
✅ Just Accepted
#IDSky
🔗 https://bit.ly/4oJIv5X

academic.oup.com/jpids/articl...

See Dr. Mejias present at #IDWeek2025. Register today before rates increase Sept. 20: https://idweek.org/registration

See Dr. Mejias present at #IDWeek2025. Register today before rates increase Sept. 20: https://idweek.org/registration
🆕🔥The mechanisms of antibiotic resistance & drug resistance transmission of Klebsiella pneumoniae #idsky
www.nature.com/articles/s41...


Continuous or extended vs intermittent infusions of beta-lactam antibiotics in ICU patients with pneumonia #IDsky #EMIMCC
journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/...

Continuous or extended vs intermittent infusions of beta-lactam antibiotics in ICU patients with pneumonia #IDsky #EMIMCC
journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/...
@unbiasedscipod.bsky.social 👏
theunbiasedscipod.substack.com/p/how-a-gove...
www.nytimes.com/interactive/...

@unbiasedscipod.bsky.social 👏
theunbiasedscipod.substack.com/p/how-a-gove...
www.nytimes.com/interactive/...

Learn more: ow.ly/y5XK50WK8GG
#IDSky #clinmicro #AMR #stewardship

Learn more: ow.ly/y5XK50WK8GG
#IDSky #clinmicro #AMR #stewardship
There's been a 65 % reduction in RSV in Ireland - #PedSky + #IDSky + #MedSky.
www.irishtimes.com/health/2025/...

There's been a 65 % reduction in RSV in Ireland - #PedSky + #IDSky + #MedSky.
www.irishtimes.com/health/2025/...
✅ Just Accepted
✍️ @mejias71.bsky.social @megias71
#IDSky

✅ Just Accepted
✍️ @mejias71.bsky.social @megias71
#IDSky
www.reuters.com/business/hea... #BlueSky #MedSky 🧪 #IDSky #SciSky #medtwitter #EMSky #EMedSky #nursesky #MedEd #fmsky #pedsky #CardioSky

www.reuters.com/business/hea... #BlueSky #MedSky 🧪 #IDSky #SciSky #medtwitter #EMSky #EMedSky #nursesky #MedEd #fmsky #pedsky #CardioSky
Our living database now includes 1,267 controlled vaccine trials - 501 with inert (mostly saline) placebos - involving 9.36 million participants.
And MANY more studies to add.
Grateful to the incredible team making it possible. 🙏
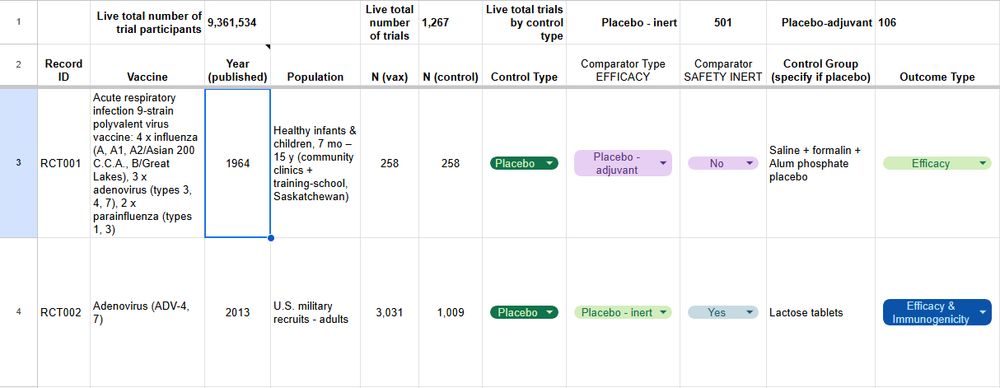
Our living database now includes 1,267 controlled vaccine trials - 501 with inert (mostly saline) placebos - involving 9.36 million participants.
And MANY more studies to add.
Grateful to the incredible team making it possible. 🙏
doi.org/10.1093/jaca...
#JACAMRNew #IDSky #GlobalEpidemiology @davidvanduin.bsky.social
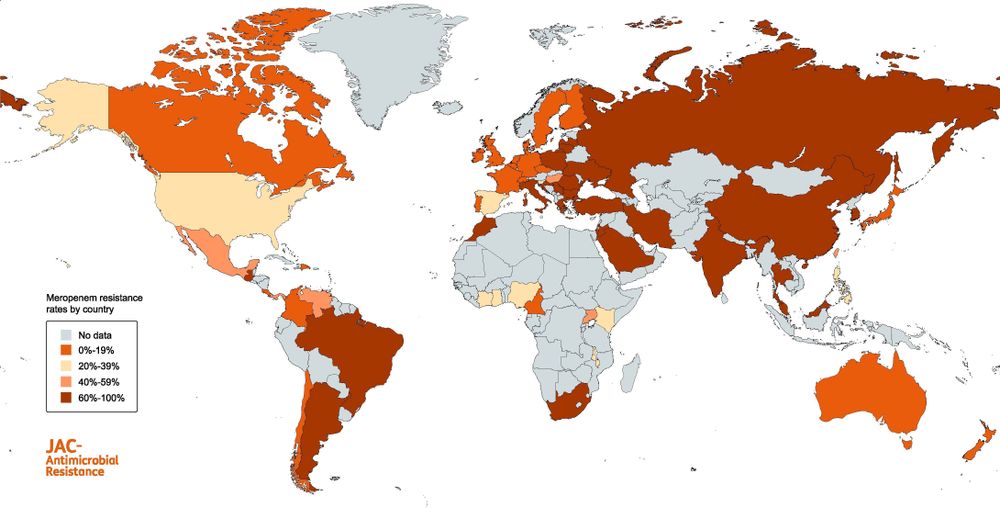
doi.org/10.1093/jaca...
#JACAMRNew #IDSky #GlobalEpidemiology @davidvanduin.bsky.social

Time to reconsider.
Dozens of authors convened at lightning speed, opposed:
Static vs. cidal: it’s not complex; it’s simply incorrect | Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/...
#IDSky #Pharmsky

Time to reconsider.
Dozens of authors convened at lightning speed, opposed:
Static vs. cidal: it’s not complex; it’s simply incorrect | Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/...
#IDSky #Pharmsky
journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/...

journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/...




