doi.org/10.1093/jeb/...
Brazier et al.
(@romanstet.bsky.social)

🔗 doi.org/10.1093/jeb/voae136
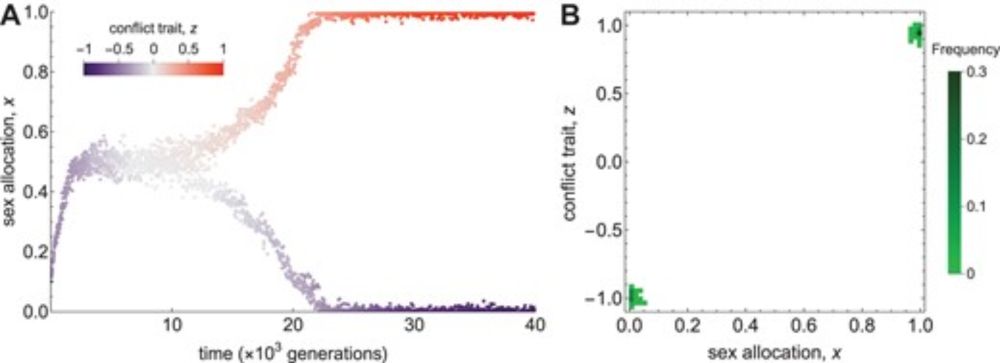
🔗 doi.org/10.1093/jeb/voae136
🔗 doi.org/10.1093/evlett/qrae059

🔗 doi.org/10.1093/evlett/qrae059
doi.org/10.1093/evle...
Now in @evolletters.bsky.social by Ewan Flintham et al.

doi.org/10.1093/evle...
Now in @evolletters.bsky.social by Ewan Flintham et al.

