Twitter: https://x.com/satoshiyoshiji
• MODY panels are undergoing refinement in the population-scale genetics era.
• We discuss how the Exeter team provides strong evidence for NEUROD1 and PDX1, but not for APPL1 or WFS1, using data from UK Biobank and gnomAD.
diabetesjournals.org/diabetes/art...

• MODY panels are undergoing refinement in the population-scale genetics era.
• We discuss how the Exeter team provides strong evidence for NEUROD1 and PDX1, but not for APPL1 or WFS1, using data from UK Biobank and gnomAD.
diabetesjournals.org/diabetes/art...



somalogic.com/us-hupo-2025/

somalogic.com/us-hupo-2025/
Join us at US HUPO 2025 in Philly for the Feb 24 SomaLogic breakfast session
I'll discuss our recent study in Nature Genetics on a protein mediating obesity’s effect on CAD & our MR atlas project.
somalogic.com/us-hupo-2025...


Join us at US HUPO 2025 in Philly for the Feb 24 SomaLogic breakfast session
I'll discuss our recent study in Nature Genetics on a protein mediating obesity’s effect on CAD & our MR atlas project.
somalogic.com/us-hupo-2025...
Join Yoshiji Lab at McGill University Dept of Human Genetics in Montreal, Canada!
yoshiji-lab.org/joinus
✅Fully Funded Positions
• 2 MSc Students
• 1 PhD Student
• 1 Postdoc
✅Goal: Using human genetics and multi-omics for drug target discovery and precision medicine


Join Yoshiji Lab at McGill University Dept of Human Genetics in Montreal, Canada!
yoshiji-lab.org/joinus
✅Fully Funded Positions
• 2 MSc Students
• 1 PhD Student
• 1 Postdoc
✅Goal: Using human genetics and multi-omics for drug target discovery and precision medicine

1–2 MSc positions, one PhD position (all fully funded), and a post-doc position will be available. Stay tuned and join us at McGill in the vibrant city of Montreal, Canada!
Lab webpage: yoshiji-lab.org

1–2 MSc positions, one PhD position (all fully funded), and a post-doc position will be available. Stay tuned and join us at McGill in the vibrant city of Montreal, Canada!
Lab webpage: yoshiji-lab.org
10/10

10/10
9/10
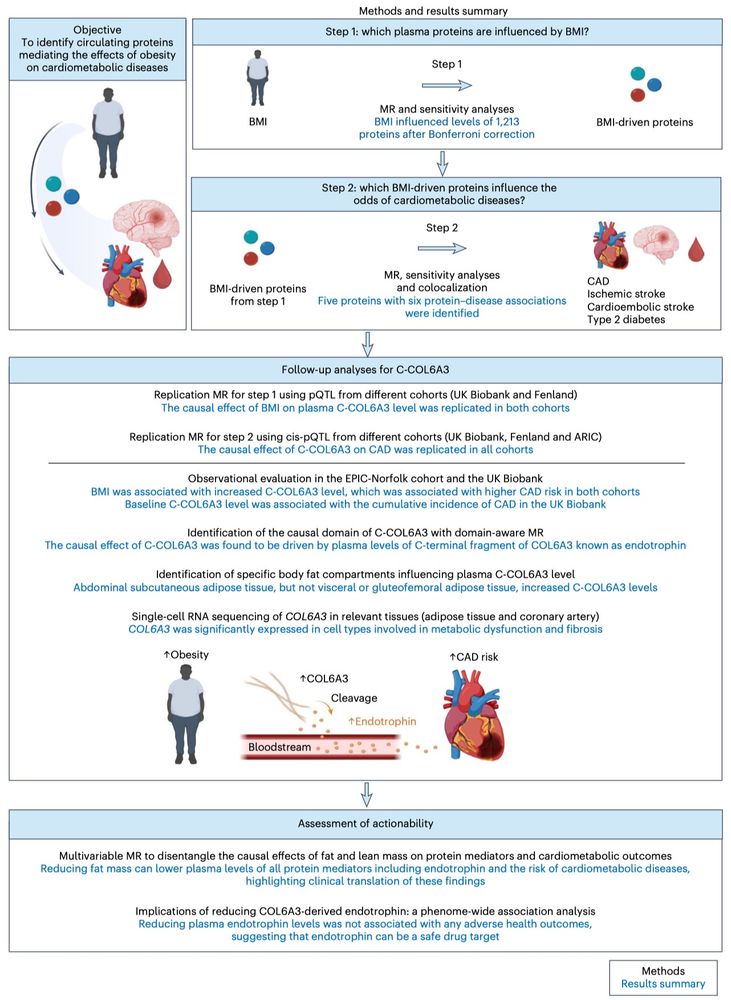
9/10
Using multivariable MR, we showed that reducing body fat (and for some proteins, increasing muscle) can lower protein mediator levels and cardiometabolic risk!
7/10

