
Ludger Woessmann
@woessmann.bsky.social
Professor of Economics, University of Munich
Director, ifo Center for the Economics of Education
https://sites.google.com/view/woessmann-e
Director, ifo Center for the Economics of Education
https://sites.google.com/view/woessmann-e
4️⃣ Robot 🤖 exposure raises early retirement among manufacturing workers 🧑🏭🏖️
5️⃣ Same for import 🌏 exposure
6️⃣ Opposite for export exposure 🔁
6/9
5️⃣ Same for import 🌏 exposure
6️⃣ Opposite for export exposure 🔁
6/9

November 11, 2025 at 5:59 AM
4️⃣ Robot 🤖 exposure raises early retirement among manufacturing workers 🧑🏭🏖️
5️⃣ Same for import 🌏 exposure
6️⃣ Opposite for export exposure 🔁
6/9
5️⃣ Same for import 🌏 exposure
6️⃣ Opposite for export exposure 🔁
6/9
Results:
1️⃣ Robot 🤖 exposure increases training 🧠—particularly in indirectly affected services 🧑💼
2️⃣ Import 🌏 exposure reduces training—particularly in manufacturing 🏭
3️⃣ Opposite for export exposure 🔁
5/9
1️⃣ Robot 🤖 exposure increases training 🧠—particularly in indirectly affected services 🧑💼
2️⃣ Import 🌏 exposure reduces training—particularly in manufacturing 🏭
3️⃣ Opposite for export exposure 🔁
5/9

November 11, 2025 at 5:59 AM
Results:
1️⃣ Robot 🤖 exposure increases training 🧠—particularly in indirectly affected services 🧑💼
2️⃣ Import 🌏 exposure reduces training—particularly in manufacturing 🏭
3️⃣ Opposite for export exposure 🔁
5/9
1️⃣ Robot 🤖 exposure increases training 🧠—particularly in indirectly affected services 🧑💼
2️⃣ Import 🌏 exposure reduces training—particularly in manufacturing 🏭
3️⃣ Opposite for export exposure 🔁
5/9
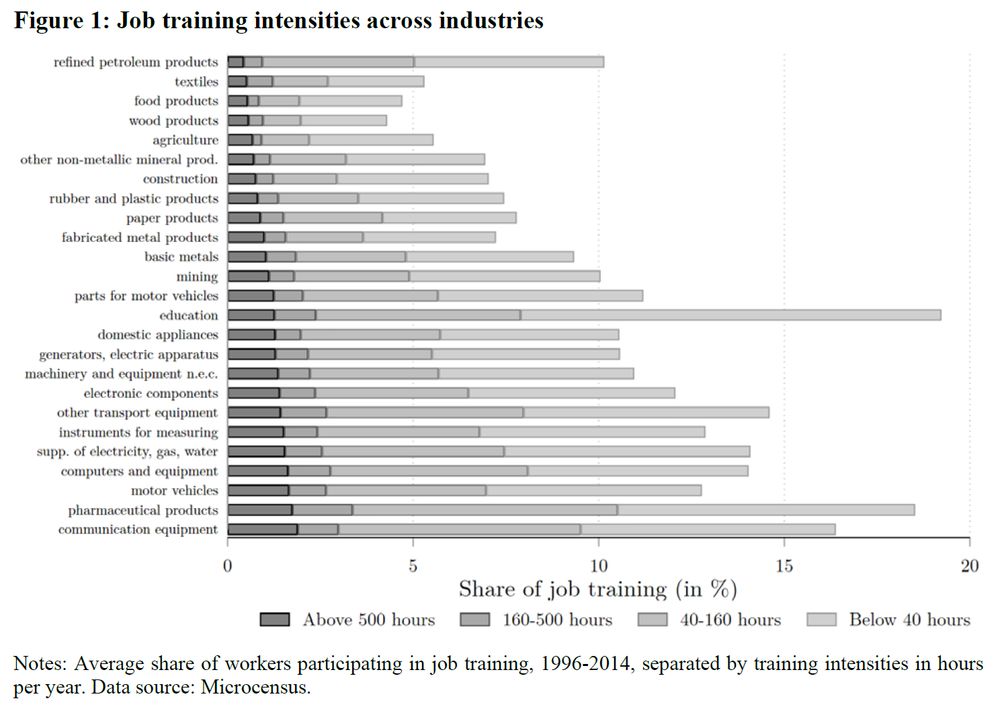
Novel data construction for German local labor markets, 1994-2014:
1️⃣ Training participation from Microcensus 📊
2️⃣ Early retirement from IAB employment records 🗂️
3/9
1️⃣ Training participation from Microcensus 📊
2️⃣ Early retirement from IAB employment records 🗂️
3/9
November 11, 2025 at 5:59 AM
Novel data construction for German local labor markets, 1994-2014:
1️⃣ Training participation from Microcensus 📊
2️⃣ Early retirement from IAB employment records 🗂️
3/9
1️⃣ Training participation from Microcensus 📊
2️⃣ Early retirement from IAB employment records 🗂️
3/9
🆕Working Paper🚨
Training or Retiring? How Labor Markets Adjust to Trade and Technology Shocks📒
w/ A.Bertermann, @dauthecon.bsky.social & @suedekum.bsky.social
🤖 Robots ➡️ ⬆️training & ⬆️early retirement
🌏 Imports ➡️ ⬇️training & ⬆️early r.
🌎 Exports ➡️ ⬆️training & ⬇️e.r.
www.ifo.de/DocDL/cesifo...
🧵1/9
Training or Retiring? How Labor Markets Adjust to Trade and Technology Shocks📒
w/ A.Bertermann, @dauthecon.bsky.social & @suedekum.bsky.social
🤖 Robots ➡️ ⬆️training & ⬆️early retirement
🌏 Imports ➡️ ⬇️training & ⬆️early r.
🌎 Exports ➡️ ⬆️training & ⬇️e.r.
www.ifo.de/DocDL/cesifo...
🧵1/9

