The GlobDB is a database of "species dereplicated" microbial genomes, and as of release 226 contains twice the number of species-representative genomes (306,260) than the latest GTDB release.
The GlobDB is a database of "species dereplicated" microbial genomes, and as of release 226 contains twice the number of species-representative genomes (306,260) than the latest GTDB release.
In particular these remarkably chimeric contigs are 😱, if rare....
Improving long read assemblers is definitely the space to be in when it comes to the future of metagenomics, as short reads won't be part of it 😉

In particular these remarkably chimeric contigs are 😱, if rare....
Improving long read assemblers is definitely the space to be in when it comes to the future of metagenomics, as short reads won't be part of it 😉
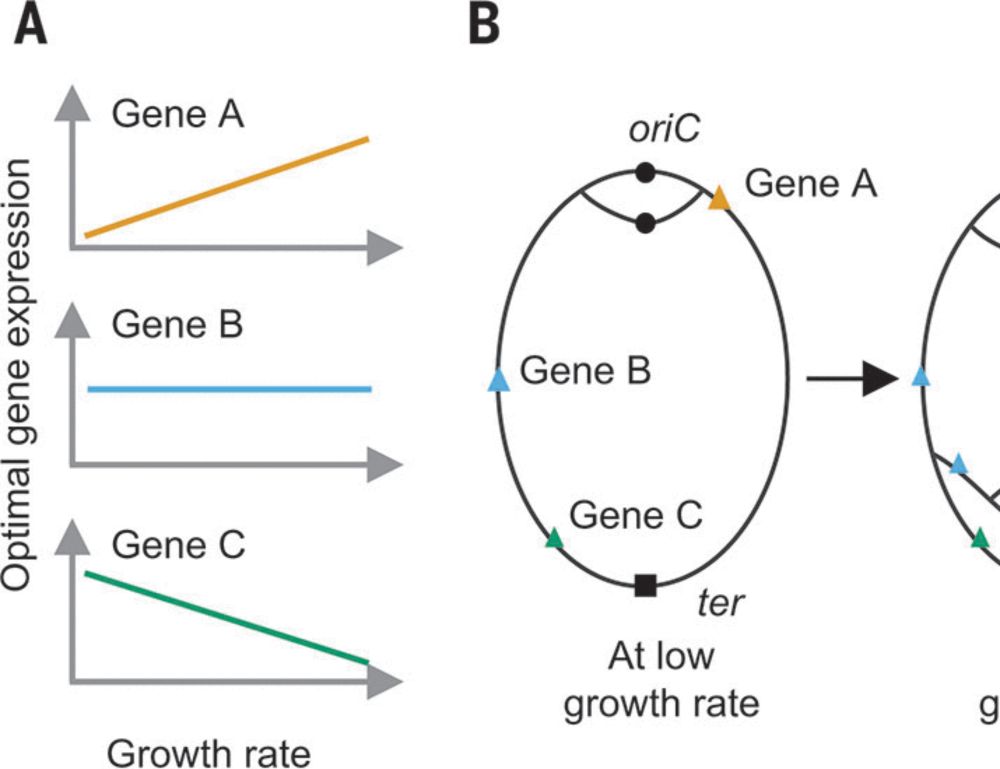
Seeing the mutants emerge & spread is an elegant demo of evolutionary change.

