N-linked glycans modulate flexibility & MPER epitope exposure #glycotime
Huge effort by @shehata92.bsky.social @lcasalino88.bsky.social with cryoET of Env in VLPs by @thevillalab.bsky.social & team 💪
Would love feedback!
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
N-linked glycans modulate flexibility & MPER epitope exposure #glycotime
Huge effort by @shehata92.bsky.social @lcasalino88.bsky.social with cryoET of Env in VLPs by @thevillalab.bsky.social & team 💪
Would love feedback!
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Collab w/ @adaozlemdemir.bsky.social & Aihara, Herzik, & Harris labs
pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/...
Collab w/ @adaozlemdemir.bsky.social & Aihara, Herzik, & Harris labs
pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/...
@rommieamaro.bsky.social
pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/...
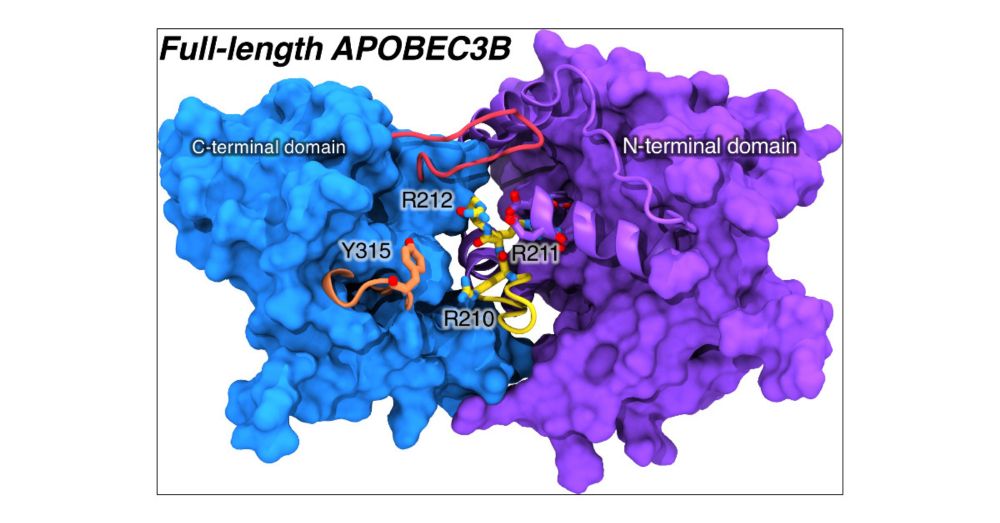
@rommieamaro.bsky.social
pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/...
Working with MDAnalysis and @westpasoftware.bsky.social on a GSoC 2025 project may be just for you! For details, read our blog post: www.mdanalysis.org/2025/02/28/g....
Pre-proposal deadline: Mar 21

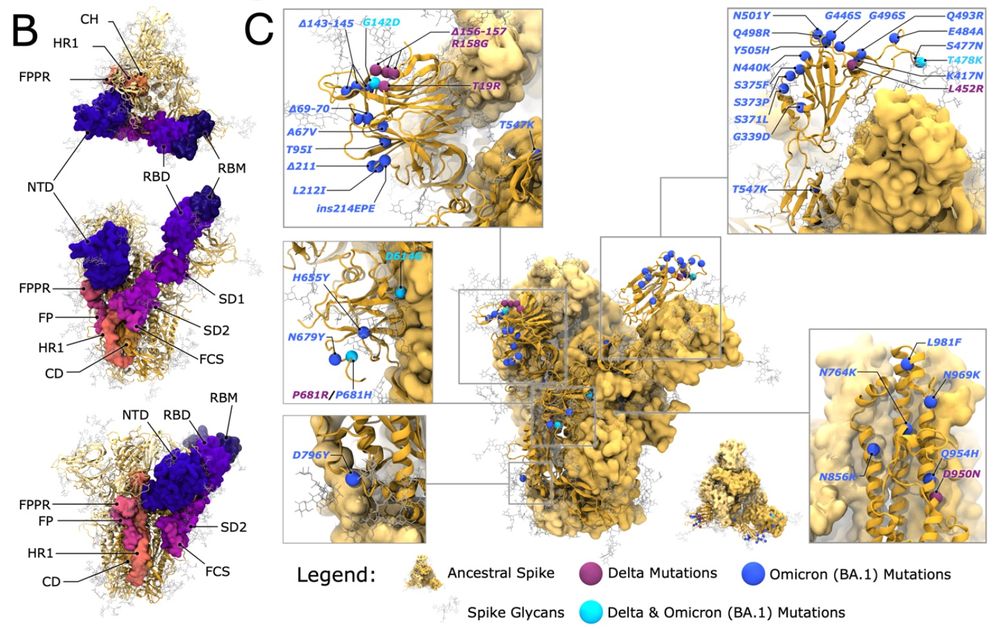
📣 NEW BIORXIV ALERT!! 🚨
Using WE MD, linguistic pathway clustering, dynamical network analyses, and HDXMS we reveal a hidden allosteric network within the SARS2 spike S1 domain and predict how the D614G mutation impacts this network!
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

📣 NEW BIORXIV ALERT!! 🚨
Using WE MD, linguistic pathway clustering, dynamical network analyses, and HDXMS we reveal a hidden allosteric network within the SARS2 spike S1 domain and predict how the D614G mutation impacts this network!
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
@mackevinbraza.bsky.social and others. This work wouldn't have been possible without our collaborators
Dr. Anthony O'Donoghue, @rommieamaro.bsky.social @marius-lemberg.bsky.social and Dr. Kvido Strisovsky
@mackevinbraza.bsky.social and others. This work wouldn't have been possible without our collaborators
Dr. Anthony O'Donoghue, @rommieamaro.bsky.social @marius-lemberg.bsky.social and Dr. Kvido Strisovsky
sciencedirect.com/science/arti...

sciencedirect.com/science/arti...

