
https://www.nature.com/nrg/
(free to read here: rdcu.be/dVNV4)
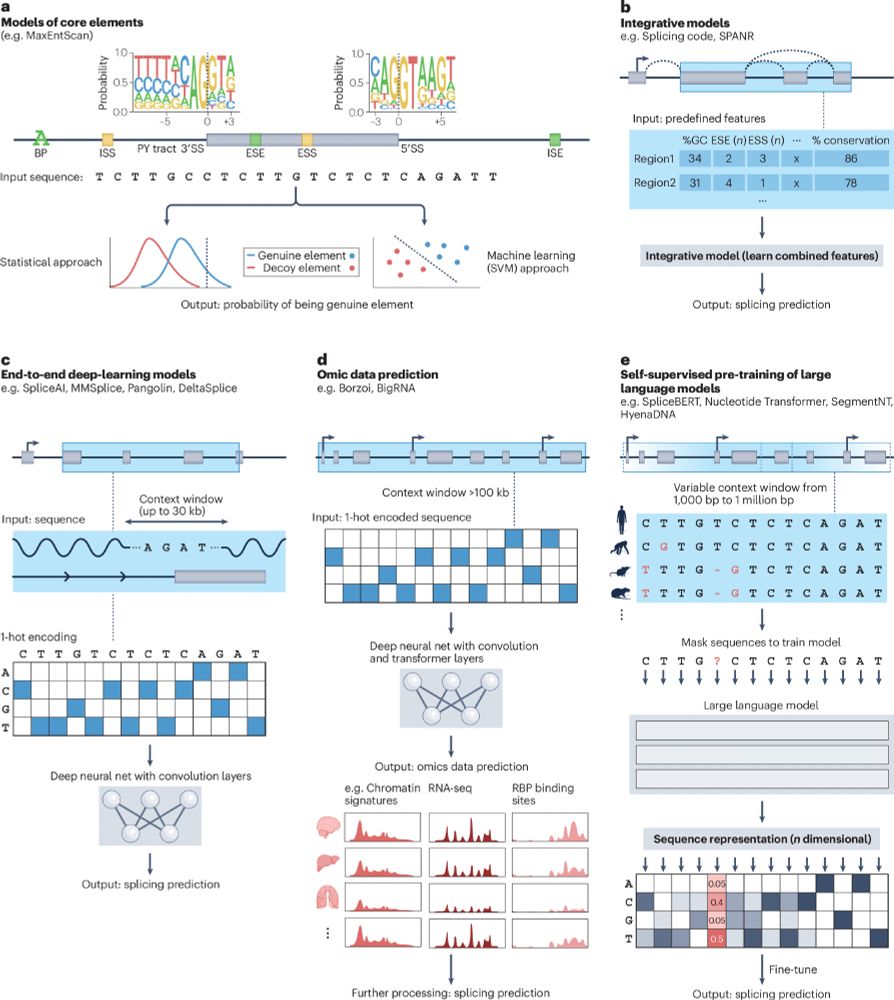
(free to read here: rdcu.be/dVNV4)
Topics include: the evolution of transcriptional regulatory mechanisms in animals; cell-type deconvolution methods for spatial transcriptomics; fine-mapping of candidate causal variants; and genomics of psychiatric disorders

Topics include: the evolution of transcriptional regulatory mechanisms in animals; cell-type deconvolution methods for spatial transcriptomics; fine-mapping of candidate causal variants; and genomics of psychiatric disorders
go.nature.com/47yAbPc

go.nature.com/47yAbPc
Topics include: the impact of structural variation on the 3D genome in disease; single-cell DNA sequencing of somatic mutations; the role of transcription compartments in gene regulation; synonymous mutations and their consequences

Topics include: the impact of structural variation on the 3D genome in disease; single-cell DNA sequencing of somatic mutations; the role of transcription compartments in gene regulation; synonymous mutations and their consequences





Read more in our editorial "Making sense of the regulatory genome": go.nature.com/3IbWP7F
And don't miss our new collection on "Long-read sequencing": go.nature.com/41Yy1Xs

Read more in our editorial "Making sense of the regulatory genome": go.nature.com/3IbWP7F
And don't miss our new collection on "Long-read sequencing": go.nature.com/41Yy1Xs

Topics include: epigenome dynamics during early mammalian development; the genetics of human height; long-read computational analysis of DNA methylation; methodological approaches to promote equity in genomics

Topics include: epigenome dynamics during early mammalian development; the genetics of human height; long-read computational analysis of DNA methylation; methodological approaches to promote equity in genomics
#Review by Pleasantine Mill @cilialab.bsky.social, @sorentc.bsky.social & @lottepedersen.bsky.social

#Review by Pleasantine Mill @cilialab.bsky.social, @sorentc.bsky.social & @lottepedersen.bsky.social
Topics include: systems biology in the single-cell era; ADAR1-mediated RNA editing; retrotransposable element reactivation and its biological impact; transcriptional condensates as temporal signal integrators; X-linked competition

Topics include: systems biology in the single-cell era; ADAR1-mediated RNA editing; retrotransposable element reactivation and its biological impact; transcriptional condensates as temporal signal integrators; X-linked competition
Figure from our recent Review: From computational models of the splicing code to regulatory mechanisms and therapeutic implications (free to read here: rdcu.be/dVNV4)

Figure from our recent Review: From computational models of the splicing code to regulatory mechanisms and therapeutic implications (free to read here: rdcu.be/dVNV4)
Topics include: structural variation in the human genome; cytoplasmic mRNA decay; the mammalian segmentation clock; genetic models and genomic studies of cancer metastasis

Topics include: structural variation in the human genome; cytoplasmic mRNA decay; the mammalian segmentation clock; genetic models and genomic studies of cancer metastasis
Figure from our #Review by Zachary D. Smith, Sara Hetzel & Alexander Meissner: DNA methylation in mammalian development and disease go.nature.com/3DlswZn
Free to read here: rdcu.be/dQEND

Figure from our #Review by Zachary D. Smith, Sara Hetzel & Alexander Meissner: DNA methylation in mammalian development and disease go.nature.com/3DlswZn
Free to read here: rdcu.be/dQEND






DNA methylation in mammalian development and disease go.nature.com/3X14Ali #Review by Zachary D. Smith @yaleschoolofmed.bsky.social, Sara Hetzel & Alexander Meissner @molgen.mpg.de
Free to read here: rdcu.be/dQEND

DNA methylation in mammalian development and disease go.nature.com/3X14Ali #Review by Zachary D. Smith @yaleschoolofmed.bsky.social, Sara Hetzel & Alexander Meissner @molgen.mpg.de
Free to read here: rdcu.be/dQEND


