
Mingyuan "Merlin" Li
@supmerlin.bsky.social
PhD candidate at Johns Hopkins | Alexis Battle lab | Computational Biology | Machine Learning | He/Him
Heading to Minneapolis next week to share this work at STATGEN2025!

May 17, 2025 at 9:23 PM
Heading to Minneapolis next week to share this work at STATGEN2025!
This is such an exciting project! Huge thanks to Wenhe Lin, @jmpopp.bsky.social, @radster95.bsky.social, Olivia Allen, Jonathan Burnett, and to @alexisbattle.bsky.social, @ygilad.bsky.social, and Matthew Stephens for their mentorships! Check out our preprint for more!
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

May 5, 2025 at 7:07 PM
This is such an exciting project! Huge thanks to Wenhe Lin, @jmpopp.bsky.social, @radster95.bsky.social, Olivia Allen, Jonathan Burnett, and to @alexisbattle.bsky.social, @ygilad.bsky.social, and Matthew Stephens for their mentorships! Check out our preprint for more!
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
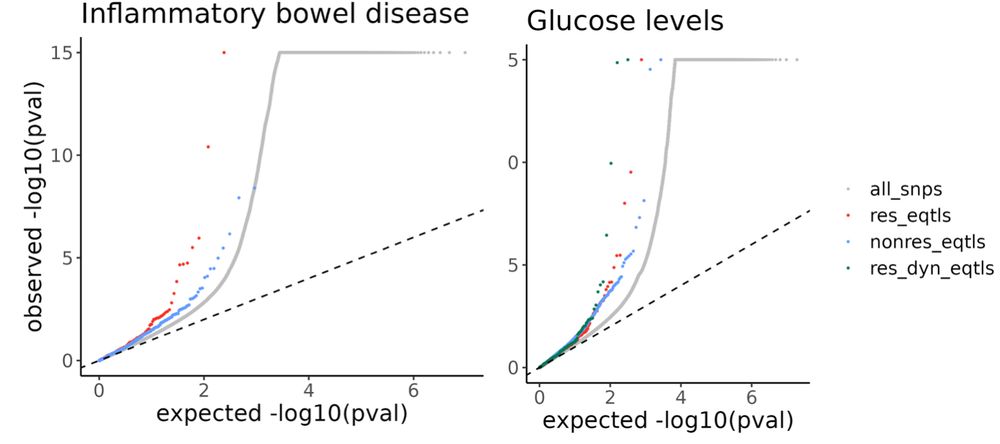
8/n We found that incorporating more context-specificity enabled us to identify regulatory effects that may enhance the functional understanding of GWAS associations. These effects would have been missed had we only explored a single tissue type or not accounted for GxE.
May 5, 2025 at 7:07 PM
8/n We found that incorporating more context-specificity enabled us to identify regulatory effects that may enhance the functional understanding of GWAS associations. These effects would have been missed had we only explored a single tissue type or not accounted for GxE.