Using multivariable MR, we showed that reducing body fat (and for some proteins, increasing muscle) can lower protein mediator levels and cardiometabolic risk!
7/10
6/10

6/10
5/10
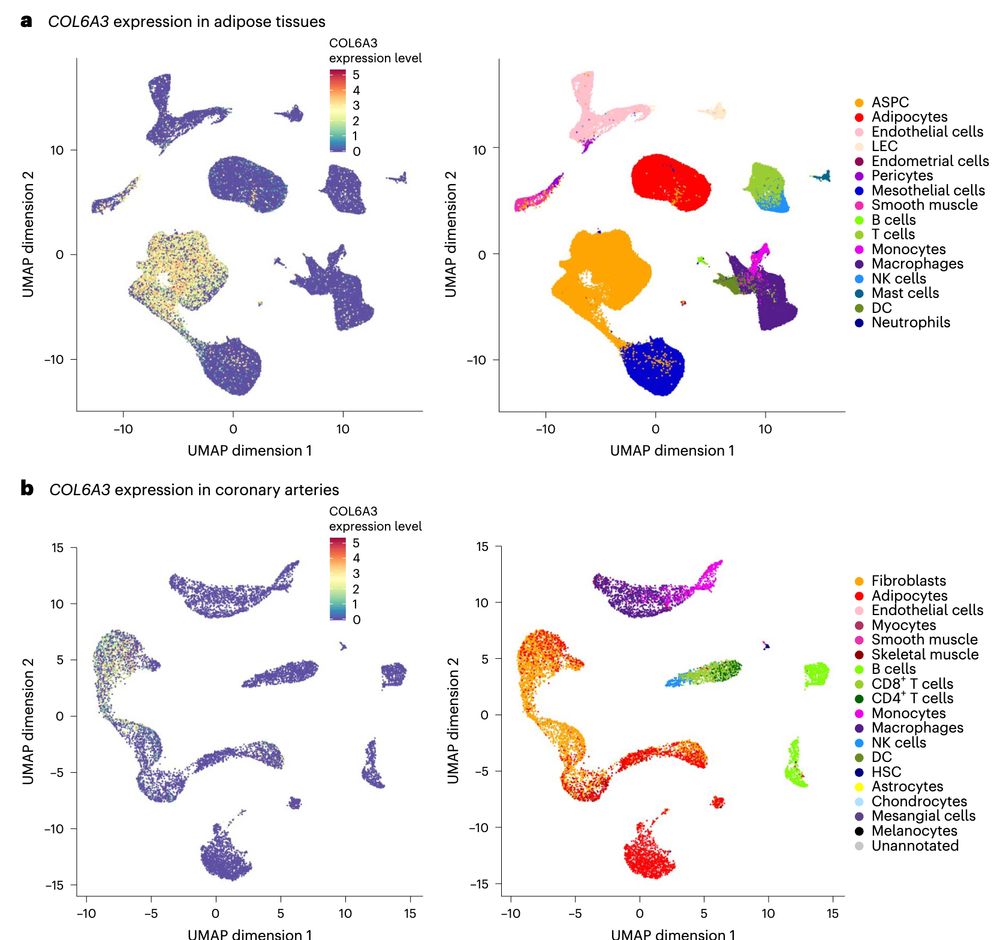
5/10
4/10
4/10
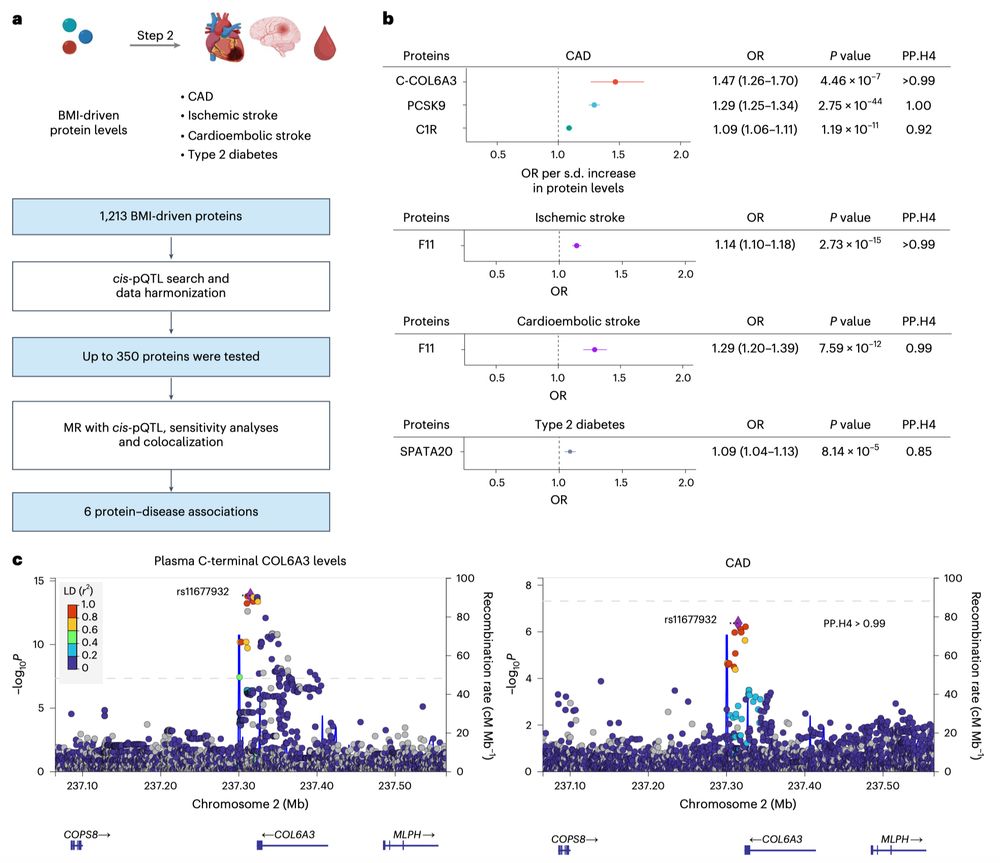
Interestingly, domain-aware MR, enabled by two aptamers targeting the C- and N-terminals of COL6A3, found that the causal effect was driven by the C-terminal, cleaved into the adipokine endotrophin.
3/10
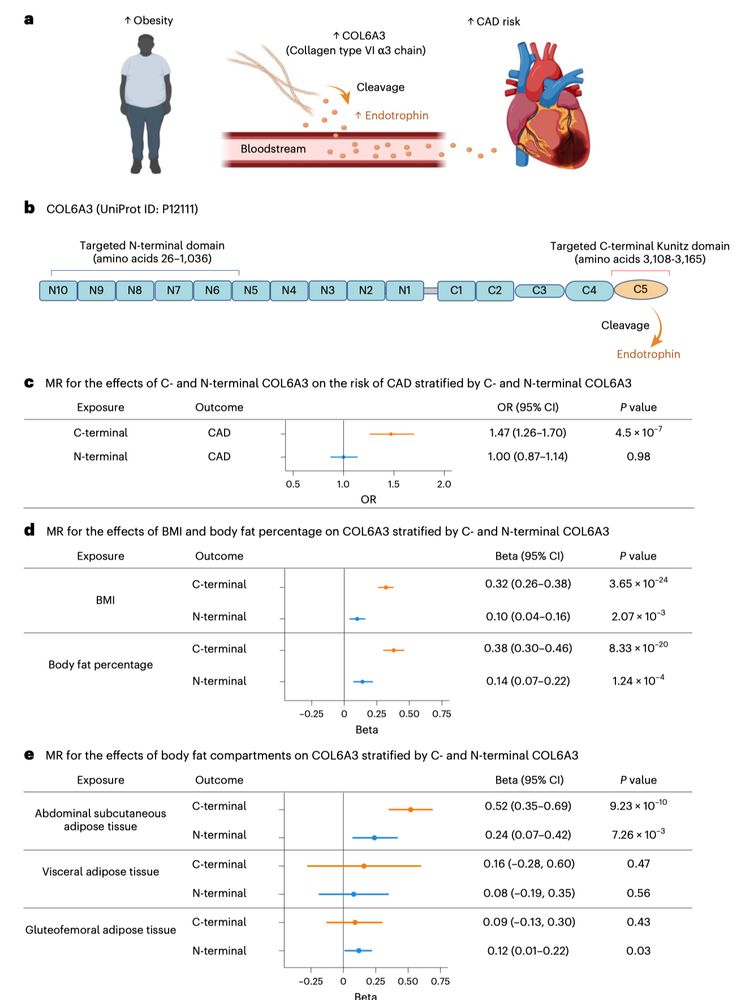
Interestingly, domain-aware MR, enabled by two aptamers targeting the C- and N-terminals of COL6A3, found that the causal effect was driven by the C-terminal, cleaved into the adipokine endotrophin.
