
PhD student in Machine Learning @ University of Cambridge | Previously MSc & Bsc @ ETH Zürich
fanconic.github.io
Paper: arxiv.org/abs/2506.11887
#LLM #MultiAgent #ICML2025

Paper: arxiv.org/abs/2506.11887
#LLM #MultiAgent #ICML2025
Paper: arxiv.org/abs/2412.13998
#LLM #AIAlignment #ICML2025

Paper: arxiv.org/abs/2412.13998
#LLM #AIAlignment #ICML2025
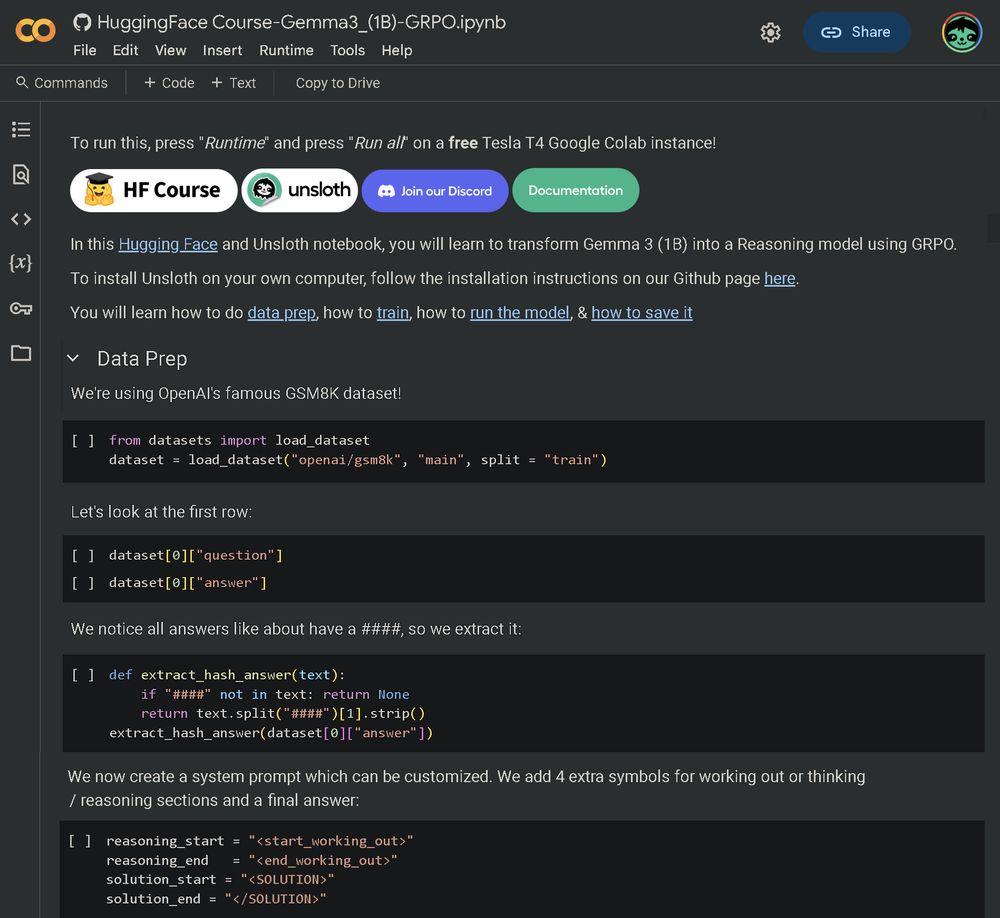
Learn to:
• Enable reasoning in Gemma 3 (1B)
• Prepare/understand reward functions
• Make GRPO work for tiny LLMs
Notebook: colab.research.google.com/github/unslo...
Details: huggingface.co/reasoning-co...
Learn to:
• Enable reasoning in Gemma 3 (1B)
• Prepare/understand reward functions
• Make GRPO work for tiny LLMs
Notebook: colab.research.google.com/github/unslo...
Details: huggingface.co/reasoning-co...
youtube.com/watch?v=1kwb...

youtube.com/watch?v=1kwb...
- 800k total samples dataset similar in composition to the data used to train DeepSeek-R1 Distill models.
- 300k from DeepSeek-R1
- 300k from Gemini 2.0 flash thinking
- 200k from Dolphin chat
huggingface.co/datasets/cog...

- 800k total samples dataset similar in composition to the data used to train DeepSeek-R1 Distill models.
- 300k from DeepSeek-R1
- 300k from Gemini 2.0 flash thinking
- 200k from Dolphin chat
huggingface.co/datasets/cog...

