Bloom lab
@jbloomlab.bsky.social
Lab studying molecular evolution of proteins and viruses. Affiliated with Fred Hutch & HHMI.
Opinions are my own and do not reflect those of my employer.
https://jbloomlab.org/
Opinions are my own and do not reflect those of my employer.
https://jbloomlab.org/
Reposted by Bloom lab
Just out📢 Our new paper published in @natmicrobiol.nature.com describes highly potent cross-neutralizing human monoclonal antibodies against H5Nx influenza viruses. Close collaboration with Sara Andrews lab and Tongqing Zhou lab at the VRC. Link to the article: rdcu.be/eKV9T 1/2
October 14, 2025 at 3:10 PM
Just out📢 Our new paper published in @natmicrobiol.nature.com describes highly potent cross-neutralizing human monoclonal antibodies against H5Nx influenza viruses. Close collaboration with Sara Andrews lab and Tongqing Zhou lab at the VRC. Link to the article: rdcu.be/eKV9T 1/2
In new study led by @ckikawa.bsky.social, we provide near real-time data on human neutralizing antibody landscape to influenza by measuring ~26,000 titers to >100 recent viral strains
Data can inform vaccine selection & evolutionary/epidemiological modeling
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Data can inform vaccine selection & evolutionary/epidemiological modeling
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

Near real-time data on the human neutralizing antibody landscape to influenza virus to inform vaccine-strain selection in September 2025
The hemagglutinin of human influenza virus evolves rapidly to erode neutralizing antibody immunity. Twice per year, new vaccine strains are selected with the goal of providing maximum protection again...
www.biorxiv.org
September 8, 2025 at 9:48 PM
In new study led by @ckikawa.bsky.social, we provide near real-time data on human neutralizing antibody landscape to influenza by measuring ~26,000 titers to >100 recent viral strains
Data can inform vaccine selection & evolutionary/epidemiological modeling
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Data can inform vaccine selection & evolutionary/epidemiological modeling
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
In new study led by Xiaohui Ju, we define how mutations to Chikungunya virus envelope proteins affect entry in human vs mosquito cells.
Sheds light on functional constraints & enables us to make loss-of-tropism mutants, which could be of use for vaccines.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Sheds light on functional constraints & enables us to make loss-of-tropism mutants, which could be of use for vaccines.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

Determinants of human versus mosquito cell entry by the Chikungunya virus envelope proteins
Chikungunya virus (CHIKV) infects both humans and mosquitoes during its transmission cycle. How the virus’s envelope proteins mediate entry in cells from such different species is unclear. MXRA8 is a ...
www.biorxiv.org
September 4, 2025 at 11:12 PM
In new study led by Xiaohui Ju, we define how mutations to Chikungunya virus envelope proteins affect entry in human vs mosquito cells.
Sheds light on functional constraints & enables us to make loss-of-tropism mutants, which could be of use for vaccines.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Sheds light on functional constraints & enables us to make loss-of-tropism mutants, which could be of use for vaccines.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
In new study led by @bdadonaite.bsky.social, we measure how spike mutations affect function & antigenicity of spike of KP.3.1.1 strain of SARS-CoV-2.
Sheds light on how key neutralizing epitopes are changing & importance of RBD up/down motion.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Sheds light on how key neutralizing epitopes are changing & importance of RBD up/down motion.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

Spike mutations that affect the function and antigenicity of recent KP.3.1.1-like SARS-CoV-2 variants
SARS-CoV-2 is under strong evolutionary selection to acquire mutations in its spike protein that reduce neutralization by human polyclonal antibodies. Here we use pseudovirus-based deep mutational sca...
www.biorxiv.org
August 20, 2025 at 5:22 AM
In new study led by @bdadonaite.bsky.social, we measure how spike mutations affect function & antigenicity of spike of KP.3.1.1 strain of SARS-CoV-2.
Sheds light on how key neutralizing epitopes are changing & importance of RBD up/down motion.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Sheds light on how key neutralizing epitopes are changing & importance of RBD up/down motion.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Our lab has an opening for a research technician to contribute to our efforts to understand RSV evolution & its impact on antibody countermeasures (see journals.asm.org/doi/full/10....). The tech will also help w lab management.
If interested, apply here: careers-fhcrc.icims.com/jobs/29940/job
If interested, apply here: careers-fhcrc.icims.com/jobs/29940/job
August 20, 2025 at 12:19 AM
Our lab has an opening for a research technician to contribute to our efforts to understand RSV evolution & its impact on antibody countermeasures (see journals.asm.org/doi/full/10....). The tech will also help w lab management.
If interested, apply here: careers-fhcrc.icims.com/jobs/29940/job
If interested, apply here: careers-fhcrc.icims.com/jobs/29940/job
Wanted to flag this interesting study led by our collaborators
@kinglabipd.bsky.social suggesting that at least in some contexts, the immunogenicity of H5 influenza vaccines can be improved by mutations that stabilize the HA protein.
@kinglabipd.bsky.social suggesting that at least in some contexts, the immunogenicity of H5 influenza vaccines can be improved by mutations that stabilize the HA protein.
🚨 New paper alert! 🚨
Here we show that stabilized influenza hemagglutinin HPAI H5 immunogens improve the quality of elicited antibody responses. Thank you to @open_phil for funding this work! bit.ly/4lgr0rM
Here we show that stabilized influenza hemagglutinin HPAI H5 immunogens improve the quality of elicited antibody responses. Thank you to @open_phil for funding this work! bit.ly/4lgr0rM