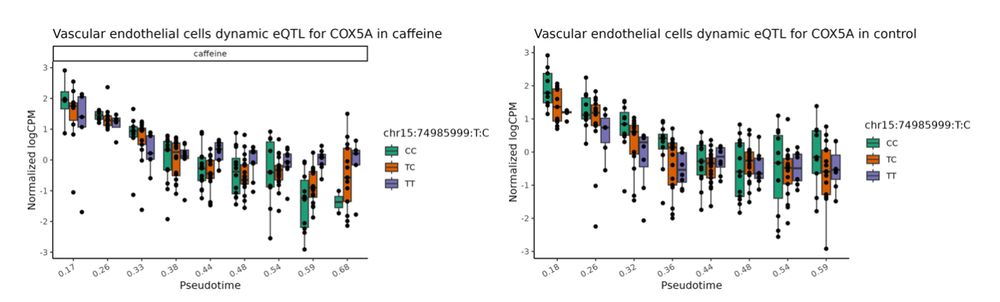
7/n We also mapped dynamic response eQTLs that vary their regulatory effects throughout cellular differentiation. Example: A caffeine-response dynamic eQTL affecting COX5A emerged exclusively in late-stage vascular differentiation. ☕️🩸✨
May 5, 2025 at 7:07 PM
7/n We also mapped dynamic response eQTLs that vary their regulatory effects throughout cellular differentiation. Example: A caffeine-response dynamic eQTL affecting COX5A emerged exclusively in late-stage vascular differentiation. ☕️🩸✨
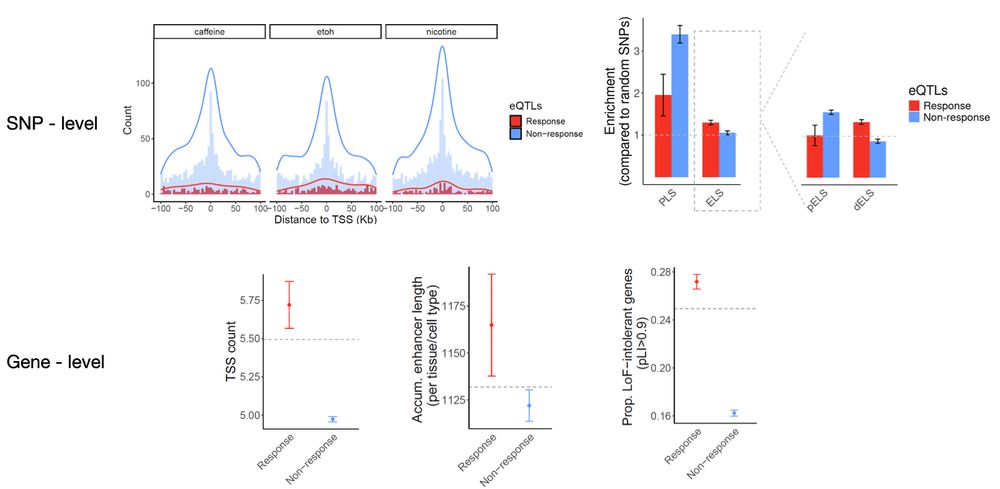
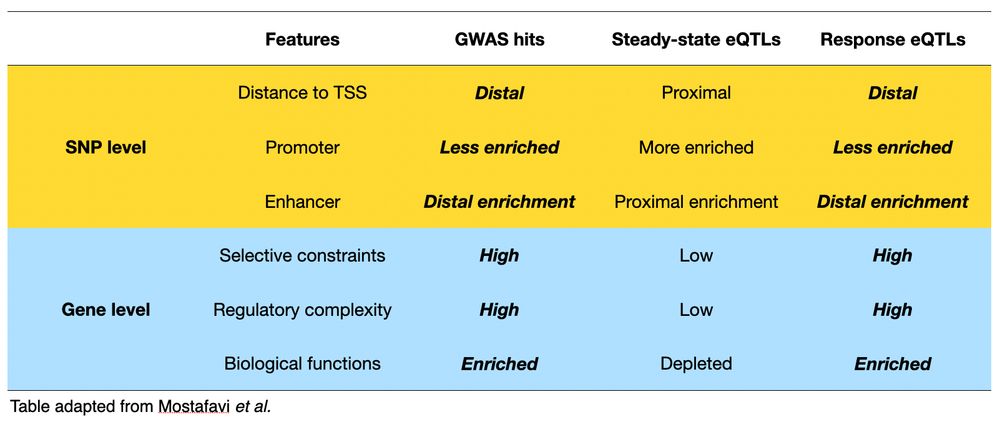
6/n Importantly, we found that response eQTLs share important properties with disease-associated GWAS loci, including similar regulatory landscapes, gene-level constraint, and functional enrichments.📍🔍
May 5, 2025 at 7:07 PM
6/n Importantly, we found that response eQTLs share important properties with disease-associated GWAS loci, including similar regulatory landscapes, gene-level constraint, and functional enrichments.📍🔍
