
Pablo M. Lucas
@pablomlucas.bsky.social
Postdoc @ Univ. of Seville | 🌍 Macroecology & 🐾 Conservation Biology | Studying global change effects on biodiversity 🌡️🌱 | Focus on large mammals 🐻🐺 🐐
1⃣6⃣🔑 KEY MESSAGES:
1⃣ Ecological networks help improve biodiversity & #speciesdistributionmodels under #climate & #land-use change.
2⃣ Global change reshapes #foodwebs, affecting #ecosystem structure & function.
3⃣ We need better data on species #interactions.
1⃣ Ecological networks help improve biodiversity & #speciesdistributionmodels under #climate & #land-use change.
2⃣ Global change reshapes #foodwebs, affecting #ecosystem structure & function.
3⃣ We need better data on species #interactions.
June 9, 2025 at 10:00 AM
1⃣6⃣🔑 KEY MESSAGES:
1⃣ Ecological networks help improve biodiversity & #speciesdistributionmodels under #climate & #land-use change.
2⃣ Global change reshapes #foodwebs, affecting #ecosystem structure & function.
3⃣ We need better data on species #interactions.
1⃣ Ecological networks help improve biodiversity & #speciesdistributionmodels under #climate & #land-use change.
2⃣ Global change reshapes #foodwebs, affecting #ecosystem structure & function.
3⃣ We need better data on species #interactions.
1⃣5⃣Brown bears have a wide potential distribution in Europe, but future #climatechange and land-use changes—through abiotic and biotic factors—will affect each subpopulation differently.

June 9, 2025 at 10:00 AM
1⃣5⃣Brown bears have a wide potential distribution in Europe, but future #climatechange and land-use changes—through abiotic and biotic factors—will affect each subpopulation differently.
1⃣4⃣The inclusion of biotic interactions considerably improved our understanding of brown bear distribution at large (continental) scales compared with Bayesian models including only abiotic factors (climate and land use)

June 9, 2025 at 10:00 AM
1⃣4⃣The inclusion of biotic interactions considerably improved our understanding of brown bear distribution at large (continental) scales compared with Bayesian models including only abiotic factors (climate and land use)
1⃣3⃣Bear diet depends of climate and land use variables, for example subpopulations located in areas with higher temperatures eat more plants, which means that bears have different roles in the ecosystems

June 9, 2025 at 10:00 AM
1⃣3⃣Bear diet depends of climate and land use variables, for example subpopulations located in areas with higher temperatures eat more plants, which means that bears have different roles in the ecosystems
1⃣2⃣🚨 RESULTS🚨 What brown bear eats?

June 9, 2025 at 10:00 AM
1⃣2⃣🚨 RESULTS🚨 What brown bear eats?
1⃣1⃣ We fitted three models explaining the distribution of brown bear (Using the historical range data and the current data): 1) A model with only abiotic variables 2) A model only biotic variables 3) A model combining abiotic and biotic variables

June 9, 2025 at 10:00 AM
1⃣1⃣ We fitted three models explaining the distribution of brown bear (Using the historical range data and the current data): 1) A model with only abiotic variables 2) A model only biotic variables 3) A model combining abiotic and biotic variables
8⃣… and (2) high-resolution occurrences of brown bears from all European and Turkish subpopulations. We built a database with over 3 million 🐻 occurrences from more than 3,000 individuals, covering a broad environmental range.”

June 9, 2025 at 10:00 AM
8⃣… and (2) high-resolution occurrences of brown bears from all European and Turkish subpopulations. We built a database with over 3 million 🐻 occurrences from more than 3,000 individuals, covering a broad environmental range.”
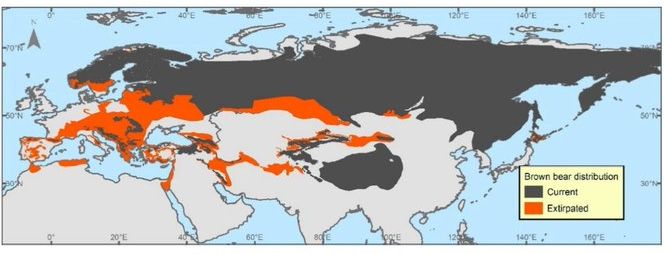
7⃣We combined distribution data for brown bears by using (1) range-scale data from the Eurasian range, complemented with historical range info from historical sources. Avilable at zenodo.org/records/1537...
June 9, 2025 at 10:00 AM
7⃣We combined distribution data for brown bears by using (1) range-scale data from the Eurasian range, complemented with historical range info from historical sources. Avilable at zenodo.org/records/1537...
6⃣ To fill the biotic‑interaction gap, we reviewed 47 studies on the 🐻 brown bear’s diet🍏🌿🐜🦌🫎 across Europe and built a detailed trophic database — a #foodweb with >1,300 quantitative, empirical links, available at zenodo.org/records/1536...

