Views are my own.
“Live as though life was created for you."
Maya Angelou
Legacy.
🇺🇸❤️

Legacy.
🇺🇸❤️
An interim analysis of trial data finds that tebipenem HBr met its primary efficacy end point in patients with complicated urinary tract infections, including pyelonephritis.
www.cidrap.umn.edu/a...
An interim analysis of trial data finds that tebipenem HBr met its primary efficacy end point in patients with complicated urinary tract infections, including pyelonephritis.
www.cidrap.umn.edu/a...
New PK/PD data says: it’s not just about higher doses—MIC matters.
2g q6h works only if MIC <=0.5 mg/L
For MIC:1-2 mg/L, continuous infusion (10–12g/day) may be needed to hit PD targets #idsky
journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/...
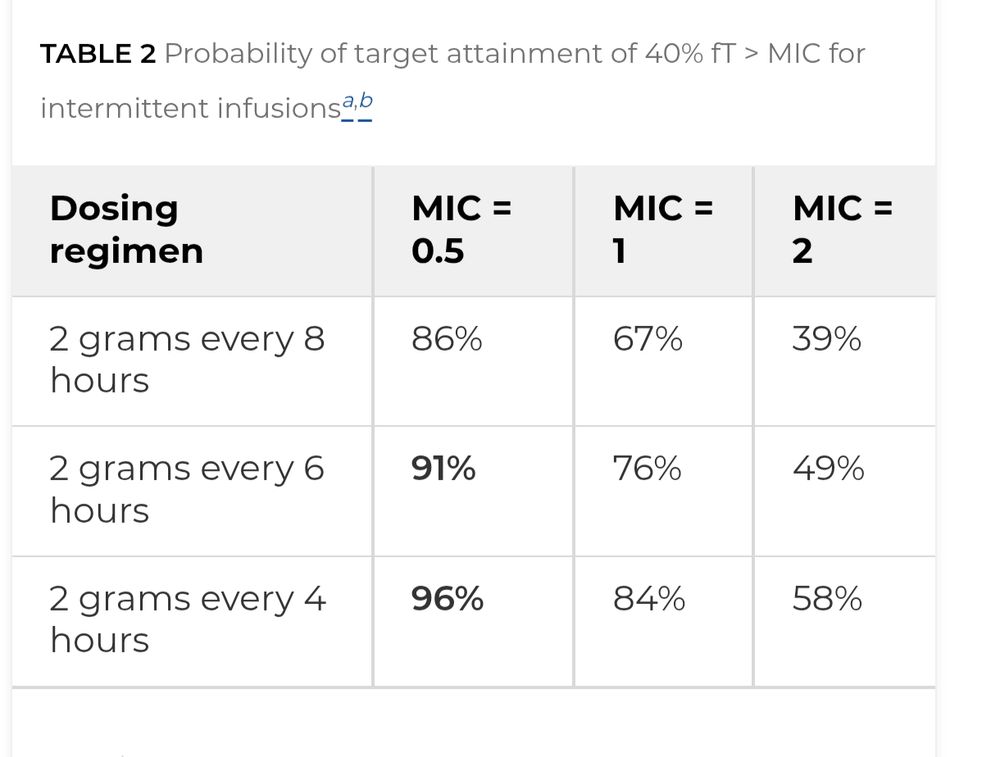
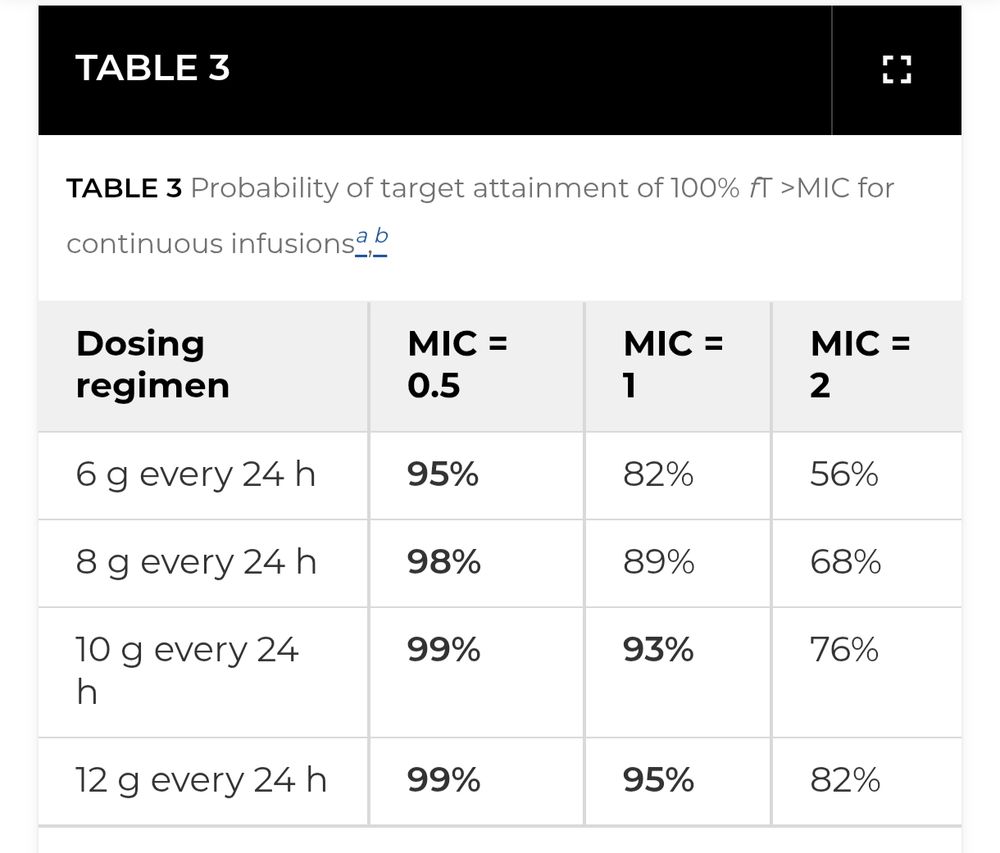
New PK/PD data says: it’s not just about higher doses—MIC matters.
2g q6h works only if MIC <=0.5 mg/L
For MIC:1-2 mg/L, continuous infusion (10–12g/day) may be needed to hit PD targets #idsky
journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/...
@sidpharm.bsky.social

