
I use computational and experimental methods to understand beliefs, particularly as they relate to issues like misinformation and climate change.


The effect of repetition is about ¼ the size in the low-quality condition. This moderation occurs for true and false items. 6/
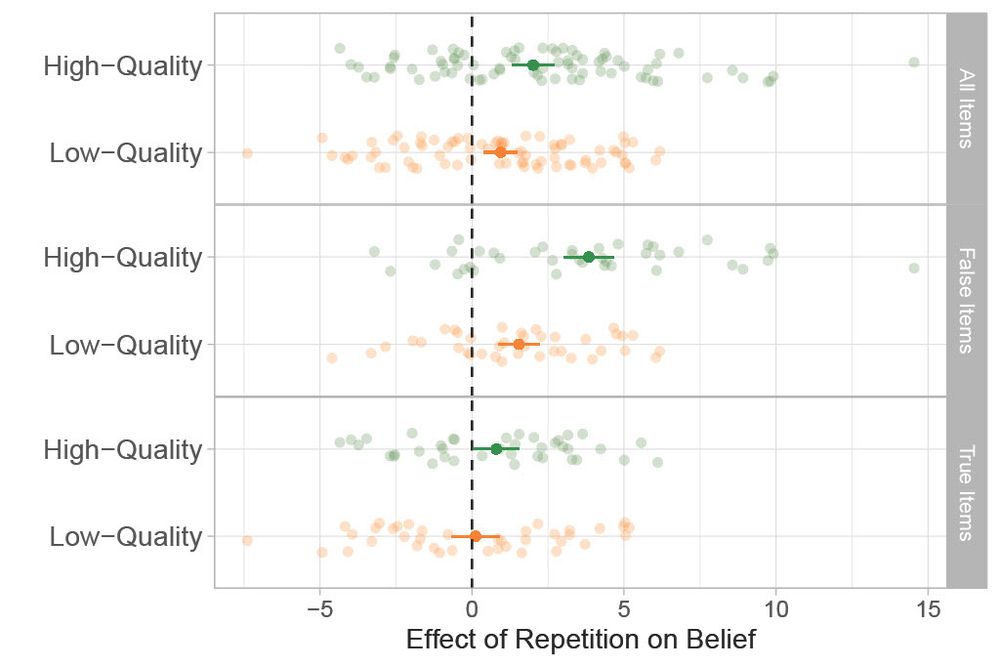
The effect of repetition is about ¼ the size in the low-quality condition. This moderation occurs for true and false items. 6/