Stabilization of H5 highly pathogenic avian influenza hemagglutinin improves vaccine-elicited neutralizing antibody responses
Transmission of highly pathogenic avian influenza from H5 clade 2.3.4.4b has expanded in recent years to infect large populations of birds and mammals, heightening the risk of a human pandemic. Influe...
bit.ly
August 4, 2025 at 7:14 PM
Wanted to flag this interesting study led by our collaborators
@kinglabipd.bsky.social suggesting that at least in some contexts, the immunogenicity of H5 influenza vaccines can be improved by mutations that stabilize the HA protein.
@kinglabipd.bsky.social suggesting that at least in some contexts, the immunogenicity of H5 influenza vaccines can be improved by mutations that stabilize the HA protein.
In new study led by @timyu.bsky.social, we measure how mutations to H3 flu HA affect cell entry, stability & antibody escape
We find pleiotropic effects of mutations on these phenotypes shape evolution: epistasis alleviates cell-entry but not stability constraints
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
We find pleiotropic effects of mutations on these phenotypes shape evolution: epistasis alleviates cell-entry but not stability constraints
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

Pleiotropic mutational effects on function and stability constrain the antigenic evolution of influenza hemagglutinin
The evolution of human influenza virus hemagglutinin (HA) involves simultaneous selection to acquire antigenic mutations that escape population immunity while preserving protein function and stability...
www.biorxiv.org
May 27, 2025 at 4:23 PM
In new study led by @timyu.bsky.social, we measure how mutations to H3 flu HA affect cell entry, stability & antibody escape
We find pleiotropic effects of mutations on these phenotypes shape evolution: epistasis alleviates cell-entry but not stability constraints
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
We find pleiotropic effects of mutations on these phenotypes shape evolution: epistasis alleviates cell-entry but not stability constraints
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
In study led by @ckikawa.bsky.social & Andrea Loes, we use new assay to measure ~10,000 neutralization titers to recent influenza strains & show titers correlate w evolutionary success of viral strains
Similar data could help forecast evolution for vaccine selection
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Similar data could help forecast evolution for vaccine selection
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

High-throughput neutralization measurements correlate strongly with evolutionary success of human influenza strains
Human influenza viruses rapidly acquire mutations in their hemagglutinin (HA) protein that erode neutralization by antibodies from prior exposures. Here, we use a sequencing-based assay to measure neu...
www.biorxiv.org
March 12, 2025 at 11:48 PM
In study led by @ckikawa.bsky.social & Andrea Loes, we use new assay to measure ~10,000 neutralization titers to recent influenza strains & show titers correlate w evolutionary success of viral strains
Similar data could help forecast evolution for vaccine selection
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Similar data could help forecast evolution for vaccine selection
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
In study led by @csimonich.bsky.social & Teagan McMahon, we quantify antigenic evolution of RSV F
Important because:
1️⃣ RSV top cause of infant hospitalization in USA
2️⃣ New antibodies & vax can prevent hospitalizations
3️⃣ Will virus evolution erode their efficacy?
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Important because:
1️⃣ RSV top cause of infant hospitalization in USA
2️⃣ New antibodies & vax can prevent hospitalizations
3️⃣ Will virus evolution erode their efficacy?
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