@sidpharm.bsky.social
The pharmacokinetics of antibiotics in patients with obesity: a systematic review and consensus guidelines for dose adjustments
www.thelancet.com/journals/lan...
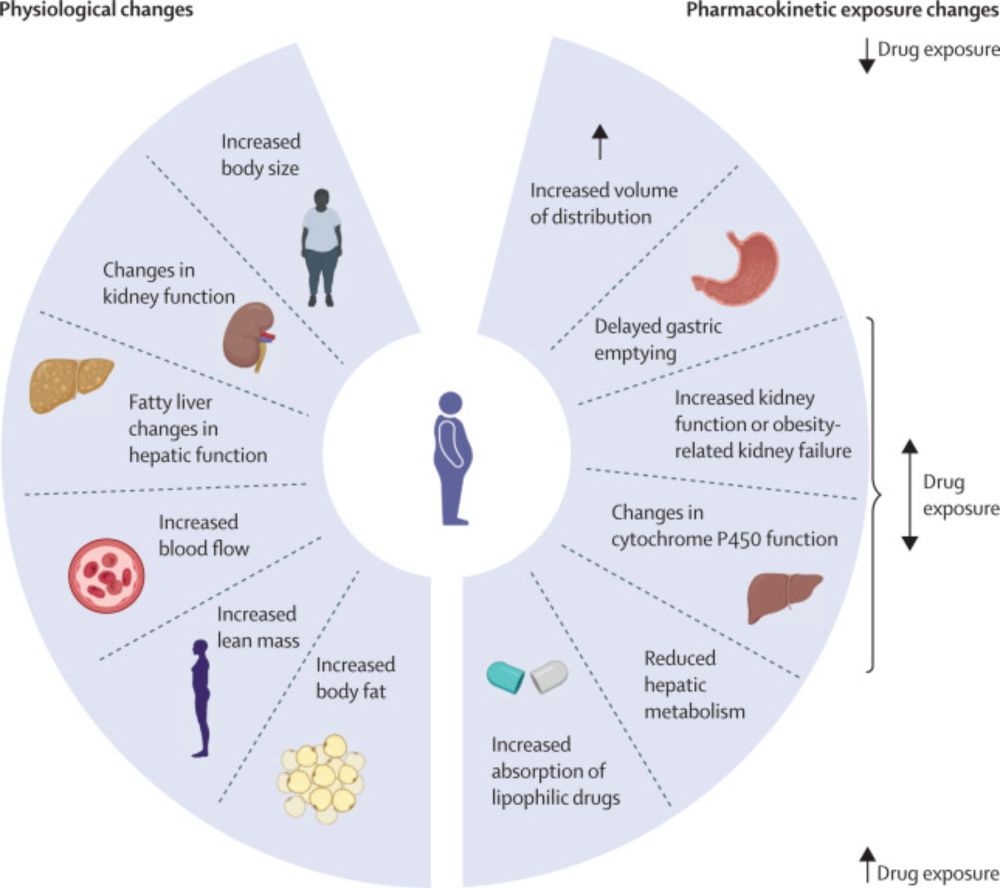
The pharmacokinetics of antibiotics in patients with obesity: a systematic review and consensus guidelines for dose adjustments
www.thelancet.com/journals/lan...
👉 Register today: bit.ly/3DGu684

