
Cognitive Neuroscientist and Associate Professor of Psychology at George Mason University. Perception of Time, Memory, & Action. Exec Director @ http://timingforum.org
Martin Joel Wiener is an American academic and author. He is currently a research professor at Rice University.
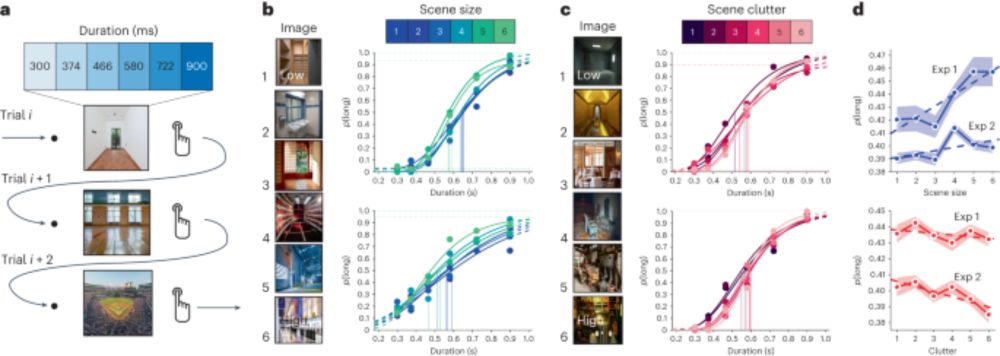
Memorability shapes perceived time (and vice versa)
#academicsky #neuroskyence #psychscisky #science
Reposted by Martin Wiener
But, as a parent of an ADHD kid, these results match a lot of what I see! Great work!

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Farzaneh Najafi will be giving a talk on her recent work on intrinsic timing and ramping dynamics in visual and parietal cortices. Registration link below!
Wed 12/10 @ 10am EST
mailchi.mp/864719714f87...


Farzaneh Najafi will be giving a talk on her recent work on intrinsic timing and ramping dynamics in visual and parietal cortices. Registration link below!
Wed 12/10 @ 10am EST
mailchi.mp/864719714f87...

Very cool review on image memorability (hint: priority coding is key) by Wilma Bainbridge, @dirkbwalther.bsky.social @keisukefukuda.bsky.social, Lore Goetschalckx
rdcu.be/eSyjz

I did a post once on the other place noting that LLMs like ChatGPT have no sense of time (ask them)
There's also this paper, with some great insights: arxiv.org/abs/1905.13469

mailchi.mp/bec6a9d9cf6a...
Time, space, memory and brain–body rhythms
György Buzsáki
(2025)
Physical time is measured using arbitrary units whereas experienced time is linked to a hierarchy of brain–body rhythms... these rhythms, may be the source of our subjective feeling of time. 👇💥
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

Reposted by Martin Wiener

Time, space, memory and brain–body rhythms
György Buzsáki
(2025)
Physical time is measured using arbitrary units whereas experienced time is linked to a hierarchy of brain–body rhythms... these rhythms, may be the source of our subjective feeling of time. 👇💥
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Reposted by Martin Wiener

Bees can discriminate long 🟡🟡 vs short🟡 flashes, a bit like the "dash" and "dot" of the Morse code.
Check our new paper royalsocietypublishing.org/doi/10.1098/... and videoclip youtu.be/hsGxU65OMQk?... @preparedmindslab.bsky.social
Reposted by Martin Wiener

Ever wonder how to model the temporal generalization task? Interested in cross-modal comparisons? Our paper (w/ the magnificent Nir Ofir!) is for you! @timingresforum.bsky.social this could make for a solid post-conference decompression read
link.springer.com/article/10.3...
Reposted by Martin Wiener, Nate Breznau

The position is funded as part of the Excellence Cluster "The Adaptive Mind" at @jlugiessen.bsky.social.
Please apply here until Nov 25:
www.uni-giessen.de/de/ueber-uns...
Reposted by Martin Wiener

tl;dr: you can now chat with a brain scan 🧠💬
1/n
I'll be working with the amazing @ayeletlandau.bsky.social and Yuval Benjamini to explore and understand how our sense of time and image memorability are linked. ⌛🧠
We have 2(!) post-doc opportunities available - details coming soon!
If interested, please DM or email me for more information!
Tenure track assistant professor in Psychology at George Mason University, with a focus on cognitive computational neuroscience. Reviews begin October 21st and continue thereafter.
Email me for more questions/inquiries
listings.jobs.gmu.edu/jobs/tenure-...
Altogether, we think this provides evidence that visual time is guided by information content.

ALSO, the effect was moderated by how subjectively meaningful subjects found the stimuli
doi.org/10.1016/j.co...

Here, we found that symbols that contained more edges were dilated. In the attached image, the symbols on the right all seemed to last longer than the ones on the left.
osf.io/preprints/ps...