RSV F evolution escapes some monoclonal antibodies but does not strongly erode neutralization by human polyclonal sera
Vaccines and monoclonal antibodies targeting the respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) fusion protein (F) have recently begun to be widely used to protect infants and high-risk adults. Some other viral pr...
www.biorxiv.org
March 12, 2025 at 10:31 PM
In study led by @csimonich.bsky.social & Teagan McMahon, we quantify antigenic evolution of RSV F
Important because:
1️⃣ RSV top cause of infant hospitalization in USA
2️⃣ New antibodies & vax can prevent hospitalizations
3️⃣ Will virus evolution erode their efficacy?
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Important because:
1️⃣ RSV top cause of infant hospitalization in USA
2️⃣ New antibodies & vax can prevent hospitalizations
3️⃣ Will virus evolution erode their efficacy?
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
In a new study led by Caelan Radford, we use deep mutational scanning to systematically compare the escape mutations from two broadly neutralizing antibodies in a clade A versus clade B HIV Envelope.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

Comprehensive maps of escape mutations from antibodies 10-1074 and 3BNC117 for Envs from two divergent HIV strains
Antibodies capable of neutralizing many strains of HIV are being explored as prophylactic and therapeutic agents, but viral escape mutations pose a major challenge. Efforts have been made to experimen...
www.biorxiv.org
January 31, 2025 at 9:31 PM
In a new study led by Caelan Radford, we use deep mutational scanning to systematically compare the escape mutations from two broadly neutralizing antibodies in a clade A versus clade B HIV Envelope.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
In new study, we find dramatic differences in specificities of serum neutralizing antibodies in infants w single infection by a recent SARS-CoV-2 strain versus adults/children imprinted by an early viral strain.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody specificities differ dramatically between recently infected infants and immune-imprinted individuals
The immune response to viral infection is shaped by past exposures to related virus strains, a phenomenon known as imprinting. For SARS-CoV-2, much of the population has been imprinted by a viral spik...
www.biorxiv.org
January 21, 2025 at 5:52 PM
In new study, we find dramatic differences in specificities of serum neutralizing antibodies in infants w single infection by a recent SARS-CoV-2 strain versus adults/children imprinted by an early viral strain.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
In new study, we measure how all mutations to rabies G affect cell entry & antibody neutralization
Sheds light on constraints on type III fusion proteins, suggests ways to stabilize G vaccine antigens, and quantifies antibody robustness to rabies variation
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Sheds light on constraints on type III fusion proteins, suggests ways to stabilize G vaccine antigens, and quantifies antibody robustness to rabies variation
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