👉 Register today: bit.ly/3DGu684
Over 6 months, 10 ID pharmacists were "curbsided" w/ 1,518 Qs, 3/4 from ID attendings
89% of answers led to changes in management!!!
@erinmccreary.bsky.social @sidpharm.bsky.social
#IDSky #PharmSky

Over 6 months, 10 ID pharmacists were "curbsided" w/ 1,518 Qs, 3/4 from ID attendings
89% of answers led to changes in management!!!
@erinmccreary.bsky.social @sidpharm.bsky.social
#IDSky #PharmSky
Sir David Attenborough, thank you for a lifetime dedicated to the natural world, and for sharing its story with wisdom, wonder, and grace.
You've inspired generations to fall in love with nature.
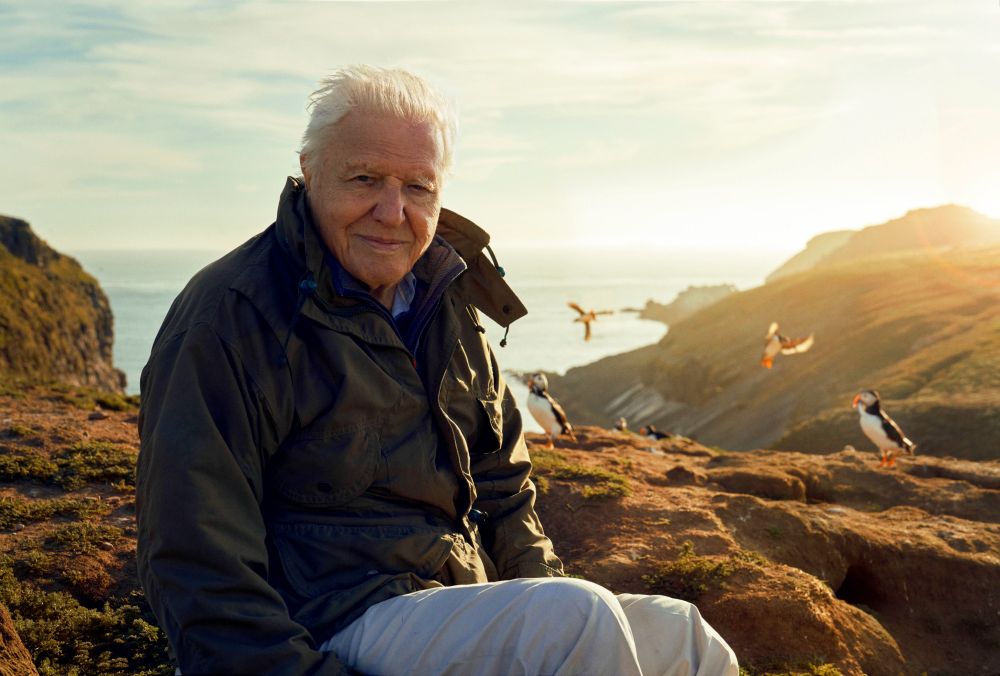