November 11, 2025 at 5:59 AM
🆕Working Paper🚨
Training or Retiring? How Labor Markets Adjust to Trade and Technology Shocks📒
w/ A.Bertermann, @dauthecon.bsky.social & @suedekum.bsky.social
🤖 Robots ➡️ ⬆️training & ⬆️early retirement
🌏 Imports ➡️ ⬇️training & ⬆️early r.
🌎 Exports ➡️ ⬆️training & ⬇️e.r.
www.ifo.de/DocDL/cesifo...
🧵1/9
Training or Retiring? How Labor Markets Adjust to Trade and Technology Shocks📒
w/ A.Bertermann, @dauthecon.bsky.social & @suedekum.bsky.social
🤖 Robots ➡️ ⬆️training & ⬆️early retirement
🌏 Imports ➡️ ⬇️training & ⬆️early r.
🌎 Exports ➡️ ⬆️training & ⬇️e.r.
www.ifo.de/DocDL/cesifo...
🧵1/9
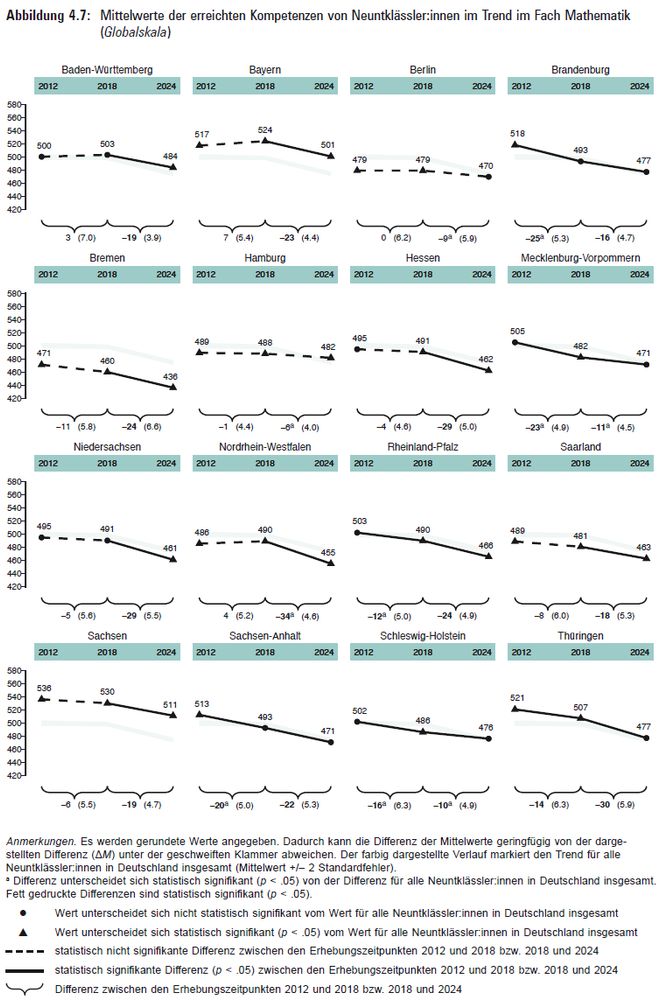
Alle sozio-demographischen Gruppen betroffen.
Rückgang in allen Bundesländern. (Lediglich Hamburg (in allen Fächern) nicht signifikant.) Z.B. Mathe:
NRW -34⬇️
Bayern -23⬇️
2/3
Rückgang in allen Bundesländern. (Lediglich Hamburg (in allen Fächern) nicht signifikant.) Z.B. Mathe:
NRW -34⬇️
Bayern -23⬇️
2/3
October 17, 2025 at 5:32 AM
Alle sozio-demographischen Gruppen betroffen.
Rückgang in allen Bundesländern. (Lediglich Hamburg (in allen Fächern) nicht signifikant.) Z.B. Mathe:
NRW -34⬇️
Bayern -23⬇️
2/3
Rückgang in allen Bundesländern. (Lediglich Hamburg (in allen Fächern) nicht signifikant.) Z.B. Mathe:
NRW -34⬇️
Bayern -23⬇️
2/3
⚡9.-Klässler:innen 2024 vs. 2018:
Mathe -24⬇️
Bio -24⬇️
Chemie -24⬇️
Physik -23⬇️
Die neuen Ergebnisse des IQB-Bildungstrends.
Ganz grob gesprochen: 9.-Klässler:innen liegen heute etwa auf Niveau der 8.-Klässler:innen noch vor 6 Jahren.
1/3
Mathe -24⬇️
Bio -24⬇️
Chemie -24⬇️
Physik -23⬇️
Die neuen Ergebnisse des IQB-Bildungstrends.
Ganz grob gesprochen: 9.-Klässler:innen liegen heute etwa auf Niveau der 8.-Klässler:innen noch vor 6 Jahren.
1/3

