
Currently Professor at Freie Universität Berlin, also affiliated with the Bernstein Center for Computational Neuroscience.
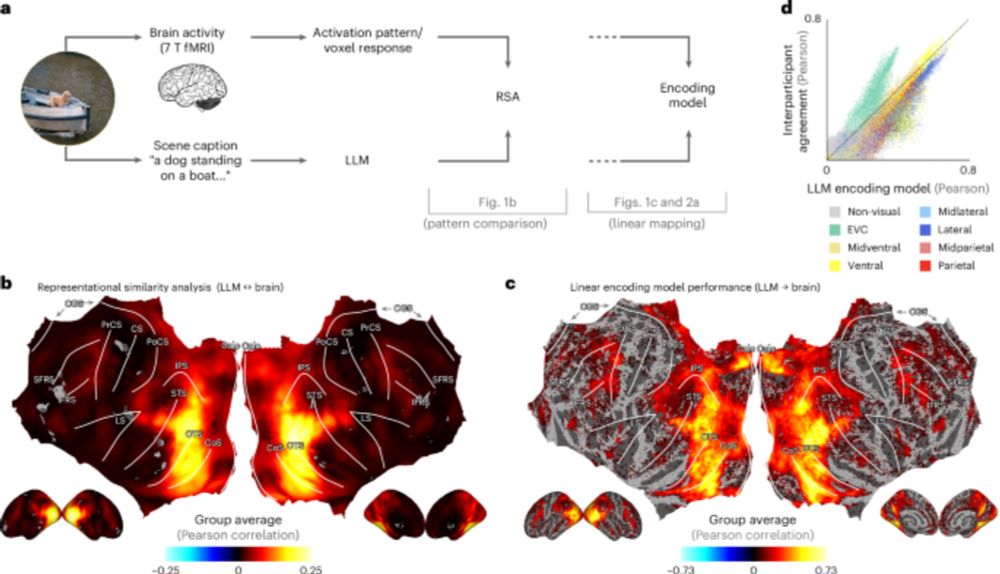
"Visual representations in the human brain are aligned with large language models"
🔗 www.nature.com/articles/s42...
Mass-univariate analysis is still the bread-and-butter: intuitive, fast… and chronically overfitted. Add harsh multiple-comparison penalties, and we patch the workflow with statistical band-aids. No wonder the stringency debates never die.
Mass-univariate analysis is still the bread-and-butter: intuitive, fast… and chronically overfitted. Add harsh multiple-comparison penalties, and we patch the workflow with statistical band-aids. No wonder the stringency debates never die.
Rich, brain-like scene representations built from acrive vision
How can we model natural scene representations in visual cortex? A solution is in active vision: predict the features of the next glimpse! arxiv.org/abs/2511.12715
+ @adriendoerig.bsky.social , @alexanderkroner.bsky.social , @carmenamme.bsky.social , @timkietzmann.bsky.social
🧵 1/14

Rich, brain-like scene representations built from acrive vision
Using EEG + fMRI, we show that when humans recognize images that feedforward CNNs fail on, the brain recruits cortex-wide recurrent resources.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1... (1/n)
This is incredible work led by Victoria Bosch @initself.bsky.social at the Kietzmann Lab @timkietzmann.bsky.social, developing interactive and flexible brain decoding.
I'm excited to see where this goes next.
tl;dr: you can now chat with a brain scan 🧠💬
1/n

This is incredible work led by Victoria Bosch @initself.bsky.social at the Kietzmann Lab @timkietzmann.bsky.social, developing interactive and flexible brain decoding.
I'm excited to see where this goes next.
"Non-commitment in mental imagery is distinct from perceptual inattention, and supports hierarchical scene construction"
(by Li, Hammond, & me)
link: doi.org/10.31234/osf...
-- the title's a bit of a mouthful, but the nice thing is that it's a pretty decent summary


"Non-commitment in mental imagery is distinct from perceptual inattention, and supports hierarchical scene construction"
(by Li, Hammond, & me)
link: doi.org/10.31234/osf...
-- the title's a bit of a mouthful, but the nice thing is that it's a pretty decent summary
Today I want to share two new works on this topic:
Eliciting higher alignment: arxiv.org/abs/2510.02425
Unpaired learning of unified reps: arxiv.org/abs/2510.08492
1/9
Today I want to share two new works on this topic:
Eliciting higher alignment: arxiv.org/abs/2510.02425
Unpaired learning of unified reps: arxiv.org/abs/2510.08492
1/9
Paper: arxiv.org/abs/2510.03684
🧵
Paper: arxiv.org/abs/2510.03684
🧵

Charlotte has developed a theory for how learning curriculum influences learning generalization.
Our theory makes straightforward neural predictions that can be tested in future experiments. (1/4)
🧠🤖 🧠📈 #MLSky
🧠🤖
We propose a theory of how learning curriculum affects generalization through neural population dimensionality. Learning curriculum is a determining factor of neural dimensionality - where you start from determines where you end up.
🧠📈
A 🧵:
tinyurl.com/yr8tawj3

Charlotte has developed a theory for how learning curriculum influences learning generalization.
Our theory makes straightforward neural predictions that can be tested in future experiments. (1/4)
🧠🤖 🧠📈 #MLSky
1. Unique variance is easy to interpret as a lower bound of what a variable explains (the upper bound being either what the variable explains alone or what the other variables cannot explain uniquely)
@martinhebart.bsky.social @gallantlab.org
diedrichsenlab.org/BrainDataSci...