Sir David Attenborough, thank you for a lifetime dedicated to the natural world, and for sharing its story with wisdom, wonder, and grace.
You've inspired generations to fall in love with nature.
Modern Approach to #Nocardiosis —Diagnosis, Management, and Uncertainties
@zyetmar.bsky.social and colleagues
#IDSky #TxID @cidjournal.bsky.social
academic.oup.com/cid/article/...
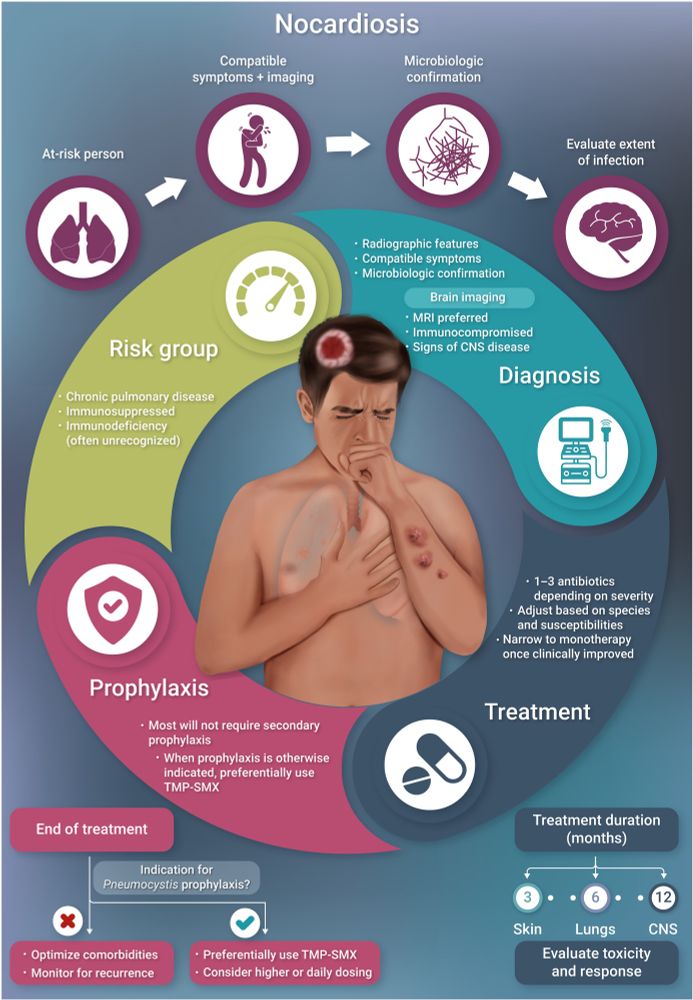
Modern Approach to #Nocardiosis —Diagnosis, Management, and Uncertainties
@zyetmar.bsky.social and colleagues
#IDSky #TxID @cidjournal.bsky.social
academic.oup.com/cid/article/...
Have already used this algorithm several times!
doi.org/10.1093/cid/...
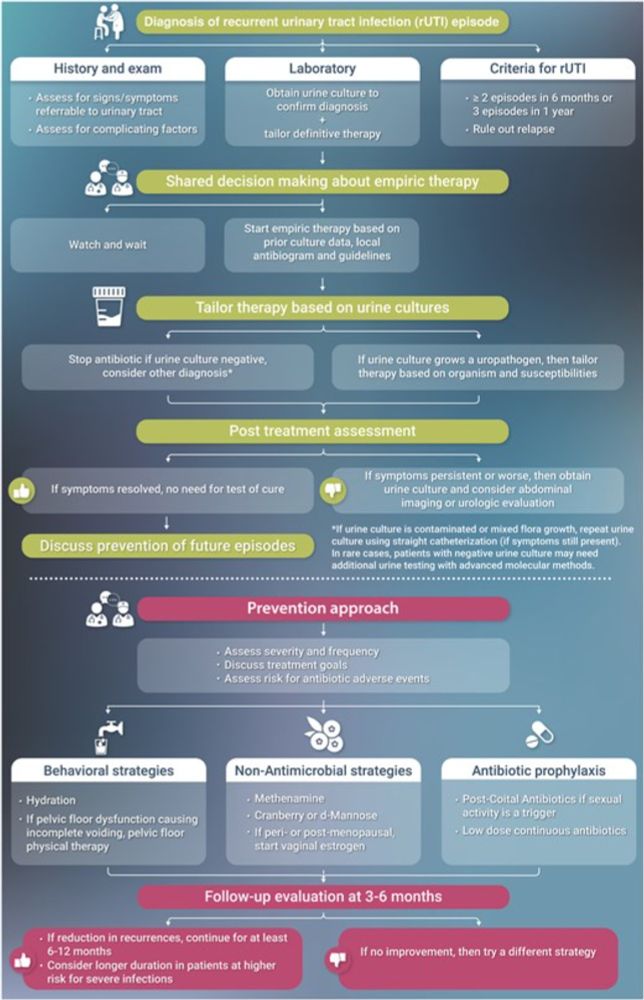
Have already used this algorithm several times!
doi.org/10.1093/cid/...
👀 Figure 2 & Table 2
doi.org/10.1001/jama.2025.4288
#IDSky #rxsky #pharmsky #AMSsky #medsky #SIDP

pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC...
Written by trauma surgeons with many common injuries that DON’T require ppx or alternatively ppx <48 hours
#IDSky

pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC...
Written by trauma surgeons with many common injuries that DON’T require ppx or alternatively ppx <48 hours
#IDSky
Here are 5 things to consider when interpreting MRSA nares swab results. Check it out here ➡️ www.idstewardship.com/5-things-kno...
@idstewardship.bsky.social

