Previously: Student Researcher @ Google DeepMind, @École polytechnique
https://nicolaszucchet.github.io
On top of that, fine-tuning struggles to add new knowledge: existing memories are quickly corrupted when learning new ones.

On top of that, fine-tuning struggles to add new knowledge: existing memories are quickly corrupted when learning new ones.
This suggests exciting new data scheduling strategies for training - we show that a simple warmup works well!
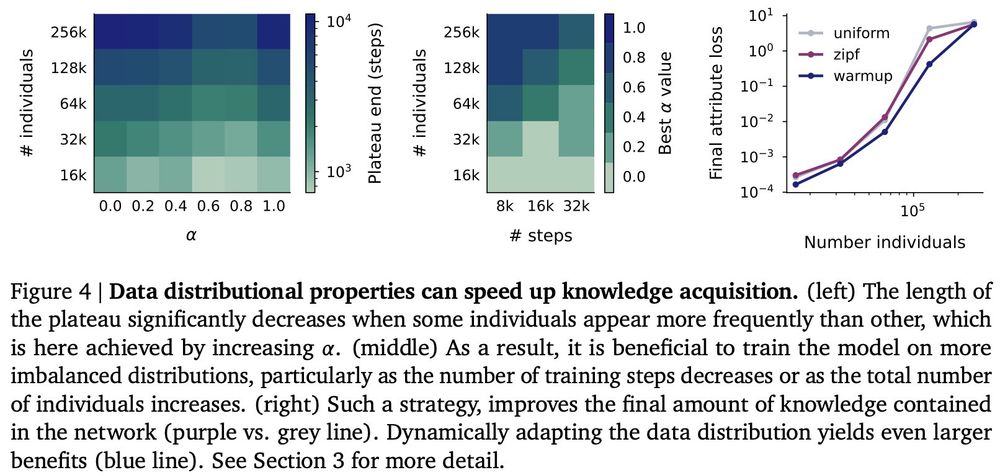
This suggests exciting new data scheduling strategies for training - we show that a simple warmup works well!
This is when the model learns how to recall facts, and it only remembers specific facts afterward!

This is when the model learns how to recall facts, and it only remembers specific facts afterward!
1. Models initially learn generic statistics
2. Performance plateaus while attention-based circuits form
3. Knowledge emerges as models learn individual-specific facts

1. Models initially learn generic statistics
2. Performance plateaus while attention-based circuits form
3. Knowledge emerges as models learn individual-specific facts
Excited to share my Google DeepMind internship results, which reveal the fascinating dynamics behind factual knowledge acquisition in LLMs!

Excited to share my Google DeepMind internship results, which reveal the fascinating dynamics behind factual knowledge acquisition in LLMs!