1. Unique variance is easy to interpret as a lower bound of what a variable explains (the upper bound being either what the variable explains alone or what the other variables cannot explain uniquely)
@martinhebart.bsky.social @gallantlab.org
diedrichsenlab.org/BrainDataSci...

@martinhebart.bsky.social @gallantlab.org
diedrichsenlab.org/BrainDataSci...
We find a striking dissociation: it’s not shared object recognition. Alignment is driven by sensitivity to texture-like local statistics.
📊 Study: n=57, 624k trials, 5 models doi.org/10.1101/2025...

We find a striking dissociation: it’s not shared object recognition. Alignment is driven by sensitivity to texture-like local statistics.
📊 Study: n=57, 624k trials, 5 models doi.org/10.1101/2025...
1/ How does deep sleep reshape our memories? Our new study shows that slow-wave sleep (SWS) reorganises episodic memory networks, shifting recall from the parietal cortex to the anterior temporal lobe (ATL). With Polina Perzich and @bstaresina.bsky.social . A thread below👇
1/ How does deep sleep reshape our memories? Our new study shows that slow-wave sleep (SWS) reorganises episodic memory networks, shifting recall from the parietal cortex to the anterior temporal lobe (ATL). With Polina Perzich and @bstaresina.bsky.social . A thread below👇
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Our study proposes a bio-plausible meta-plasticity rule that shapes synapses over time, enabling selective recall based on context

Our study proposes a bio-plausible meta-plasticity rule that shapes synapses over time, enabling selective recall based on context
Is “unconscious mental imagery” real? The evidence is weaker than it seems. We explain why—and how to move the debate forward.
🔗 www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti...

Is “unconscious mental imagery” real? The evidence is weaker than it seems. We explain why—and how to move the debate forward.
🔗 www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti...
New study by @adriendoerig.bsky.social @freieuniversitaet.bsky.social with colleagues from Osnabrück, Minnesota and @umontreal-en.bsky.social
Read the whole story 👉 bit.ly/3JXlYmO

New study by @adriendoerig.bsky.social @freieuniversitaet.bsky.social with colleagues from Osnabrück, Minnesota and @umontreal-en.bsky.social
Read the whole story 👉 bit.ly/3JXlYmO
www.nature.com/articles/s42...
www.nature.com/articles/s42...

Huge thanks to our two amazing reviewers who pushed us to make the paper much stronger. A truly joyful collaboration with @lucasgruaz.bsky.social, @sobeckerneuro.bsky.social, and Johanni Brea! 🥰
Tweeprint on an earlier version: bsky.app/profile/modi... 🧠🧪👩🔬
Huge thanks to our two amazing reviewers who pushed us to make the paper much stronger. A truly joyful collaboration with @lucasgruaz.bsky.social, @sobeckerneuro.bsky.social, and Johanni Brea! 🥰
Tweeprint on an earlier version: bsky.app/profile/modi... 🧠🧪👩🔬
Using novel behavioral tasks, fMRI, RL & RNN modeling, and transcranial ultrasound stimulation (TUS), we demonstrate the causal role of hippocampus in relational structure learning.
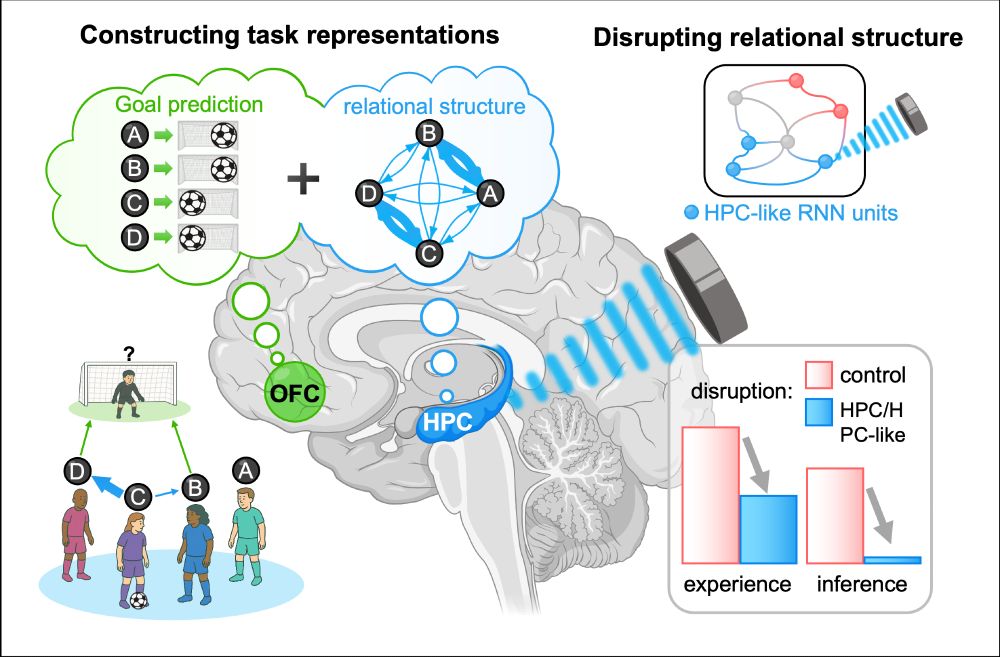
Using novel behavioral tasks, fMRI, RL & RNN modeling, and transcranial ultrasound stimulation (TUS), we demonstrate the causal role of hippocampus in relational structure learning.
Using RIFT we reveal how the competition between top-down goals and bottom-up saliency unfolds within visual cortex.

Using RIFT we reveal how the competition between top-down goals and bottom-up saliency unfolds within visual cortex.