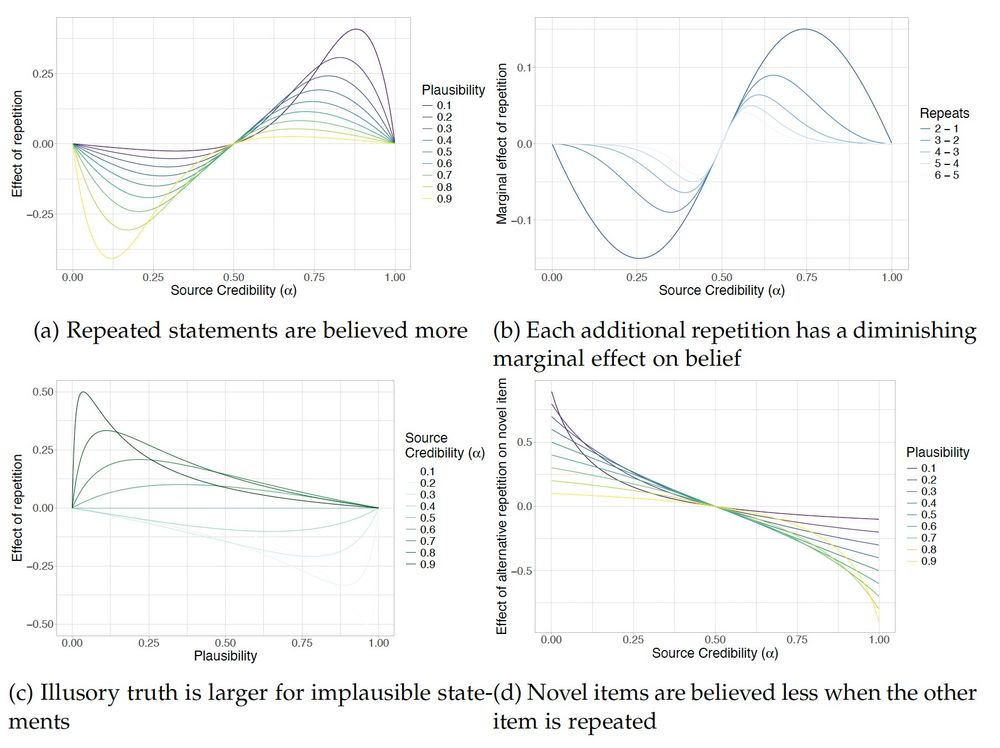

In a formal model, we investigate what this implies for repeated info. 2/
In a formal model, we investigate what this implies for repeated info. 2/
The illusory truth effect (repetition -> belief) is core to psych of beliefs, & thought to be a deep bias impacting misinfo, persuasion & advertising
Why would cognition include such a flaw? We argue it is a rational adaptation to high-quality info environments 🧵1/

The illusory truth effect (repetition -> belief) is core to psych of beliefs, & thought to be a deep bias impacting misinfo, persuasion & advertising
Why would cognition include such a flaw? We argue it is a rational adaptation to high-quality info environments 🧵1/