October 17, 2025 at 5:32 AM
⚡9.-Klässler:innen 2024 vs. 2018:
Mathe -24⬇️
Bio -24⬇️
Chemie -24⬇️
Physik -23⬇️
Die neuen Ergebnisse des IQB-Bildungstrends.
Ganz grob gesprochen: 9.-Klässler:innen liegen heute etwa auf Niveau der 8.-Klässler:innen noch vor 6 Jahren.
1/3
Mathe -24⬇️
Bio -24⬇️
Chemie -24⬇️
Physik -23⬇️
Die neuen Ergebnisse des IQB-Bildungstrends.
Ganz grob gesprochen: 9.-Klässler:innen liegen heute etwa auf Niveau der 8.-Klässler:innen noch vor 6 Jahren.
1/3
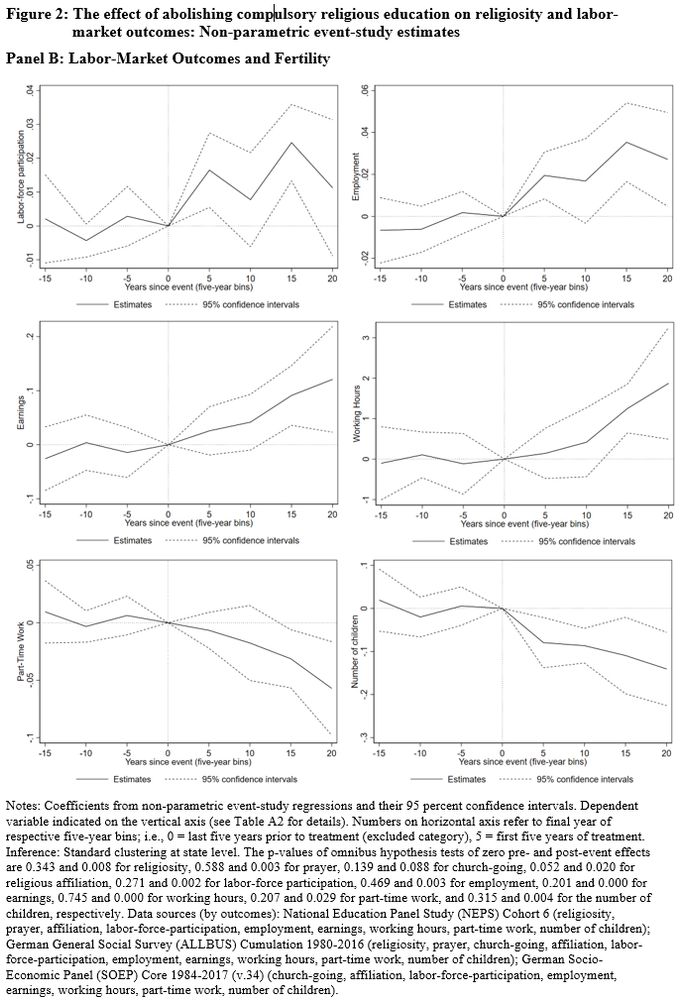
Effects beyond religion:
🧑🏭 Higher labor-market participation + earnings (consistent with shift towards worldly norms + economic activities) 🌎
👨👩👧👦 Reduced fertility
By contrast, no effects on ethical + political values or non-religious school outcomes
5/6
🧑🏭 Higher labor-market participation + earnings (consistent with shift towards worldly norms + economic activities) 🌎
👨👩👧👦 Reduced fertility
By contrast, no effects on ethical + political values or non-religious school outcomes
5/6



October 10, 2025 at 5:01 AM
Effects beyond religion:
🧑🏭 Higher labor-market participation + earnings (consistent with shift towards worldly norms + economic activities) 🌎
👨👩👧👦 Reduced fertility
By contrast, no effects on ethical + political values or non-religious school outcomes
5/6
🧑🏭 Higher labor-market participation + earnings (consistent with shift towards worldly norms + economic activities) 🌎
👨👩👧👦 Reduced fertility
By contrast, no effects on ethical + political values or non-religious school outcomes
5/6
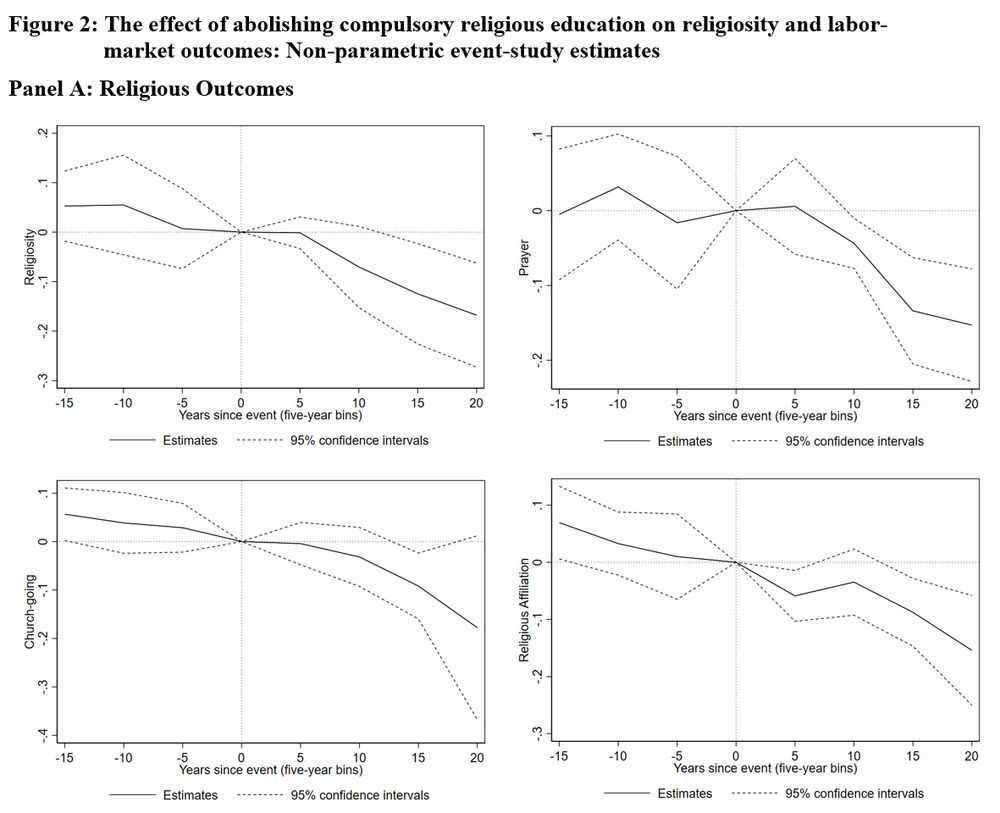
👉 Reform abolishing compulsory religious education significantly reduced religiosity of affected students in adulthood
Similar reductions in specific religious actions:
1️⃣ personal act of prayer
2️⃣ public act of church-going
3️⃣ formal (+costly) act of church membership
4/6
Similar reductions in specific religious actions:
1️⃣ personal act of prayer
2️⃣ public act of church-going
3️⃣ formal (+costly) act of church membership
4/6


