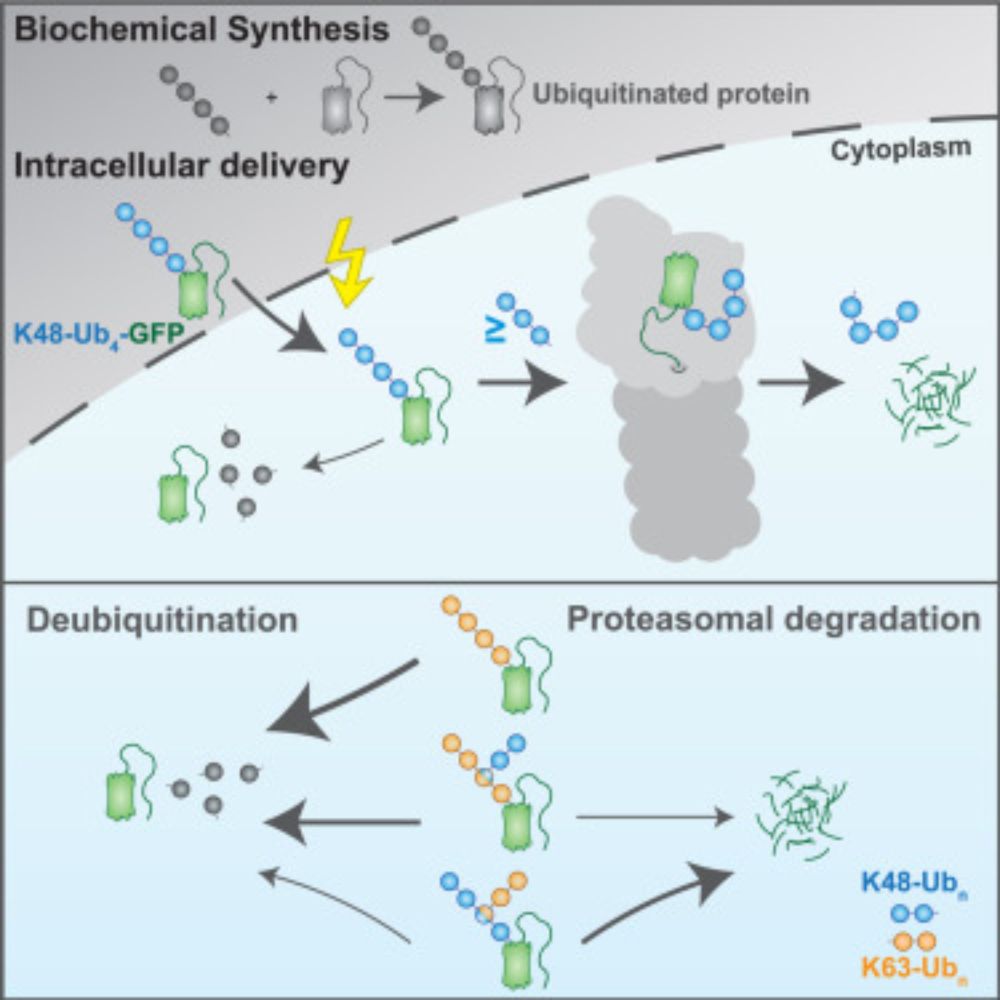
We are excited to share our recent work on #E3 ligase regulation in #metabolism!
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.6...
#ubiquitin #targetedproteindegradation #chemicalbiology
1/6
We are excited to share our recent work on #E3 ligase regulation in #metabolism!
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.6...
#ubiquitin #targetedproteindegradation #chemicalbiology
1/6
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

www.nature.com/articles/s41...
We reveal the structural basis of a partnership between the ER membrane complex (EMC) and the P5A-ATPase Spf1 — an insertase–dislocase duo that coordinates membrane protein biogenesis and quality control.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

We reveal the structural basis of a partnership between the ER membrane complex (EMC) and the P5A-ATPase Spf1 — an insertase–dislocase duo that coordinates membrane protein biogenesis and quality control.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
1/9
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
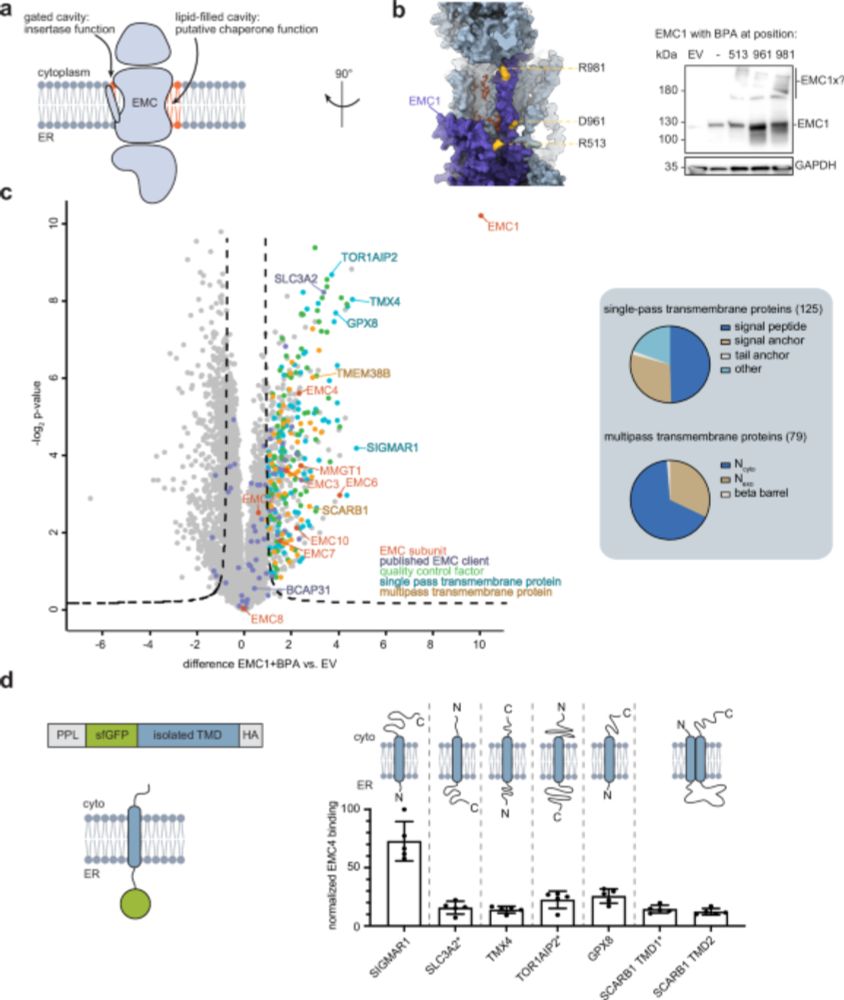
1/9
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
#wUeBI2025 @grk2243.bsky.social
@jakobfarnung.bsky.social @samuelmaiwald.bsky.social @hannahbkmpr.bsky.social