Introducing Collaborative Gym (Co-Gym), a framework for enabling & evaluating human-agent collaboration! I now get used to agents proactively seeking confirmations or my deep thinking.(🧵 with video)

Introducing Collaborative Gym (Co-Gym), a framework for enabling & evaluating human-agent collaboration! I now get used to agents proactively seeking confirmations or my deep thinking.(🧵 with video)
https://buff.ly/4gQV9wt

https://buff.ly/4gQV9wt
docs.google.com/presentation...

docs.google.com/presentation...
Let me know if you want to chat about alignment, LLMs, and AI applications in medicine!
arxiv.org/abs/2406.08414

Let me know if you want to chat about alignment, LLMs, and AI applications in medicine!
arxiv.org/abs/2406.08414
After 7 amazing years at Google Brain/DM, I am joining OpenAI. Together with @xzhai.bsky.social and @giffmana.ai, we will establish OpenAI Zurich office. Proud of our past work and looking forward to the future.
After 7 amazing years at Google Brain/DM, I am joining OpenAI. Together with @xzhai.bsky.social and @giffmana.ai, we will establish OpenAI Zurich office. Proud of our past work and looking forward to the future.
Procedural knowledge in pretraining drives LLM reasoning ⚙️🔢
🧵⬇️
Procedural knowledge in pretraining drives LLM reasoning ⚙️🔢
🧵⬇️
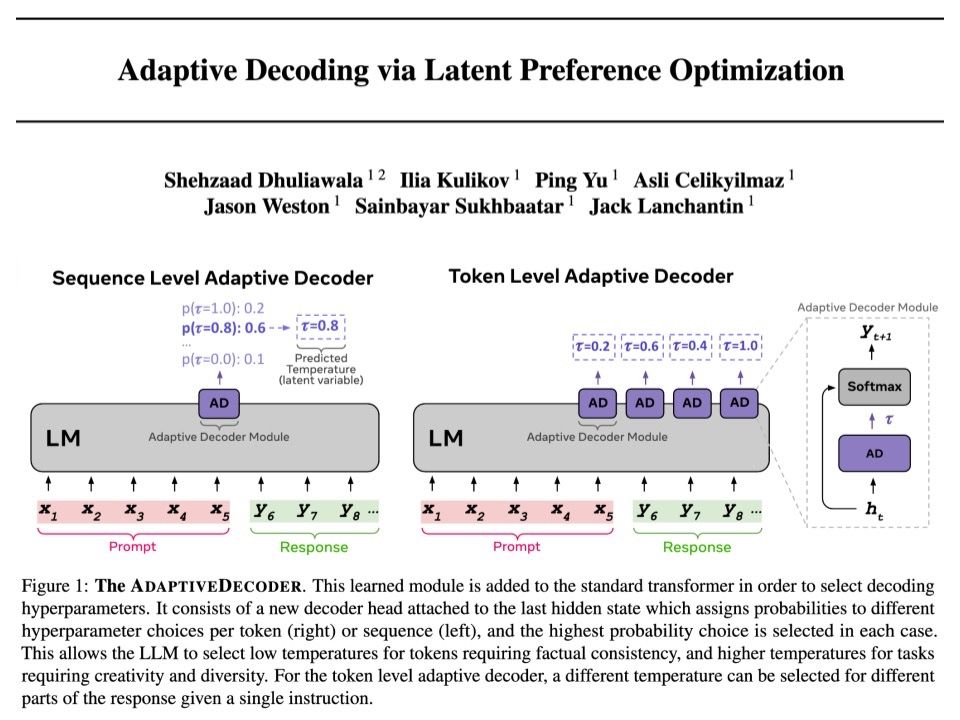
- New layer for Transformer, selects decoding params automatically *per token*
- Learnt via new method Latent Preference Optimization
- Outperforms any fixed temperature decoding, choosing creativity or factuality
arxiv.org/abs/2411.09661
🧵1/4
- New layer for Transformer, selects decoding params automatically *per token*
- Learnt via new method Latent Preference Optimization
- Outperforms any fixed temperature decoding, choosing creativity or factuality
arxiv.org/abs/2411.09661
🧵1/4
RLHF = 30% *more* copying than base!
Awesome work from the awesome Ximing Lu (gloriaximinglu.github.io) et al. 🤩
arxiv.org/pdf/2410.04265

RLHF = 30% *more* copying than base!
Awesome work from the awesome Ximing Lu (gloriaximinglu.github.io) et al. 🤩
arxiv.org/pdf/2410.04265