October 10, 2025 at 5:01 AM
👉 Reform abolishing compulsory religious education significantly reduced religiosity of affected students in adulthood
Similar reductions in specific religious actions:
1️⃣ personal act of prayer
2️⃣ public act of church-going
3️⃣ formal (+costly) act of church membership
4/6
Similar reductions in specific religious actions:
1️⃣ personal act of prayer
2️⃣ public act of church-going
3️⃣ formal (+costly) act of church membership
4/6
Unique German setting:
🏫 Religious education was compulsory in state schools: 1000 hours over school career (>4x physics)
Abolished in staggered reforms across states 1972-2004
Replaced by option to choose between religious education + non-denominational “ethics”
2/6
🏫 Religious education was compulsory in state schools: 1000 hours over school career (>4x physics)
Abolished in staggered reforms across states 1972-2004
Replaced by option to choose between religious education + non-denominational “ethics”
2/6

October 10, 2025 at 5:01 AM
Unique German setting:
🏫 Religious education was compulsory in state schools: 1000 hours over school career (>4x physics)
Abolished in staggered reforms across states 1972-2004
Replaced by option to choose between religious education + non-denominational “ethics”
2/6
🏫 Religious education was compulsory in state schools: 1000 hours over school career (>4x physics)
Abolished in staggered reforms across states 1972-2004
Replaced by option to choose between religious education + non-denominational “ethics”
2/6
🚨 Now out in Journal of Human Resources:
⛪️ Can Schools Change Religious Attitudes?
Evidence from German State Reforms of Compulsory Religious Education
w/ @benjaminarold.bsky.social & Larissa Zierow
👉 Religious education in school affects adult lives
🔗 jhr.uwpress.org/content/earl...
A 🧵 1/6
⛪️ Can Schools Change Religious Attitudes?
Evidence from German State Reforms of Compulsory Religious Education
w/ @benjaminarold.bsky.social & Larissa Zierow
👉 Religious education in school affects adult lives
🔗 jhr.uwpress.org/content/earl...
A 🧵 1/6

October 10, 2025 at 5:01 AM
🚨 Now out in Journal of Human Resources:
⛪️ Can Schools Change Religious Attitudes?
Evidence from German State Reforms of Compulsory Religious Education
w/ @benjaminarold.bsky.social & Larissa Zierow
👉 Religious education in school affects adult lives
🔗 jhr.uwpress.org/content/earl...
A 🧵 1/6
⛪️ Can Schools Change Religious Attitudes?
Evidence from German State Reforms of Compulsory Religious Education
w/ @benjaminarold.bsky.social & Larissa Zierow
👉 Religious education in school affects adult lives
🔗 jhr.uwpress.org/content/earl...
A 🧵 1/6
📢 Call for papers:
🚀 4th CESifo Junior Workshop on the Economics of Education 🤩
30-31 March 2026, Munich
Keynote: Michela Carlana (Harvard)
PhD students & early postdocs, please apply!
www.ifo.de/en/cesifo/ev...
Deadline: 11 Jan 2026
@caterinapavese.bsky.social @mtotarelli.bsky.social
🚀 4th CESifo Junior Workshop on the Economics of Education 🤩
30-31 March 2026, Munich
Keynote: Michela Carlana (Harvard)
PhD students & early postdocs, please apply!
www.ifo.de/en/cesifo/ev...
Deadline: 11 Jan 2026
@caterinapavese.bsky.social @mtotarelli.bsky.social