All parties think that scientists are more skilled as consensus increases. But, perceived bias also increases.
These attributions are predictive of the effect on climate belief.
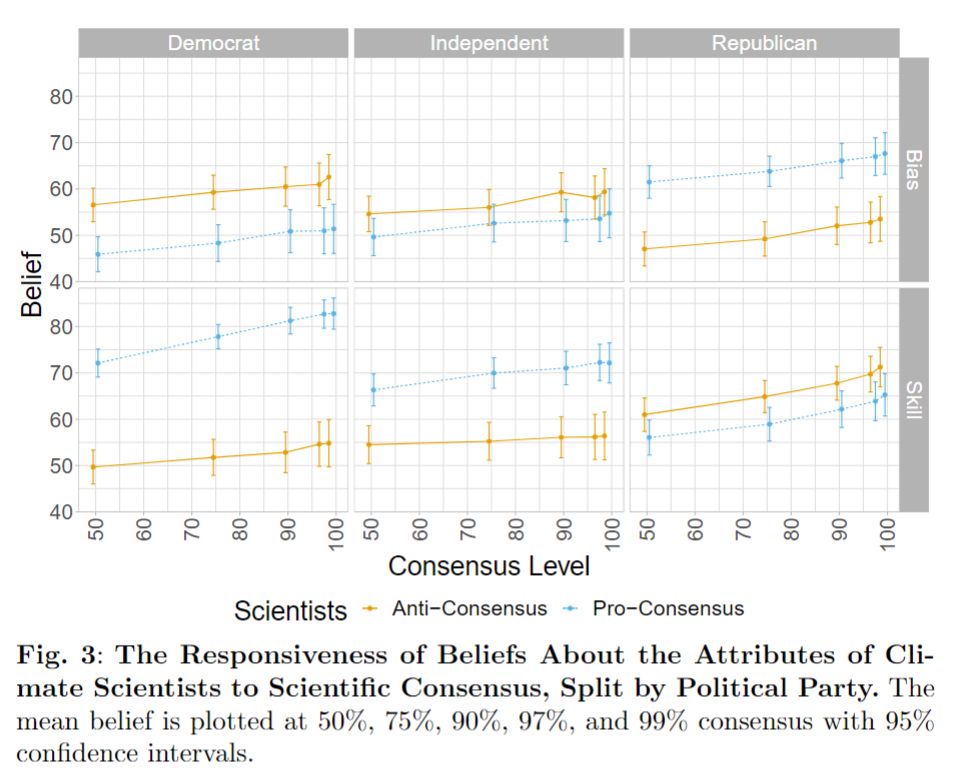
All parties think that scientists are more skilled as consensus increases. But, perceived bias also increases.
These attributions are predictive of the effect on climate belief.
First, we find that higher consensus increases belief in climate change across parties!
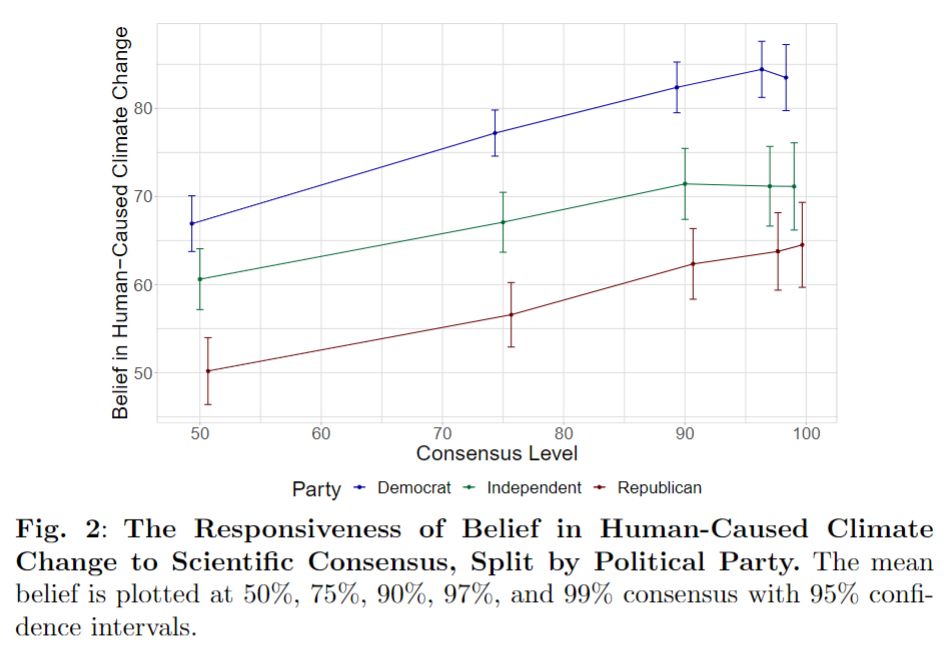
First, we find that higher consensus increases belief in climate change across parties!
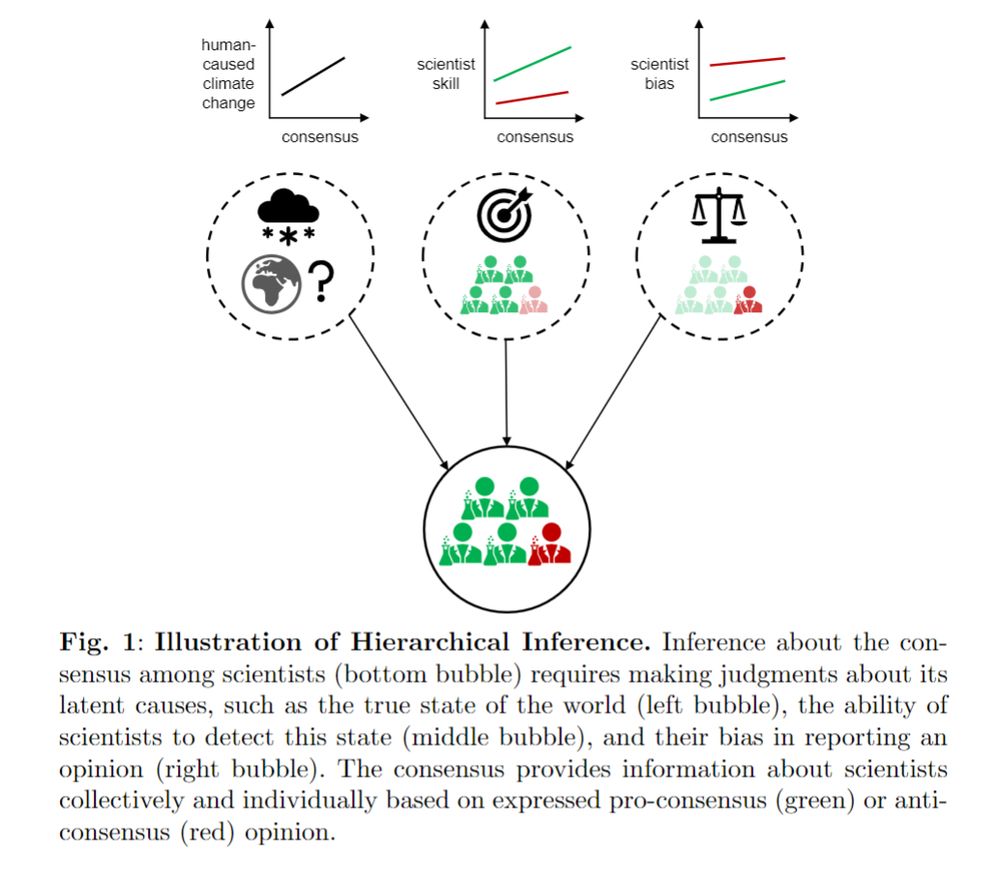

97% of climate scientists agree that human-caused climate change is occurring. But how do people interpret this consensus? Is it a testament to expertise or a signal of bias?
psyarxiv.com/ezua5/
97% of climate scientists agree that human-caused climate change is occurring. But how do people interpret this consensus? Is it a testament to expertise or a signal of bias?
psyarxiv.com/ezua5/