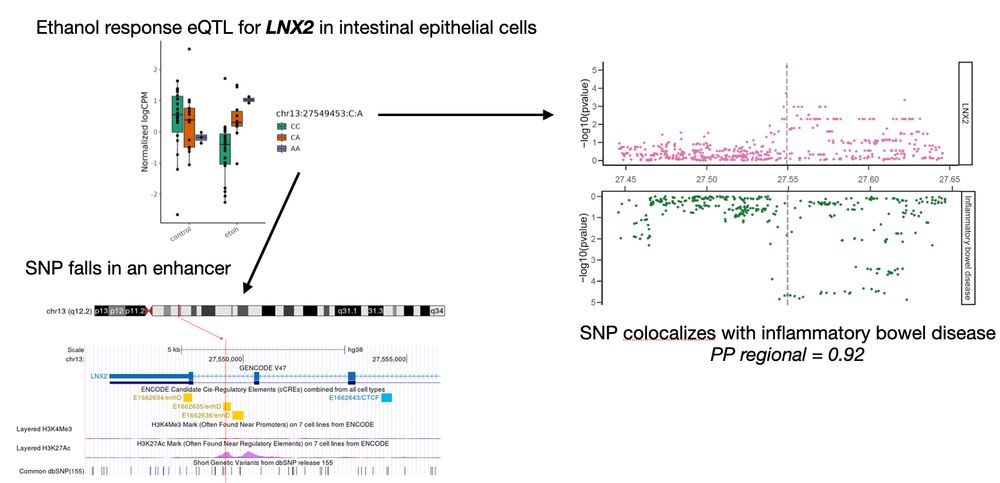
5/n suggesting a functional mechanistic connection between a gene regulatory variant, ethanol exposure, LNX2 expression in the intestinal epithelium, and IBD. 🍷➡️🩺
May 5, 2025 at 7:07 PM
5/n suggesting a functional mechanistic connection between a gene regulatory variant, ethanol exposure, LNX2 expression in the intestinal epithelium, and IBD. 🍷➡️🩺
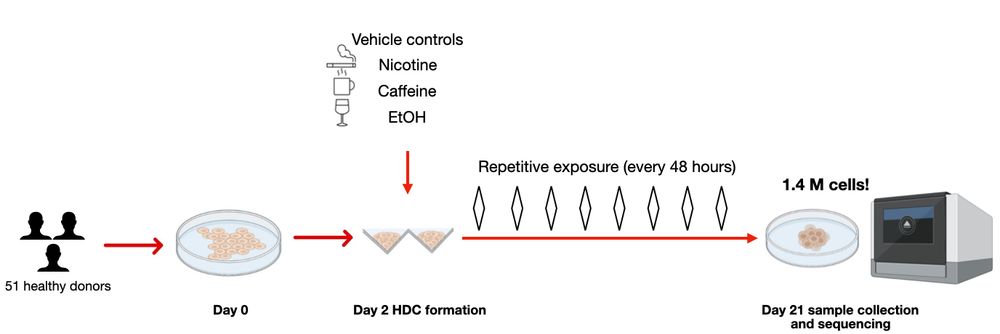
2/n Here, we utilized heterogeneous differentiating cultures (HDCs) to do this. Using single-cell RNA-seq data from 1.4 MILLION cells across 51 genetically diverse individuals, we studied eQTLs under environmental exposures: caffeine, ethanol, and nicotine. ☕️🍷🚬
May 5, 2025 at 7:07 PM
2/n Here, we utilized heterogeneous differentiating cultures (HDCs) to do this. Using single-cell RNA-seq data from 1.4 MILLION cells across 51 genetically diverse individuals, we studied eQTLs under environmental exposures: caffeine, ethanol, and nicotine. ☕️🍷🚬