October 7, 2025 at 8:05 AM
📢 Call for papers:
🚀 4th CESifo Junior Workshop on the Economics of Education 🤩
30-31 March 2026, Munich
Keynote: Michela Carlana (Harvard)
PhD students & early postdocs, please apply!
www.ifo.de/en/cesifo/ev...
Deadline: 11 Jan 2026
@caterinapavese.bsky.social @mtotarelli.bsky.social
🚀 4th CESifo Junior Workshop on the Economics of Education 🤩
30-31 March 2026, Munich
Keynote: Michela Carlana (Harvard)
PhD students & early postdocs, please apply!
www.ifo.de/en/cesifo/ev...
Deadline: 11 Jan 2026
@caterinapavese.bsky.social @mtotarelli.bsky.social
In Zeiten von ständigen Transformationen sollten wir Bildung als Befähigung zu stetigem Wandel verstehen.
Mein Einleitungsvortrag in das Bildungspolitische Forum 2025 des @leibnizbildung.bsky.social
Livestream: www.youtube.com/@Leibniz_bil...
www.leibniz-bildung.de/veranstaltun...
Mein Einleitungsvortrag in das Bildungspolitische Forum 2025 des @leibnizbildung.bsky.social
Livestream: www.youtube.com/@Leibniz_bil...
www.leibniz-bildung.de/veranstaltun...

October 1, 2025 at 9:03 AM
In Zeiten von ständigen Transformationen sollten wir Bildung als Befähigung zu stetigem Wandel verstehen.
Mein Einleitungsvortrag in das Bildungspolitische Forum 2025 des @leibnizbildung.bsky.social
Livestream: www.youtube.com/@Leibniz_bil...
www.leibniz-bildung.de/veranstaltun...
Mein Einleitungsvortrag in das Bildungspolitische Forum 2025 des @leibnizbildung.bsky.social
Livestream: www.youtube.com/@Leibniz_bil...
www.leibniz-bildung.de/veranstaltun...
66% der Jugendlichen und 46% der Erwachsenen sind dafür, dass der Umgang mit KI im Unterricht gelehrt wird.
7/7
7/7
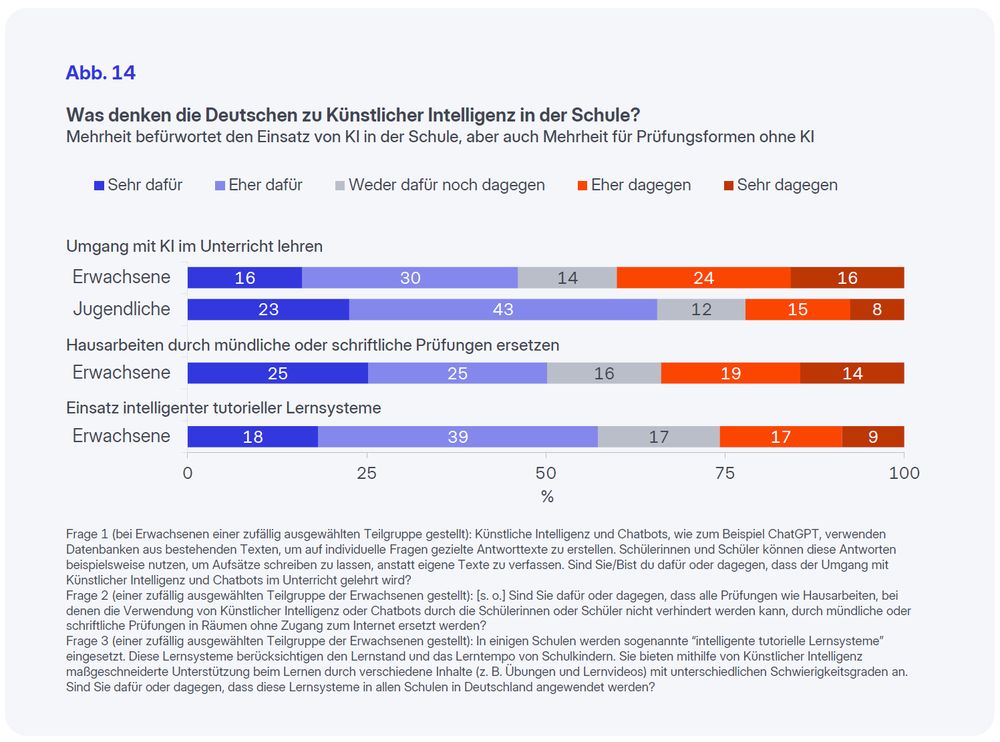
September 9, 2025 at 8:00 AM
66% der Jugendlichen und 46% der Erwachsenen sind dafür, dass der Umgang mit KI im Unterricht gelehrt wird.
7/7
7/7
82% der Jugendlichen und 50% der Erwachsenen nutzen Künstliche Intelligenz für schulische bzw. berufliche Zwecke.
6/7
6/7

