PCBP2גורם להתעגלות של הגנום למטרת תרגום ע"י קישור ל – 3’UTR ו – 5’UTR
miR-122 מעלה את רמת הקישור של5’UTR בגנום HCV לפולימראז הנגיפי, ובכך תורם לרפליקציה
קישור miR-122 מתחרה ומפחית את הקישור של PCBP2 ל – S2, ובכך מונע תרגום ותומך ברפליקציה

PCBP2גורם להתעגלות של הגנום למטרת תרגום ע"י קישור ל – 3’UTR ו – 5’UTR
miR-122 מעלה את רמת הקישור של5’UTR בגנום HCV לפולימראז הנגיפי, ובכך תורם לרפליקציה
קישור miR-122 מתחרה ומפחית את הקישור של PCBP2 ל – S2, ובכך מונע תרגום ותומך ברפליקציה
במאמר נבדק הקישור של המולקולות ל-HCV: miR-122 נקשר בשני אתרים – S1 ו-S2, ו-PCBP2 נקשר לאתר בתוך S2. מכאן נובע שבין miR-122 ו-PCBP2 יש תחרות על הקישור לגנום הנגיפי.

במאמר נבדק הקישור של המולקולות ל-HCV: miR-122 נקשר בשני אתרים – S1 ו-S2, ו-PCBP2 נקשר לאתר בתוך S2. מכאן נובע שבין miR-122 ו-PCBP2 יש תחרות על הקישור לגנום הנגיפי.
השאלה שנותרה בעינה - האם הנגיף משפיע על הריכוזים הפיזיולוגיים של miR-122 ו-PCBP2?


השאלה שנותרה בעינה - האם הנגיף משפיע על הריכוזים הפיזיולוגיים של miR-122 ו-PCBP2?
PCBP2גורם להתעגלות של הגנום למטרת תרגום ע"י קישור ל – 3’UTR ו – 5’UTR
miR-122 מעלה את רמת הקישור של5’UTR בגנום HCV לפולימראז הנגיפי, ובכך תורם לרפליקציה
קישור miR-122 מתחרה ומפחית את הקישור של PCBP2 ל – S2, ובכך מונע תרגום ותומך ברפליקציה

PCBP2גורם להתעגלות של הגנום למטרת תרגום ע"י קישור ל – 3’UTR ו – 5’UTR
miR-122 מעלה את רמת הקישור של5’UTR בגנום HCV לפולימראז הנגיפי, ובכך תורם לרפליקציה
קישור miR-122 מתחרה ומפחית את הקישור של PCBP2 ל – S2, ובכך מונע תרגום ותומך ברפליקציה
במאמר נבדק הקישור של המולקולות ל-HCV: miR-122 נקשר בשני אתרים – S1 ו-S2, ו-PCBP2 נקשר לאתר בתוך S2. מכאן נובע שבין miR-122 ו-PCBP2 יש תחרות על הקישור לגנום הנגיפי.

במאמר נבדק הקישור של המולקולות ל-HCV: miR-122 נקשר בשני אתרים – S1 ו-S2, ו-PCBP2 נקשר לאתר בתוך S2. מכאן נובע שבין miR-122 ו-PCBP2 יש תחרות על הקישור לגנום הנגיפי.
עד היום, מנגנון המעבר בין תרגום לרפליקציה ב - HCV לא ידוע. המחקר בא לבחון את המנגנון ולצאת עם תובנות חדשות לגבי הנגיף.


עד היום, מנגנון המעבר בין תרגום לרפליקציה ב - HCV לא ידוע. המחקר בא לבחון את המנגנון ולצאת עם תובנות חדשות לגבי הנגיף.





זה מה שהוביל חוקרים לאסוף אלפי דגימות מאיילים לבנים ברחבי ארה"ב ולבדוק את נוכחות הנגיף SARS-CoV-2 בהן. באוכלוסייה זו התגלו 34 תתי-שושלות גנטיות של הנגיף, חלקן נדירות או בלתי צפויות.