Deep mutational scanning of rabies glycoprotein defines mutational constraint and antibody-escape mutations
Rabies virus causes nearly 60,000 human deaths annually. Antibodies that target the rabies glycoprotein (G) are being developed as post-exposure prophylactics, but mutations in G can render such antib...
www.biorxiv.org
December 18, 2024 at 8:39 PM
In new study, we measure how all mutations to rabies G affect cell entry & antibody neutralization
Sheds light on constraints on type III fusion proteins, suggests ways to stabilize G vaccine antigens, and quantifies antibody robustness to rabies variation
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Sheds light on constraints on type III fusion proteins, suggests ways to stabilize G vaccine antigens, and quantifies antibody robustness to rabies variation
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
I’ve updated SARSCoV2 RBD antibody-escape calculator w new deep mutational scanning data of Yunlong Cao & Fanchong Jian.
My interpretation: antigenic evolution currently constrained by pleiotropic effects of mutations on RBD-ACE2 affinity, RBD up-down position & antibody neutralization
My interpretation: antigenic evolution currently constrained by pleiotropic effects of mutations on RBD-ACE2 affinity, RBD up-down position & antibody neutralization
November 21, 2024 at 11:22 PM
I’ve updated SARSCoV2 RBD antibody-escape calculator w new deep mutational scanning data of Yunlong Cao & Fanchong Jian.
My interpretation: antigenic evolution currently constrained by pleiotropic effects of mutations on RBD-ACE2 affinity, RBD up-down position & antibody neutralization
My interpretation: antigenic evolution currently constrained by pleiotropic effects of mutations on RBD-ACE2 affinity, RBD up-down position & antibody neutralization
Reposted by Bloom lab
Hi friends new and old! I study how microbes interact and evolve in complex communities like the human gut microbiome.🦠🧬💩 I'm thrilled to share that I'm starting a lab at UC Irvine in April 2025 and am recruiting at all levels - please spread the word! kxuelab.com More about my work below...🧵1/n
Xue lab at UC Irvine
Ecology and evolution in the human gut microbiome
kxuelab.com
November 19, 2024 at 6:57 PM
Hi friends new and old! I study how microbes interact and evolve in complex communities like the human gut microbiome.🦠🧬💩 I'm thrilled to share that I'm starting a lab at UC Irvine in April 2025 and am recruiting at all levels - please spread the word! kxuelab.com More about my work below...🧵1/n
Reposted by Bloom lab
If you are searching literature, these sites are E190 and Q226 in H3 numbering, E186 and Q222 in mature H5 numbering, and E202 and Q238 in sequential H5 numbering (see: dms-vep.org/Flu_H5_Ameri...)
HA sequencing numbering | Deep mutational scanning of H5 influenza HA
Interactive figures and detailed results for deep mutational scanning of the HA from the clade 2.3.4.4b A/American Wigeon/South Carolina/USDA-000345-001/2021 (H5N1) strain.
dms-vep.org
November 16, 2024 at 3:57 PM
If you are searching literature, these sites are E190 and Q226 in H3 numbering, E186 and Q222 in mature H5 numbering, and E202 and Q238 in sequential H5 numbering (see: dms-vep.org/Flu_H5_Ameri...)
Reposted by Bloom lab
Excellent summary thread here by @scottehensley.bsky.social. To add a few more important notes, the sequence (GISAID EPI_ISL_19548836) is ambiguous at *both* site Q226 (as Scott mentions above) and site E190 (H3 numbering)
Both these sites play an important role in sialic acid binding specificity
Both these sites play an important role in sialic acid binding specificity
November 16, 2024 at 3:55 PM
Excellent summary thread here by @scottehensley.bsky.social. To add a few more important notes, the sequence (GISAID EPI_ISL_19548836) is ambiguous at *both* site Q226 (as Scott mentions above) and site E190 (H3 numbering)
Both these sites play an important role in sialic acid binding specificity
Both these sites play an important role in sialic acid binding specificity
Reposted by Bloom lab
The preliminary sequence from the H5N1 human case in British Columbia has been posted and it is not good news. The virus potentially has a quasispecies at HA residue 226 (H3 numbering). This is bad news because we know that mutations at residue 226 can increase binding to human receptors. 1/
November 16, 2024 at 3:19 PM
The preliminary sequence from the H5N1 human case in British Columbia has been posted and it is not good news. The virus potentially has a quasispecies at HA residue 226 (H3 numbering). This is bad news because we know that mutations at residue 226 can increase binding to human receptors. 1/
The final version of our study using pseudovirus deep mutational scanning to measure the effects of mutations influenza H5 hemagglutinin to inform viral surveillance is now published in PLoS Biology:
journals.plos.org/plosbiology/...
journals.plos.org/plosbiology/...

Deep mutational scanning of H5 hemagglutinin to inform influenza virus surveillance
H5 influenza is considered a potential pandemic threat. Using deep mutational scanning, this work reveals how the >10,000 different possible amino-acid mutations in hemagglutinin affect cell entry, re...
journals.plos.org
November 13, 2024 at 2:04 PM
The final version of our study using pseudovirus deep mutational scanning to measure the effects of mutations influenza H5 hemagglutinin to inform viral surveillance is now published in PLoS Biology:
journals.plos.org/plosbiology/...
journals.plos.org/plosbiology/...
Below is brief analysis of HA mutations in two recent cases of H5N1 influenza in humans w contact w dairy cattle in California.
Summary is that while virus continues to evolve, nothing about HA mutations in these human cases is obviously alarming.
Summary is that while virus continues to evolve, nothing about HA mutations in these human cases is obviously alarming.

