University of Cambridge
Gates Cambridge Scholar
Bioinformatics, genetics, single-cell, statistics
Australian 🇦🇺

Very worryingly we find that TWAS gets the sign wrong around 1/3 of the time (compared to 50% for pure guessing). You can read more about our analysis here, and what we think is going on 👇
In a new pre-print, we find that TWAS gets the sign wrong around 20-30% of the time!
doi.org/10.64898/202...
1/n

Very worryingly we find that TWAS gets the sign wrong around 1/3 of the time (compared to 50% for pure guessing). You can read more about our analysis here, and what we think is going on 👇
In a new pre-print, we find that TWAS gets the sign wrong around 20-30% of the time!
doi.org/10.64898/202...
1/n

In a new pre-print, we find that TWAS gets the sign wrong around 20-30% of the time!
doi.org/10.64898/202...
1/n

We profiled ~10M PBMCs (snRNA-seq + snATAC-seq) from 1,108 Finnish donors to map how genetic variants drive complex disease through chromatin and gene regulation 🧵👇
🔗 Link: www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1...
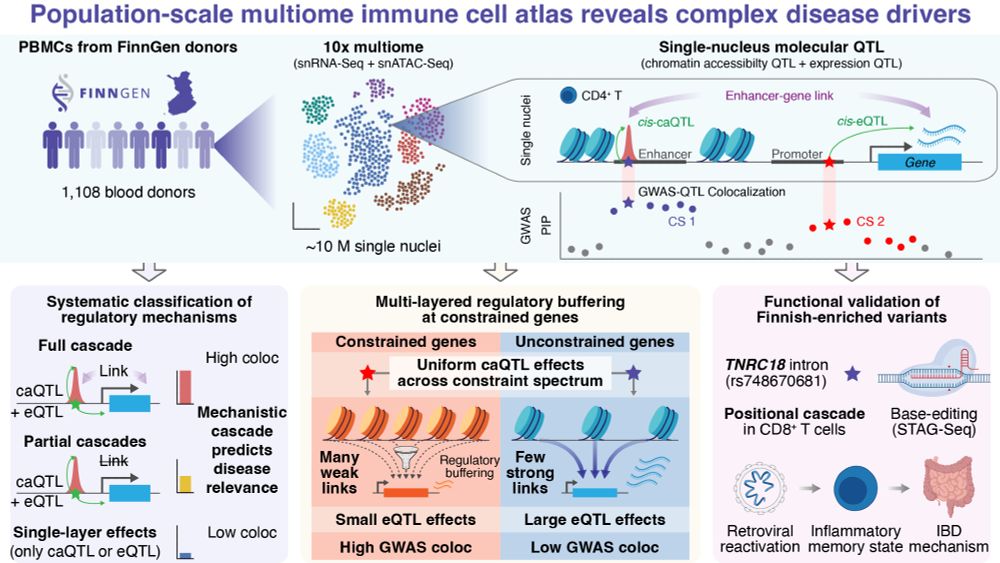
We profiled ~10M PBMCs (snRNA-seq + snATAC-seq) from 1,108 Finnish donors to map how genetic variants drive complex disease through chromatin and gene regulation 🧵👇
🔗 Link: www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1...
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
I am excited to announce that our new study explaining the missing heritability of many phenotypes using WGS data from ~347,000 UK Biobank participants has just been published in @Nature.
Our manuscript is here: www.nature.com/articles/s41....

I am excited to announce that our new study explaining the missing heritability of many phenotypes using WGS data from ~347,000 UK Biobank participants has just been published in @Nature.
Our manuscript is here: www.nature.com/articles/s41....


An Open Targets team led by Krista Freimann and @kauralasoo.bsky.social analysed 3,734 lymphoblastoid cell line samples across nine cohorts, identifying four robust loci
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

An Open Targets team led by Krista Freimann and @kauralasoo.bsky.social analysed 3,734 lymphoblastoid cell line samples across nine cohorts, identifying four robust loci
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti...

www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti...

🧵👇 (1/n)

🧵👇 (1/n)

Paper: www.nature.com/articles/s43...

Paper: www.nature.com/articles/s43...
We show how data on expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL) relates to the structure of gene regulatory networks (GRN). Much of the GRN / eQTL picture is unmapped, but what we do have says a lot… (1/)
doi.org/10.1101/2025...
We show how data on expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL) relates to the structure of gene regulatory networks (GRN). Much of the GRN / eQTL picture is unmapped, but what we do have says a lot… (1/)
doi.org/10.1101/2025...
tinyurl.com/3j9r56s8
@rociorius.bsky.social @yuyangchen.bsky.social @gregfindlay.bsky.social @dgmacarthur.bsky.social @cassimons.bsky.social @nickywhiffin.bsky.social

tinyurl.com/3j9r56s8
@rociorius.bsky.social @yuyangchen.bsky.social @gregfindlay.bsky.social @dgmacarthur.bsky.social @cassimons.bsky.social @nickywhiffin.bsky.social

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1...
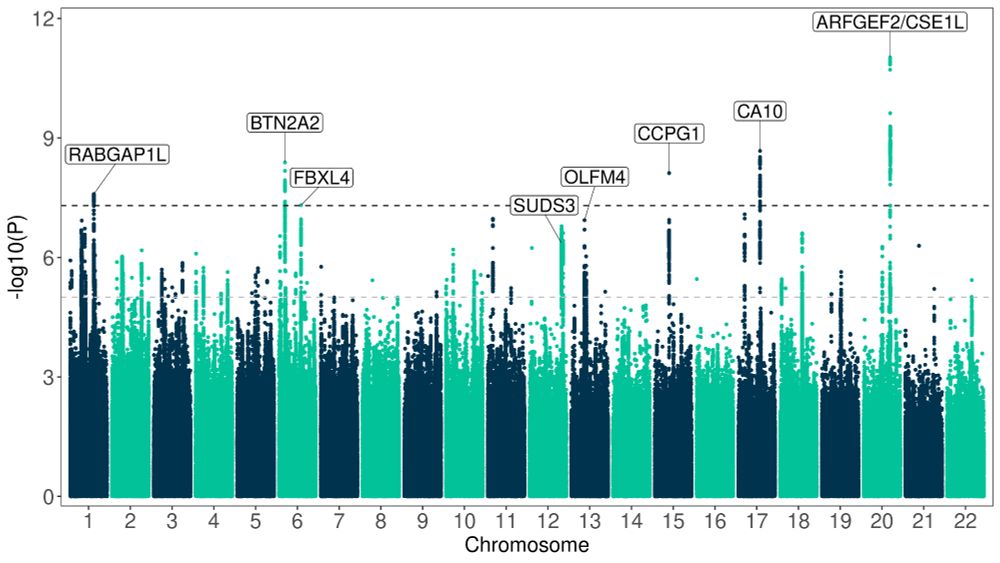
www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1...
Interested in how this works & what we found? Read along! 👇
Interested in how this works & what we found? Read along! 👇