September 9, 2025 at 8:00 AM
82% der Jugendlichen und 50% der Erwachsenen nutzen Künstliche Intelligenz für schulische bzw. berufliche Zwecke.
6/7
6/7
59% der Erwachsenen befürworten ein Handyverbot an Grundschulen in der Pause und 64% im Unterricht, an weiterführenden Schulen sind es 49% bzw. 63%.
Unter den Jugendlichen sind die Anteile nur unwesentlich geringer.
5/7
Unter den Jugendlichen sind die Anteile nur unwesentlich geringer.
5/7
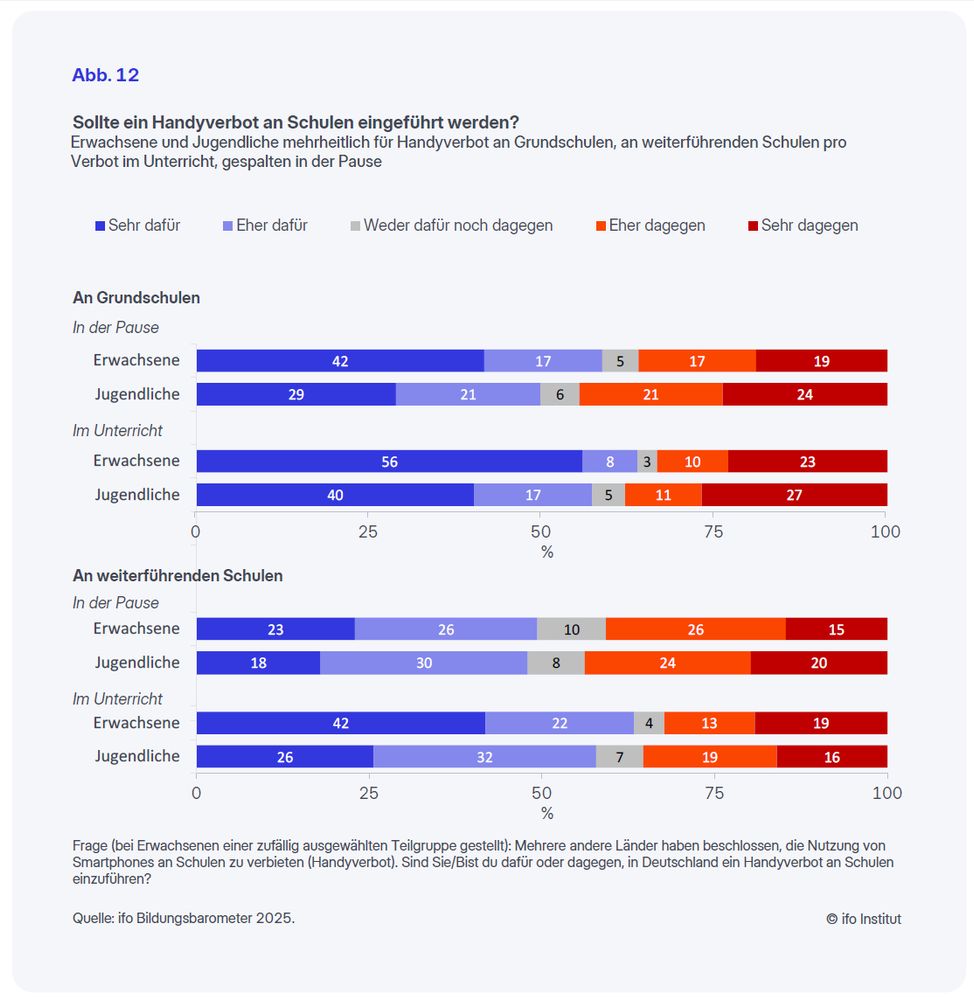
September 9, 2025 at 8:00 AM
59% der Erwachsenen befürworten ein Handyverbot an Grundschulen in der Pause und 64% im Unterricht, an weiterführenden Schulen sind es 49% bzw. 63%.
Unter den Jugendlichen sind die Anteile nur unwesentlich geringer.
5/7
Unter den Jugendlichen sind die Anteile nur unwesentlich geringer.
5/7
Deutliche Mehrheiten beider Gruppen denken, dass sich soziale Medien negativ auf die psychische und körperliche Gesundheit von Kindern und Jugendlichen, ihre Aufmerksamkeit und ihre schulischen Leistungen auswirken.
4/7
4/7
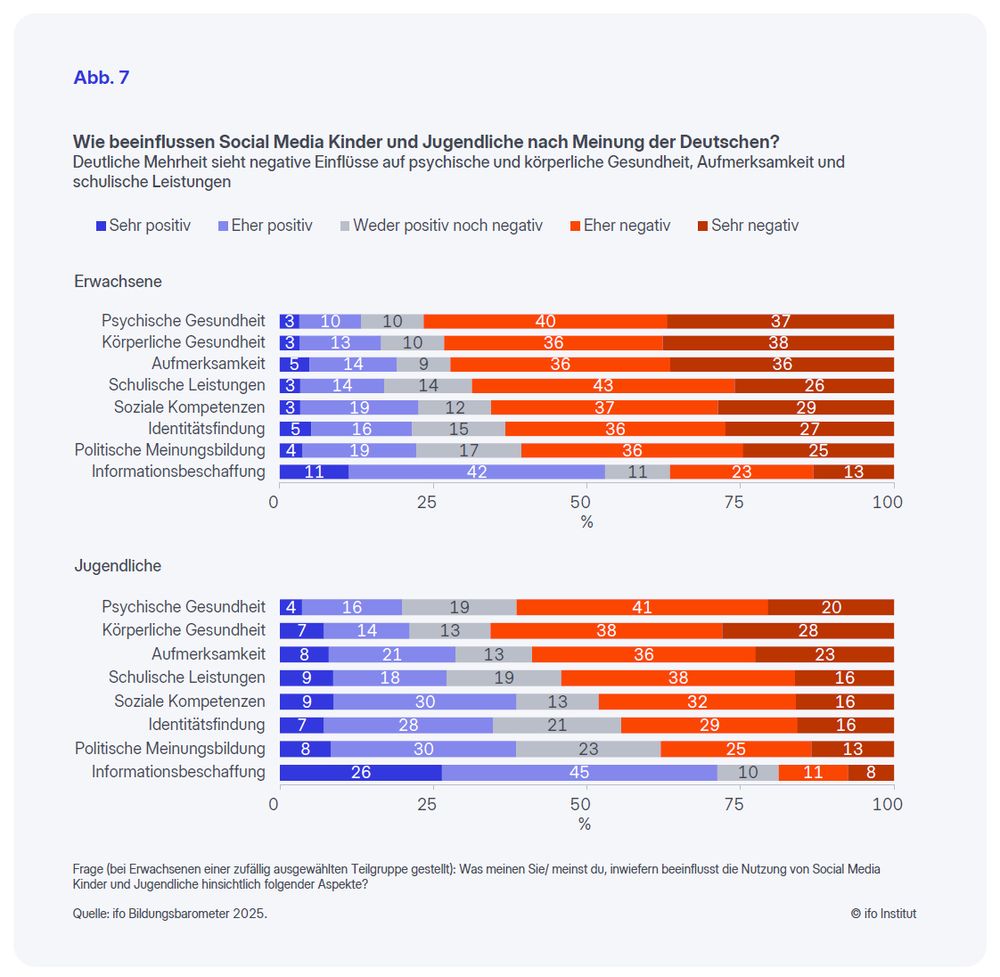
September 9, 2025 at 8:00 AM
Deutliche Mehrheiten beider Gruppen denken, dass sich soziale Medien negativ auf die psychische und körperliche Gesundheit von Kindern und Jugendlichen, ihre Aufmerksamkeit und ihre schulischen Leistungen auswirken.
4/7
4/7
Dabei würden 47% der Erwachsenen lieber in einer Welt ohne soziale Medien leben.
Bei den Jugendlichen leben hingegen 68% lieber in einer Welt mit sozialen Medien.
3/7
Bei den Jugendlichen leben hingegen 68% lieber in einer Welt mit sozialen Medien.
3/7