#wUeBI2025 @grk2243.bsky.social
@jakobfarnung.bsky.social @samuelmaiwald.bsky.social @hannahbkmpr.bsky.social
❕ www.nature.com/articles/s41...
@samuelmaiwald.bsky.social @unileiden.bsky.social
❕ www.nature.com/articles/s41...
@samuelmaiwald.bsky.social @unileiden.bsky.social

@natsmb.nature.com
1/7
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

@natsmb.nature.com
1/7
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
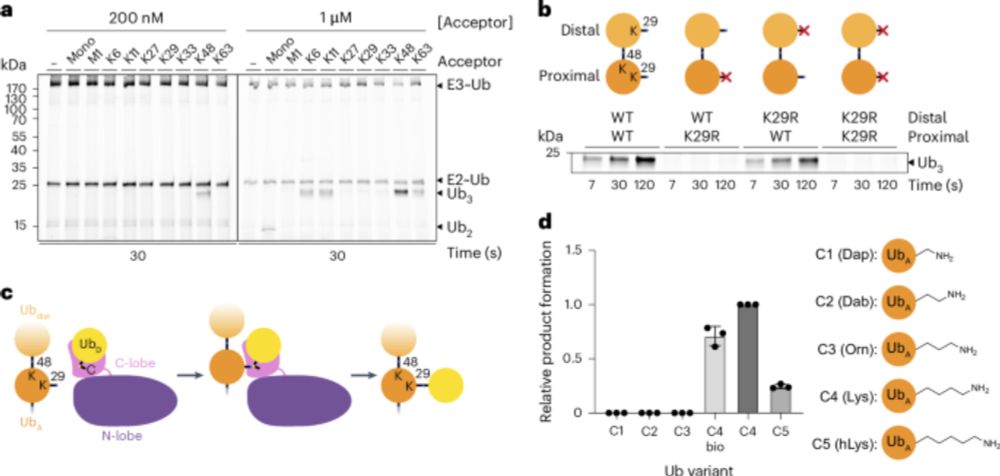
“𝗨𝗯𝗶𝗥𝗘𝗔𝗗 𝗱𝗲𝗰𝗶𝗽𝗵𝗲𝗿𝘀 𝗽𝗿𝗼𝘁𝗲𝗮𝘀𝗼𝗺𝗮𝗹 𝗱𝗲𝗴𝗿𝗮𝗱𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻 𝗰𝗼𝗱𝗲 𝗼𝗳 𝗵𝗼𝗺𝗼𝘁𝘆𝗽𝗶𝗰 𝗮𝗻𝗱 𝗯𝗿𝗮𝗻𝗰𝗵𝗲𝗱 𝗞48 𝗮𝗻𝗱 𝗞63 𝘂𝗯𝗶𝗾𝘂𝗶𝘁𝗶𝗻 𝗰𝗵𝗮𝗶𝗻𝘀”
@cp-molcell.bsky.social
1/8
www.cell.com/molecular-ce...
“𝗨𝗯𝗶𝗥𝗘𝗔𝗗 𝗱𝗲𝗰𝗶𝗽𝗵𝗲𝗿𝘀 𝗽𝗿𝗼𝘁𝗲𝗮𝘀𝗼𝗺𝗮𝗹 𝗱𝗲𝗴𝗿𝗮𝗱𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻 𝗰𝗼𝗱𝗲 𝗼𝗳 𝗵𝗼𝗺𝗼𝘁𝘆𝗽𝗶𝗰 𝗮𝗻𝗱 𝗯𝗿𝗮𝗻𝗰𝗵𝗲𝗱 𝗞48 𝗮𝗻𝗱 𝗞63 𝘂𝗯𝗶𝗾𝘂𝗶𝘁𝗶𝗻 𝗰𝗵𝗮𝗶𝗻𝘀”
@cp-molcell.bsky.social
1/8
www.cell.com/molecular-ce...

