


💡 Learning Objective: Master Flexbox properties to build responsive, organized layouts with minimal effort.
#CSS #WebDev #Flexbox #ResponsiveDesign #CodeTips



💡 Learning Objective: Master Flexbox properties to build responsive, organized layouts with minimal effort.
#CSS #WebDev #Flexbox #ResponsiveDesign #CodeTips
Understand how the ... operator simplifies array and object manipulation.
Learn to combine and clone data structures without mutating them.
Use spread and rest effectively in functions to handle arguments flexibly.

Understand how the ... operator simplifies array and object manipulation.
Learn to combine and clone data structures without mutating them.
Use spread and rest effectively in functions to handle arguments flexibly.
Real-Life Example: You have a collection of ingredients and need to pass them all into a blender (function).
Key Takeaway: Use rest to handle unknown numbers of inputs and spread to pass arrays as individual arguments.

Real-Life Example: You have a collection of ingredients and need to pass them all into a blender (function).
Key Takeaway: Use rest to handle unknown numbers of inputs and spread to pass arrays as individual arguments.
Rest for Flexible Parameters:
Real-Life Example: Picture a group of friends pitching in money for dinner. You don’t know how many will contribute, but you still need to calculate the total.

Rest for Flexible Parameters:
Real-Life Example: Picture a group of friends pitching in money for dinner. You don’t know how many will contribute, but you still need to calculate the total.
Real-Life Example: Imagine making a duplicate of your resume but adding one or two extra skills.
Key Takeaway: Use spread for combining or cloning arrays/objects without mutating the original data.

Real-Life Example: Imagine making a duplicate of your resume but adding one or two extra skills.
Key Takeaway: Use spread for combining or cloning arrays/objects without mutating the original data.
Combine or Copy Arrays:
Real-Life Example: You’re merging two lists of groceries into one. The spread operator combines them effortlessly.

Combine or Copy Arrays:
Real-Life Example: You’re merging two lists of groceries into one. The spread operator combines them effortlessly.
Key Takeaway: Think of ... as the “expand or gather” operator. Use it to work with multiple values at once!

Key Takeaway: Think of ... as the “expand or gather” operator. Use it to work with multiple values at once!
Closures retain variables in memory as long as they're referenced, risking memory leaks if unmanaged
🧠: Clear unused references (e.g., event listeners) & avoid unnecessary closures inside loops.
✅:Manage closures responsibly to prevent unwanted memory retention!

Closures retain variables in memory as long as they're referenced, risking memory leaks if unmanaged
🧠: Clear unused references (e.g., event listeners) & avoid unnecessary closures inside loops.
✅:Manage closures responsibly to prevent unwanted memory retention!
• Encapsulation: Create private variables and methods.
• Event Handlers: Maintain state in callbacks.
• Function Factories: Generate functions dynamically
𝗞𝗲𝘆 𝗧𝗮𝗸𝗲𝗮𝘄𝗮𝘆:
Closures are ideal for private variables, event handlers, generating dynamic functionality.



• Encapsulation: Create private variables and methods.
• Event Handlers: Maintain state in callbacks.
• Function Factories: Generate functions dynamically
𝗞𝗲𝘆 𝗧𝗮𝗸𝗲𝗮𝘄𝗮𝘆:
Closures are ideal for private variables, event handlers, generating dynamic functionality.
𝟭. 𝗪𝗵𝗮𝘁 𝗔𝗿𝗲 𝗖𝗹𝗼𝘀𝘂𝗿𝗲𝘀?
Closures are when a function "remembers" variables from its outer scope, even after that scope is gone. They let functions access their lexical environment.Example: A returned function keeps access to variables from its parent, enabling cases like private state!

𝟭. 𝗪𝗵𝗮𝘁 𝗔𝗿𝗲 𝗖𝗹𝗼𝘀𝘂𝗿𝗲𝘀?
Closures are when a function "remembers" variables from its outer scope, even after that scope is gone. They let functions access their lexical environment.Example: A returned function keeps access to variables from its parent, enabling cases like private state!
or maybe im using it wrongly .
its been only like five minutes ago though.


or maybe im using it wrongly .
its been only like five minutes ago though.
• Key Takeaway: Good error handling improves user experience and prevents crashes.

• Key Takeaway: Good error handling improves user experience and prevents crashes.
• JavaScript lets you throw custom errors to handle specific scenarios:
• Key Takeaway: Throw custom errors to make debugging easier and provide meaningful error messages.

• JavaScript lets you throw custom errors to handle specific scenarios:
• Key Takeaway: Throw custom errors to make debugging easier and provide meaningful error messages.
• The try-catch block helps you manage runtime errors gracefully without crashing your program.
• You can add a finally block to execute code whether an error occurs or not.
• Use try-catch for code that might fail, esp. when dealing with APIs, file reading, or user input.

• The try-catch block helps you manage runtime errors gracefully without crashing your program.
• You can add a finally block to execute code whether an error occurs or not.
• Use try-catch for code that might fail, esp. when dealing with APIs, file reading, or user input.




Great for aggregation tasks.
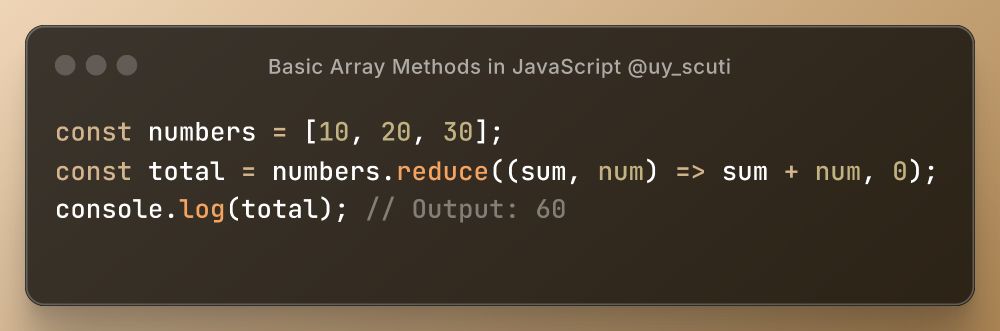
Great for aggregation tasks.
Perfect for filtering datasets.

Perfect for filtering datasets.
1. map(): Transform every element in an array.
Use it to create new arrays without altering the original.

1. map(): Transform every element in an array.
Use it to create new arrays without altering the original.
JavaScript can implicitly convert types in surprising ways!

JavaScript can implicitly convert types in surprising ways!
Primitive: Immutable, stored directly (e.g., string, number, boolean).
Reference: Mutable, stored by reference (e.g., array, object).

Primitive: Immutable, stored directly (e.g., string, number, boolean).
Reference: Mutable, stored by reference (e.g., array, object).
1. let, const, and var:
let: Block-scoped, great for reassignable values.
const: Block-scoped, but immutable (perfect for constants!).
var: Function-scoped (use sparingly—it’s outdated for modern JS).

1. let, const, and var:
let: Block-scoped, great for reassignable values.
const: Block-scoped, but immutable (perfect for constants!).
var: Function-scoped (use sparingly—it’s outdated for modern JS).