3/10
2/10
2/10
First, we used MR to evaluate the causal effect of obesity on plasma proteins to identify “BMI-driven proteins.”
1/10
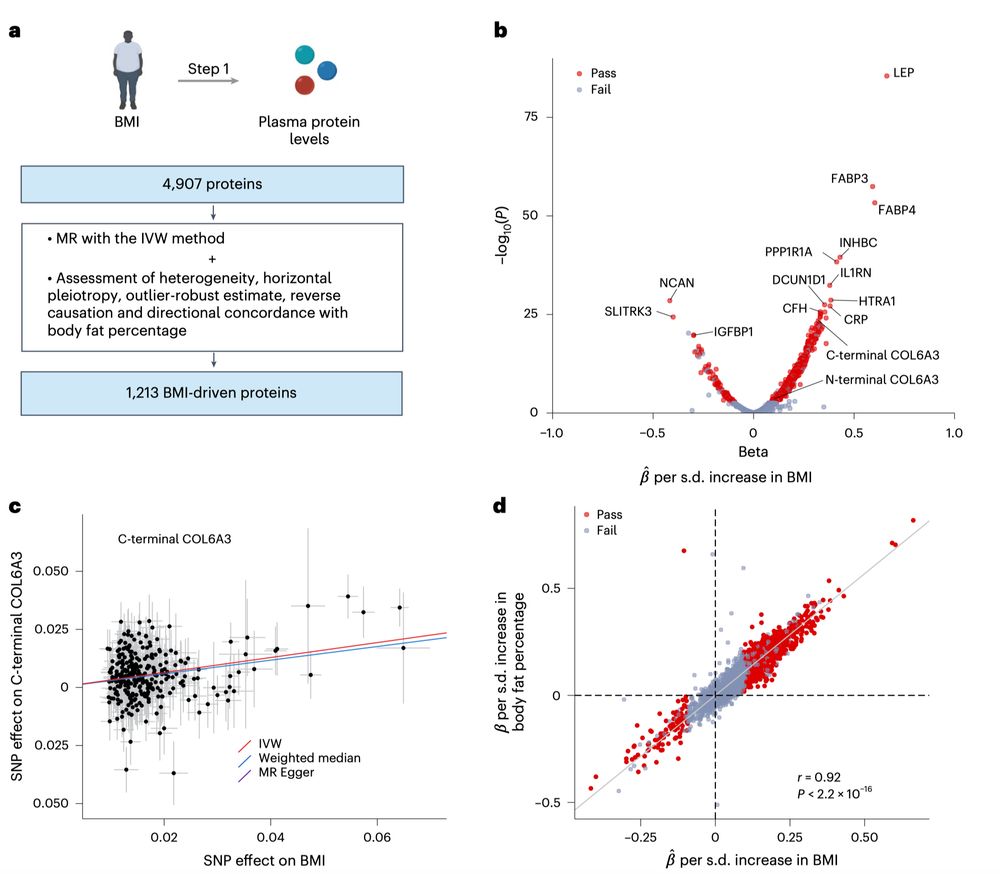
First, we used MR to evaluate the causal effect of obesity on plasma proteins to identify “BMI-driven proteins.”
1/10
• ↓Body fat → ↓endotrophin → ↓CAD risk
• Two-step proteome-wide MR identifies proteins linking risk factors to disease
• Domain-aware MR shows only C-terminal COL6A3, cleaved into endotrophin, is causal for CAD
• Supports Endotrophin as a potential CAD target