October 8, 2024 at 6:24 PM
Below is brief analysis of HA mutations in two recent cases of H5N1 influenza in humans w contact w dairy cattle in California.
Summary is that while virus continues to evolve, nothing about HA mutations in these human cases is obviously alarming.
Summary is that while virus continues to evolve, nothing about HA mutations in these human cases is obviously alarming.
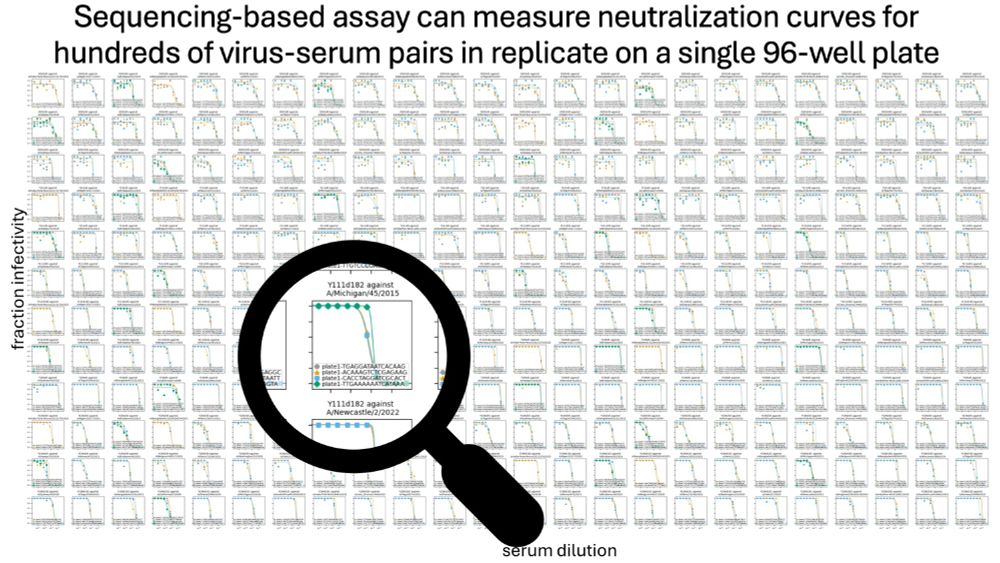
Our paper describing a new sequencing-based neutralization assay for influenza virus is now published in Journal of Virology:
journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/...
This new approach makes it possible to measure 100s (or even ~1000) neutralization titers in a single 96-well plate.
journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/...
This new approach makes it possible to measure 100s (or even ~1000) neutralization titers in a single 96-well plate.
September 24, 2024 at 6:36 PM
Our paper describing a new sequencing-based neutralization assay for influenza virus is now published in Journal of Virology:
journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/...
This new approach makes it possible to measure 100s (or even ~1000) neutralization titers in a single 96-well plate.
journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/...
This new approach makes it possible to measure 100s (or even ~1000) neutralization titers in a single 96-well plate.
Here is analysis of HA mutations in H5 influenza case in Missouri resident without known contact w animals or raw milk.
TLDR: there is one HA mutation that strongly affects antigenicity, and another that merits some further study.
TLDR: there is one HA mutation that strongly affects antigenicity, and another that merits some further study.
September 15, 2024 at 4:38 AM
Here is analysis of HA mutations in H5 influenza case in Missouri resident without known contact w animals or raw milk.
TLDR: there is one HA mutation that strongly affects antigenicity, and another that merits some further study.
TLDR: there is one HA mutation that strongly affects antigenicity, and another that merits some further study.
We’ve updated our pre-print on deep mutational scanning of influenza clade 2.3.4.4b H5 HA to identify recent viruses w mutations that alter relevant phenotypes.
This identifies viruses w >10x reduced neutralization by sera from candidate vaccine viruses: www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
This identifies viruses w >10x reduced neutralization by sera from candidate vaccine viruses: www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

August 3, 2024 at 2:47 PM
We’ve updated our pre-print on deep mutational scanning of influenza clade 2.3.4.4b H5 HA to identify recent viruses w mutations that alter relevant phenotypes.
This identifies viruses w >10x reduced neutralization by sera from candidate vaccine viruses: www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
This identifies viruses w >10x reduced neutralization by sera from candidate vaccine viruses: www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
In new study led by Bernadeta Dadonaite, we measure how all mutations to H5 influenza HA affect four molecular phenotypes relevant to pandemic risk:
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Results can inform surveillance of ongoing evolution of H5N1.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Results can inform surveillance of ongoing evolution of H5N1.

May 25, 2024 at 1:52 PM
In new study led by Bernadeta Dadonaite, we measure how all mutations to H5 influenza HA affect four molecular phenotypes relevant to pandemic risk:
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Results can inform surveillance of ongoing evolution of H5N1.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Results can inform surveillance of ongoing evolution of H5N1.
In new study led by Brendan Larsen in collab w Veesler & Crowe labs, we map functional & antigenic landscape of Nipah virus receptor binding protein (RBP)
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Results elucidate constraints on RBP function & provide insight into protein’s evolutionary potential
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Results elucidate constraints on RBP function & provide insight into protein’s evolutionary potential

Functional and antigenic landscape of the Nipah virus receptor binding protein
bioRxiv - the preprint server for biology, operated by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, a research and educational institution
www.biorxiv.org
April 20, 2024 at 1:49 AM
In new study led by Brendan Larsen in collab w Veesler & Crowe labs, we map functional & antigenic landscape of Nipah virus receptor binding protein (RBP)
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Results elucidate constraints on RBP function & provide insight into protein’s evolutionary potential
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Results elucidate constraints on RBP function & provide insight into protein’s evolutionary potential