September 9, 2025 at 8:00 AM
Dabei würden 47% der Erwachsenen lieber in einer Welt ohne soziale Medien leben.
Bei den Jugendlichen leben hingegen 68% lieber in einer Welt mit sozialen Medien.
3/7
Bei den Jugendlichen leben hingegen 68% lieber in einer Welt mit sozialen Medien.
3/7
78% der Jugendlichen und 58% der Erwachsenen verbringen unter der Woche täglich mehr als eine Stunde mit sozialen Medien.
2/7
2/7

September 9, 2025 at 8:00 AM
78% der Jugendlichen und 58% der Erwachsenen verbringen unter der Woche täglich mehr als eine Stunde mit sozialen Medien.
2/7
2/7
🚨 85% (!) der Erwachsenen sind für ein Mindestalter von 16 Jahren für Social Media.
Selbst unter den Jugendlichen ist eine relative Mehrheit dafür.
👉 Dies und mehr im neuen ifo Bildungsbarometer 2025:
www.ifo.de/fakten/2025-...
1/7
Selbst unter den Jugendlichen ist eine relative Mehrheit dafür.
👉 Dies und mehr im neuen ifo Bildungsbarometer 2025:
www.ifo.de/fakten/2025-...
1/7

September 9, 2025 at 8:00 AM
🚨 85% (!) der Erwachsenen sind für ein Mindestalter von 16 Jahren für Social Media.
Selbst unter den Jugendlichen ist eine relative Mehrheit dafür.
👉 Dies und mehr im neuen ifo Bildungsbarometer 2025:
www.ifo.de/fakten/2025-...
1/7
Selbst unter den Jugendlichen ist eine relative Mehrheit dafür.
👉 Dies und mehr im neuen ifo Bildungsbarometer 2025:
www.ifo.de/fakten/2025-...
1/7
📢Our CESifo Conference on Economics of Education is about to start!🤩
This will be so exciting!!!🥳
🔗https://www.ifo.de/en/cesifo/event/2025-09-05/cesifo-area-conference-economics-education-2025
@raffasadun.bsky.social @sandramcnally.bsky.social @christinafelfe.bsky.social @singhabhi.bsky.social …
This will be so exciting!!!🥳
🔗https://www.ifo.de/en/cesifo/event/2025-09-05/cesifo-area-conference-economics-education-2025
@raffasadun.bsky.social @sandramcnally.bsky.social @christinafelfe.bsky.social @singhabhi.bsky.social …



September 5, 2025 at 5:48 AM
📢Our CESifo Conference on Economics of Education is about to start!🤩
This will be so exciting!!!🥳
🔗https://www.ifo.de/en/cesifo/event/2025-09-05/cesifo-area-conference-economics-education-2025
@raffasadun.bsky.social @sandramcnally.bsky.social @christinafelfe.bsky.social @singhabhi.bsky.social …
This will be so exciting!!!🥳
🔗https://www.ifo.de/en/cesifo/event/2025-09-05/cesifo-area-conference-economics-education-2025
@raffasadun.bsky.social @sandramcnally.bsky.social @christinafelfe.bsky.social @singhabhi.bsky.social …
"Skills and Earnings: A Multidimensional Perspective on Human Capital"
Final version now out in Vol. 17 of the Annual Review of Economics (Open Access):
www.annualreviews.org/content/jour...
Final version now out in Vol. 17 of the Annual Review of Economics (Open Access):
www.annualreviews.org/content/jour...