• ↓Body fat → ↓endotrophin → ↓CAD risk
• Two-step proteome-wide MR identifies proteins linking risk factors to disease
• Domain-aware MR shows only C-terminal COL6A3, cleaved into endotrophin, is causal for CAD
• Supports Endotrophin as a potential CAD target
rdcu.be/d7mo0
Do plasma proteins mediate obesity’s effect on CAD risk?
→Using two-step proteome-wide MR, domain-aware MR, epigenomics & scRNA-seq, we prioritized endotrophin, cleaved from COL6A3, as a mediator & potential therapeutic target.
A 🧵↓

rdcu.be/d7mo0
Do plasma proteins mediate obesity’s effect on CAD risk?
→Using two-step proteome-wide MR, domain-aware MR, epigenomics & scRNA-seq, we prioritized endotrophin, cleaved from COL6A3, as a mediator & potential therapeutic target.
A 🧵↓
10/10

10/10
9/10

9/10
Using multivariable MR, we showed that reducing body fat (and for some proteins, increasing muscle) can lower protein mediator levels and cardiometabolic risk!
7/10

Using multivariable MR, we showed that reducing body fat (and for some proteins, increasing muscle) can lower protein mediator levels and cardiometabolic risk!
7/10
6/10

6/10
5/10

5/10

