Metabolism | Metabolomics | Mass Spec
#secmet #lassopeptides #syntheticbiology

#secmet #lassopeptides #syntheticbiology

www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Behind the paper story:
go.nature.com/45ljV4d
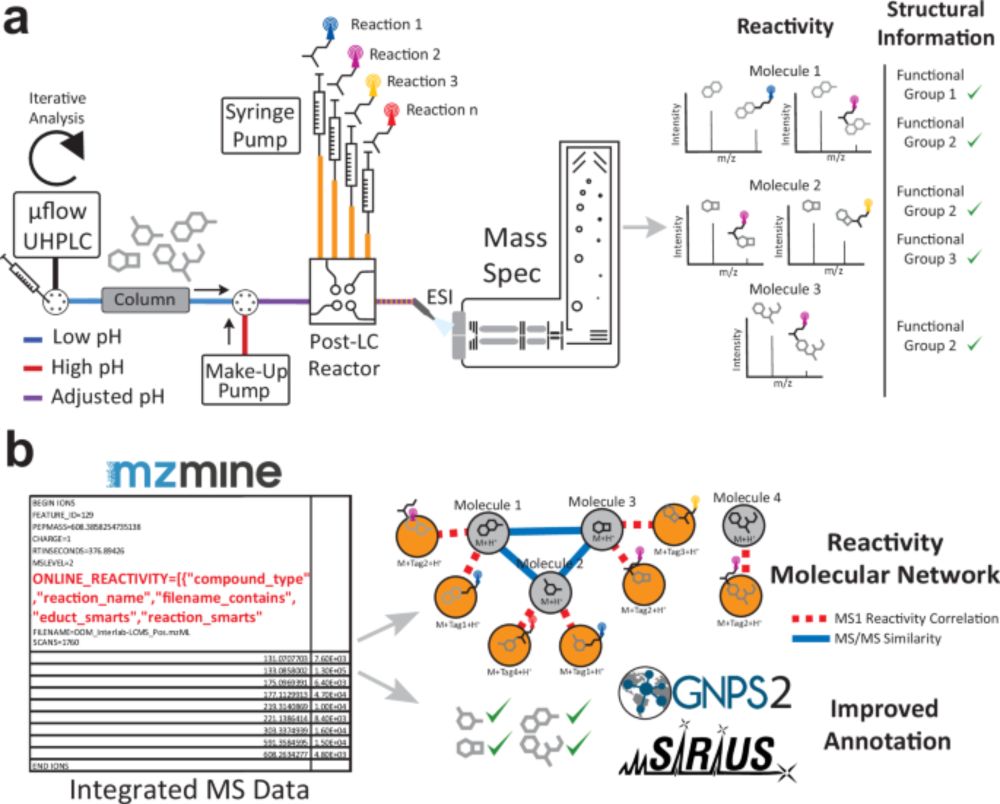
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Behind the paper story:
go.nature.com/45ljV4d
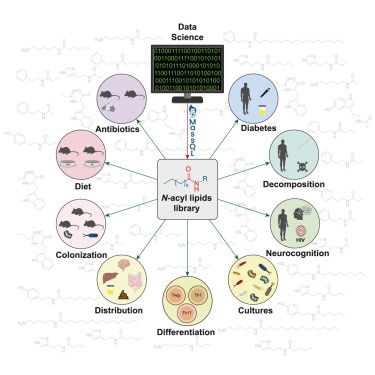
https://go.nature.com/43WhALs

https://go.nature.com/43WhALs