September 1, 2025 at 7:05 AM
"Skills and Earnings: A Multidimensional Perspective on Human Capital"
Final version now out in Vol. 17 of the Annual Review of Economics (Open Access):
www.annualreviews.org/content/jour...
Final version now out in Vol. 17 of the Annual Review of Economics (Open Access):
www.annualreviews.org/content/jour...
No bias from differential selectivity of test taking in EPI & TOEFL:
a) Results in representative (but self-rated) AES as large as non-representative (but standardized-test) EPI
b) Results robust to controlling for number of TOEFL test takers
10/12
a) Results in representative (but self-rated) AES as large as non-representative (but standardized-test) EPI
b) Results robust to controlling for number of TOEFL test takers
10/12

July 7, 2025 at 6:33 AM
No bias from differential selectivity of test taking in EPI & TOEFL:
a) Results in representative (but self-rated) AES as large as non-representative (but standardized-test) EPI
b) Results robust to controlling for number of TOEFL test takers
10/12
a) Results in representative (but self-rated) AES as large as non-representative (but standardized-test) EPI
b) Results robust to controlling for number of TOEFL test takers
10/12
Placebo test: no effect of subtitling on native-language reading
Effect is robust to accounting for
▶️ similarity of local languages with English
▶️ size of country populations & language communities
▶️ starting age & instruction time of foreign-language teaching in schools
9/12
Effect is robust to accounting for
▶️ similarity of local languages with English
▶️ size of country populations & language communities
▶️ starting age & instruction time of foreign-language teaching in schools
9/12
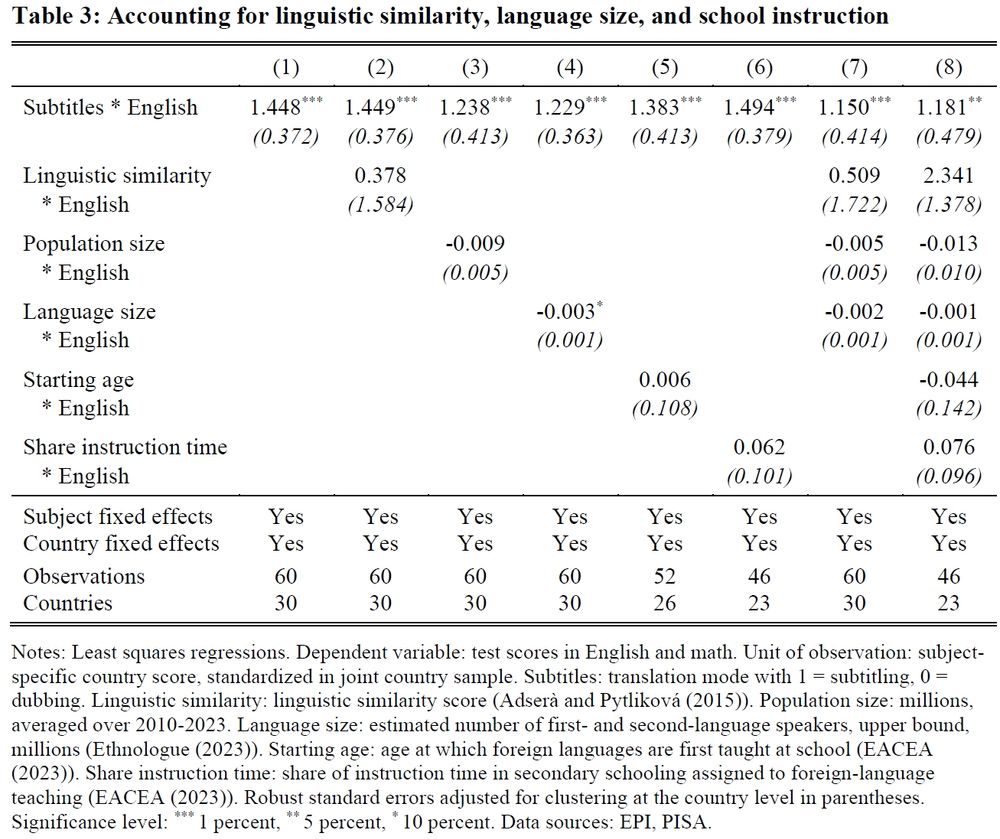
July 7, 2025 at 6:33 AM
Placebo test: no effect of subtitling on native-language reading
Effect is robust to accounting for
▶️ similarity of local languages with English
▶️ size of country populations & language communities
▶️ starting age & instruction time of foreign-language teaching in schools
9/12
Effect is robust to accounting for
▶️ similarity of local languages with English
▶️ size of country populations & language communities
▶️ starting age & instruction time of foreign-language teaching in schools
9/12
Effect is larger for listening & speaking skills 🗣️ than for reading 📚
➡️ Consistent with learning from oral TV transmission
Effect strongest in youngest age group (16-34) 👧 but also large for those aged 35-55 & 56-75 👵
8/12
➡️ Consistent with learning from oral TV transmission
Effect strongest in youngest age group (16-34) 👧 but also large for those aged 35-55 & 56-75 👵
8/12

July 7, 2025 at 6:33 AM
Effect is larger for listening & speaking skills 🗣️ than for reading 📚
➡️ Consistent with learning from oral TV transmission
Effect strongest in youngest age group (16-34) 👧 but also large for those aged 35-55 & 56-75 👵
8/12
➡️ Consistent with learning from oral TV transmission
Effect strongest in youngest age group (16-34) 👧 but also large for those aged 35-55 & 56-75 👵
8/12


