Previously: Student Researcher @ Google DeepMind, @École polytechnique
https://nicolaszucchet.github.io
@scychan.bsky.social, @lampinen.bsky.social, @razvan-pascanu.bsky.social, and @soham-de.bsky.social. I couldn't have dreamed of a better team for this collaboration!
Check out the full paper for all the technical details arxiv.org/abs/2503.21676.

@scychan.bsky.social, @lampinen.bsky.social, @razvan-pascanu.bsky.social, and @soham-de.bsky.social. I couldn't have dreamed of a better team for this collaboration!
Check out the full paper for all the technical details arxiv.org/abs/2503.21676.
1. use synthetic data early as plateau phase data isn't retained anyway
2. implement dynamic data schedulers that use low diversity during plateaus and high diversity afterward (which is similar to how we learn as infants!)
1. use synthetic data early as plateau phase data isn't retained anyway
2. implement dynamic data schedulers that use low diversity during plateaus and high diversity afterward (which is similar to how we learn as infants!)
On top of that, fine-tuning struggles to add new knowledge: existing memories are quickly corrupted when learning new ones.

On top of that, fine-tuning struggles to add new knowledge: existing memories are quickly corrupted when learning new ones.
This suggests exciting new data scheduling strategies for training - we show that a simple warmup works well!
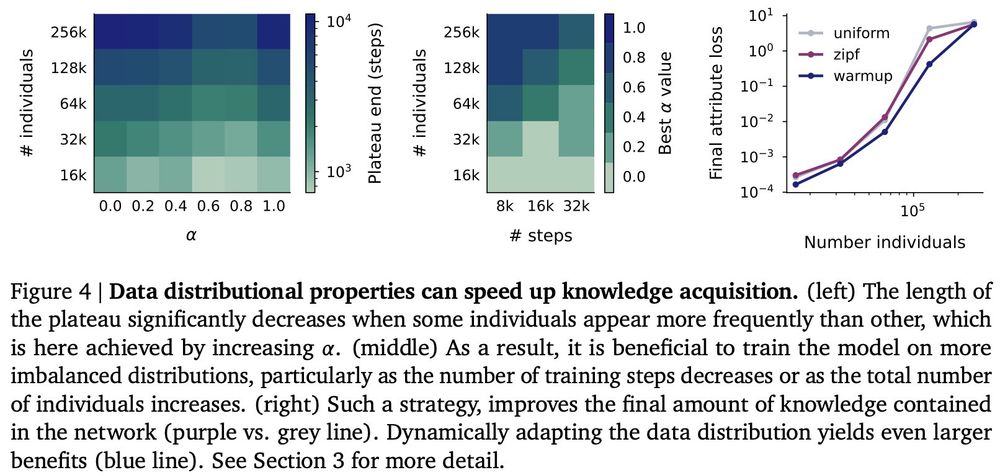
This suggests exciting new data scheduling strategies for training - we show that a simple warmup works well!
This is when the model learns how to recall facts, and it only remembers specific facts afterward!

This is when the model learns how to recall facts, and it only remembers specific facts afterward!
1. Models initially learn generic statistics
2. Performance plateaus while attention-based circuits form
3. Knowledge emerges as models learn individual-specific facts

1. Models initially learn generic statistics
2. Performance plateaus while attention-based circuits form
3. Knowledge emerges as models learn individual-specific facts