June 9, 2025 at 10:00 AM
6⃣ To fill the biotic‑interaction gap, we reviewed 47 studies on the 🐻 brown bear’s diet🍏🌿🐜🦌🫎 across Europe and built a detailed trophic database — a #foodweb with >1,300 quantitative, empirical links, available at zenodo.org/records/1536...
5⃣ …and from a #conservation perspective, the brown bear is a keystone species in some of the most important protected areas of the continent: #CordilleraCantábrica #Pyrenees #Alps #Carpathians #Apennines #Pindus #Balkans #Finland #Baltic #Scandinavia #Natura2000 #Türkiye #Tatra

June 9, 2025 at 10:00 AM
5⃣ …and from a #conservation perspective, the brown bear is a keystone species in some of the most important protected areas of the continent: #CordilleraCantábrica #Pyrenees #Alps #Carpathians #Apennines #Pindus #Balkans #Finland #Baltic #Scandinavia #Natura2000 #Türkiye #Tatra
4⃣ To address this, we focused on the #brownbear in #Europe and #Türkiye — a well-studied species and region. From an #ecosystem perspective, the brown bear is a top #predator and an #omnivorous generalist, key to ecosystems and with several subpopulations at #extinction risk e.g. #Cantabrian

June 9, 2025 at 10:00 AM
4⃣ To address this, we focused on the #brownbear in #Europe and #Türkiye — a well-studied species and region. From an #ecosystem perspective, the brown bear is a top #predator and an #omnivorous generalist, key to ecosystems and with several subpopulations at #extinction risk e.g. #Cantabrian
3⃣ However, when studying species distributions at large scales, we usually focus on abiotic variables such as climate and land use. This is partly due to the limited data on biotic interactions at broad scales — a gap known as the Eltonian shortfall. annualreviews.org/doi/abs/10.1...
Seven Shortfalls that Beset Large-Scale Knowledge of Biodiversity | Annual Reviews
Ecologists and evolutionary biologists are increasingly using big-data approaches to tackle questions at large spatial, taxonomic, and temporal scales. However, despite recent efforts to gather two ce...
annualreviews.org
June 9, 2025 at 10:00 AM
3⃣ However, when studying species distributions at large scales, we usually focus on abiotic variables such as climate and land use. This is partly due to the limited data on biotic interactions at broad scales — a gap known as the Eltonian shortfall. annualreviews.org/doi/abs/10.1...
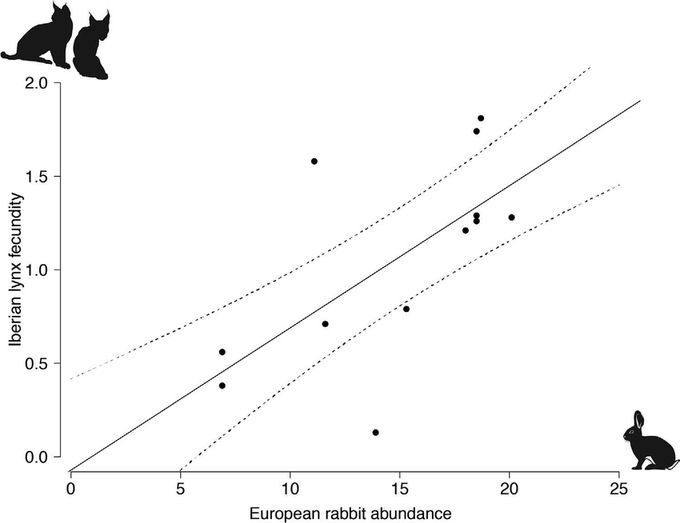
2⃣ Hutchinson proposed that species distributions are shaped by a complex set of abiotic and biotic factors. For example, the #IberianLynx 😺 depends on rabbit 🐰abundance (Monterroso et al. 2016).
June 9, 2025 at 10:00 AM
2⃣ Hutchinson proposed that species distributions are shaped by a complex set of abiotic and biotic factors. For example, the #IberianLynx 😺 depends on rabbit 🐰abundance (Monterroso et al. 2016).