Seeing the mutants emerge & spread is an elegant demo of evolutionary change.
Learn more: scim.ag/40l2z3J
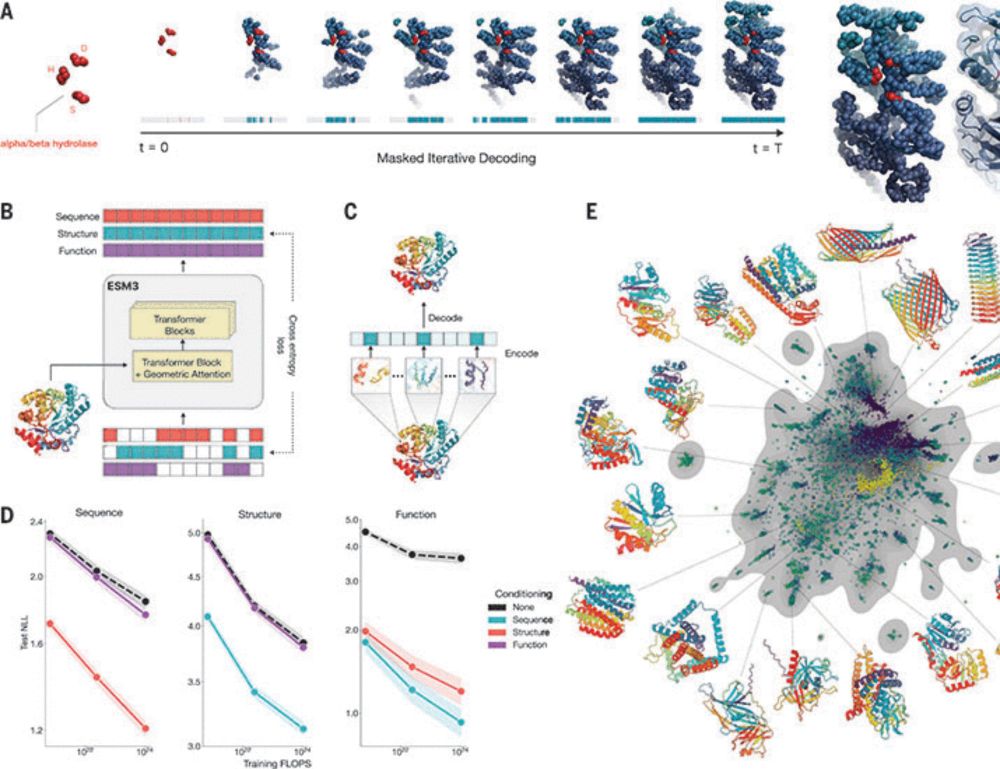
Learn more: scim.ag/40l2z3J
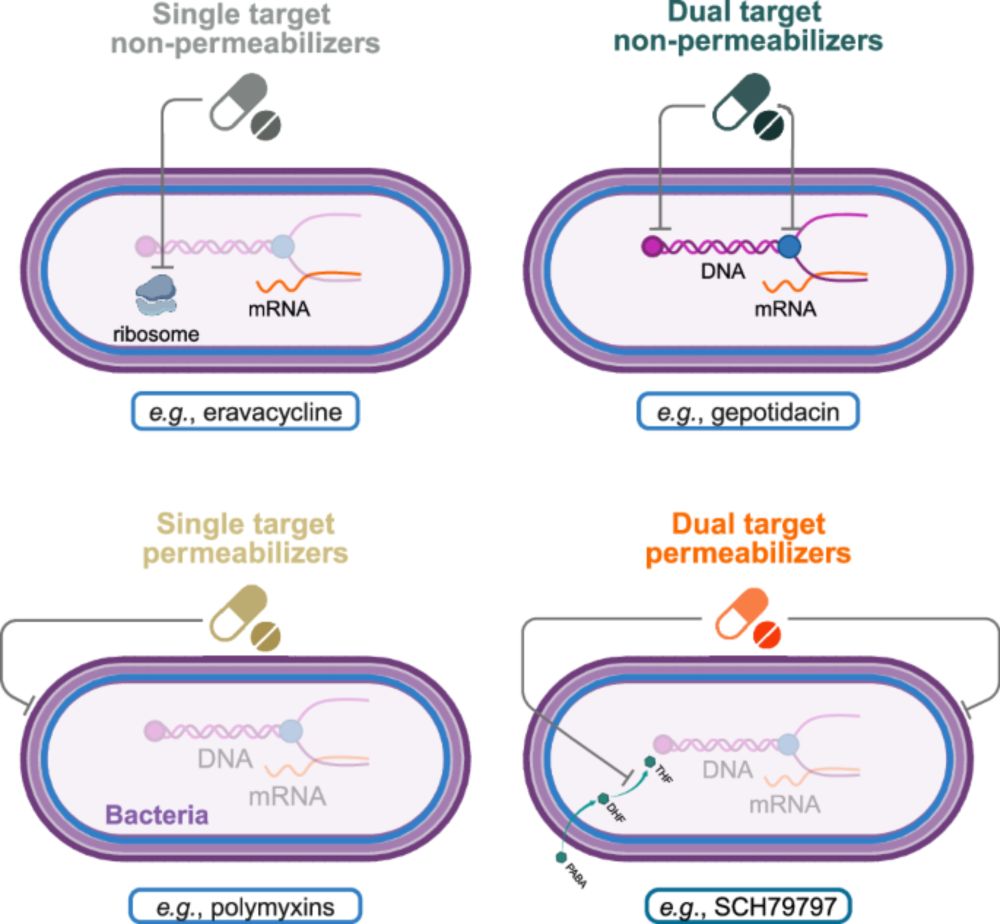
90% of the major classes of antibiotics have been discovered before 1980, only 3 out of 29 after 1980.
Pharma companies have little financial incitation to invest, as new compounds often have to be kept as “last resource” drugs.
Still, new approaches exist.
/end

90% of the major classes of antibiotics have been discovered before 1980, only 3 out of 29 after 1980.
Pharma companies have little financial incitation to invest, as new compounds often have to be kept as “last resource” drugs.
Still, new approaches exist.
/end
Just how many types of antibiotics were discovered during that time?
So, I visualized it myself!

Just how many types of antibiotics were discovered during that time?
So, I visualized it myself!
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
I'm excited to announce Autocycler, my new tool for consensus assembly of long-read bacterial genomes!
It's the successor to Trycycler, designed to be faster and less reliant on user intervention.
Check it out: github.com/rrwick/Autoc...
(1/5)
I'm excited to announce Autocycler, my new tool for consensus assembly of long-read bacterial genomes!
It's the successor to Trycycler, designed to be faster and less reliant on user intervention.
Check it out: github.com/rrwick/Autoc...
(1/5)