Here are 5 things to consider when interpreting MRSA nares swab results. Check it out here ➡️ www.idstewardship.com/5-things-kno...
@idstewardship.bsky.social
US FDA approved Blujepa (gepotidacin) for treatment of uncomplicated urinary tract infections (uUTIs) in female adults and paediatric patients 12 years of age and older
#IDsky #utisky #medsky #AMSsky
www.gsk.com/en-gb/media/...

US FDA approved Blujepa (gepotidacin) for treatment of uncomplicated urinary tract infections (uUTIs) in female adults and paediatric patients 12 years of age and older
#IDsky #utisky #medsky #AMSsky
www.gsk.com/en-gb/media/...




Image Credit: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI; D. Milisavljevic (Purdue University), T. Temim (Princeton University), I. De Looze (University of Gent)
apod.nasa.gov/apod/ap25011...
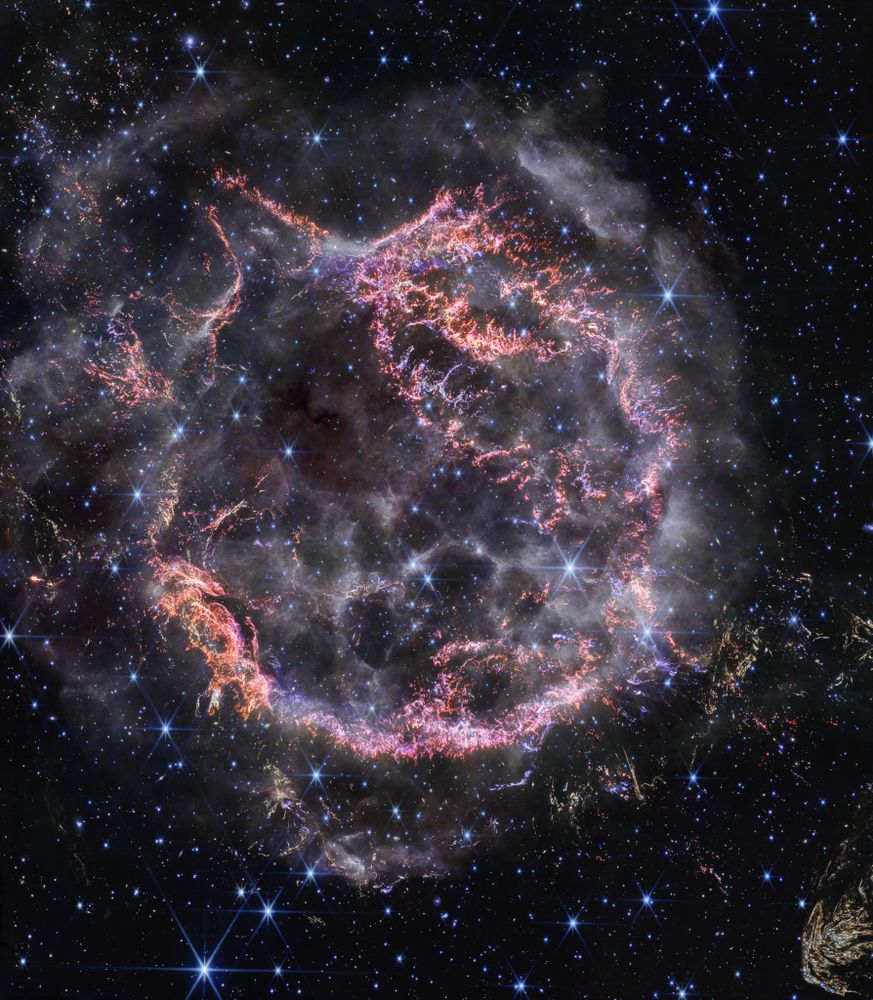

Image Credit: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI; D. Milisavljevic (Purdue University), T. Temim (Princeton University), I. De Looze (University of Gent)
apod.nasa.gov/apod/ap25011...



