Read all about it in our preprint by👉 doi.org/10.1101/2025...
#Proteomics #AI #MachineLearning

Read all about it in our preprint by👉 doi.org/10.1101/2025...
#Proteomics #AI #MachineLearning
Check it out here: www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

Check it out here: www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

Preprint & app: www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Let's chat at #EuPA2025 - Award session (Wednesday) & poster session (Thursday)!
Preprint & app: www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Let's chat at #EuPA2025 - Award session (Wednesday) & poster session (Thursday)!
To search metadata or download files via FTP, Aspera, Globus, or S3, and is perfect for bioinfo workflows.
Check it out 👉 github.com/PRIDE-Archiv...
To search metadata or download files via FTP, Aspera, Globus, or S3, and is perfect for bioinfo workflows.
Check it out 👉 github.com/PRIDE-Archiv...
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
www.matrixscience.com/blog/using-m...
www.matrixscience.com/blog/using-m...
Check it out here:
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

Check it out here:
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...



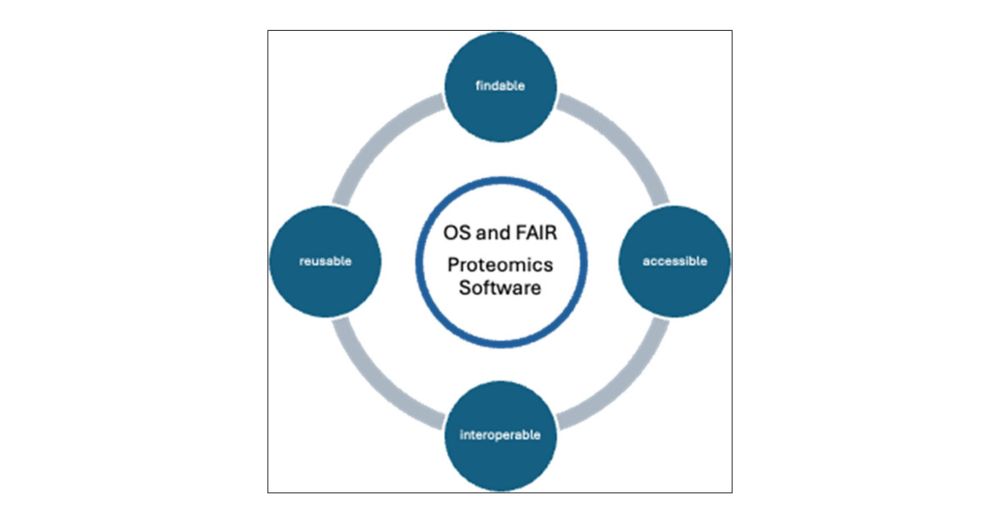
Our goal was to share a vision of #OSS #proteomics for us to build toward, and propose some ways to get there 🚀
I’m blown away by how many folks contributed and how much it evolved beyond just my voice 🙌

Our goal was to share a vision of #OSS #proteomics for us to build toward, and propose some ways to get there 🚀
I’m blown away by how many folks contributed and how much it evolved beyond just my voice 🙌
Learn more at doi.org/10.1101/2024... and proteobench.readthedocs.io.


Learn more at doi.org/10.1101/2024... and proteobench.readthedocs.io.
user-friendly platform to boost peptide
identifications, as showcased with MS Amanda 3.0 chemrxiv.org/engage/...
---
#proteomics #prot-preprint