זה מה שהוביל חוקרים לאסוף אלפי דגימות מאיילים לבנים ברחבי ארה"ב ולבדוק את נוכחות הנגיף SARS-CoV-2 בהן. באוכלוסייה זו התגלו 34 תתי-שושלות גנטיות של הנגיף, חלקן נדירות או בלתי צפויות.
This highlights the potential to target latent viral genome for therapy and finding a cure
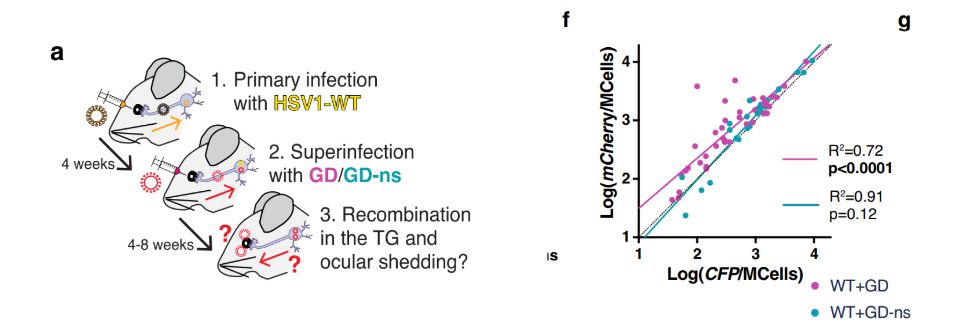
This highlights the potential to target latent viral genome for therapy and finding a cure
Infection with WT+GD was spread widely in neuronal tissues
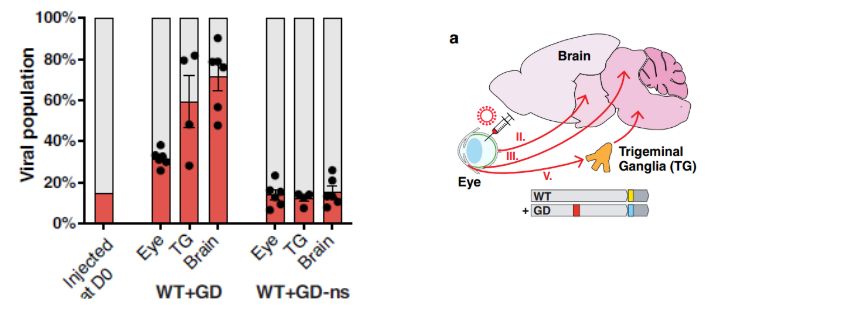
Infection with WT+GD was spread widely in neuronal tissues
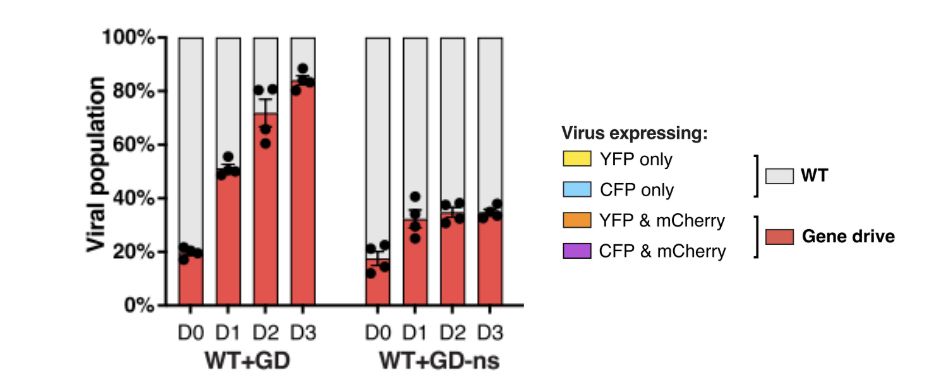
Gene Drive(GD), a self propagating gene-editing technique via Cas9 mediated homologous recombination inserts the GD with red fluorescent (mCherry) into HSV-1 genome. Specific and non-specific (GD-ns) gRNA were tested.

Gene Drive(GD), a self propagating gene-editing technique via Cas9 mediated homologous recombination inserts the GD with red fluorescent (mCherry) into HSV-1 genome. Specific and non-specific (GD-ns) gRNA were tested.

