
Mathias Munschauer
@munschauerlab.bsky.social
Professor at Heidelberg University (@uniheidelberg.bsky.social). Director Molecular Virology. Interested in RNA viruses, RNA-binding proteins and RNA medicine. www.munschauerlab.de
Thanks a lot Marco!
July 11, 2025 at 4:51 PM
Thanks a lot Marco!
Thanks a lot Stefan!
July 11, 2025 at 4:50 PM
Thanks a lot Stefan!
We’re gearing up to grow the Heidelberg team and will soon post several exciting positions. Stay tuned! 4/4
July 1, 2025 at 1:31 PM
We’re gearing up to grow the Heidelberg team and will soon post several exciting positions. Stay tuned! 4/4
A huge thank you to my mentors, colleagues & friends, and especially my team - your hard work got us here. Also, many thanks to the broader virology community; it’s a privilege to contribute to such an amazing and dynamic field. 3/4
July 1, 2025 at 1:31 PM
A huge thank you to my mentors, colleagues & friends, and especially my team - your hard work got us here. Also, many thanks to the broader virology community; it’s a privilege to contribute to such an amazing and dynamic field. 3/4
I’m excited to take on this new task and look forward to working alongside the incredible teams at the Center for Integrative Infectious Disease Research (@ciid-heidelberg.bsky.social) and across the Heidelberg Medical Campus. 2/4
July 1, 2025 at 1:31 PM
I’m excited to take on this new task and look forward to working alongside the incredible teams at the Center for Integrative Infectious Disease Research (@ciid-heidelberg.bsky.social) and across the Heidelberg Medical Campus. 2/4
In conclusion, SHIFTR enables the systematic mapping of region-resolved RNA interactomes for any RNA in any cell type and has the potential to revolutionize our understanding of transcriptomes and their regulation.
February 12, 2024 at 8:09 AM
In conclusion, SHIFTR enables the systematic mapping of region-resolved RNA interactomes for any RNA in any cell type and has the potential to revolutionize our understanding of transcriptomes and their regulation.
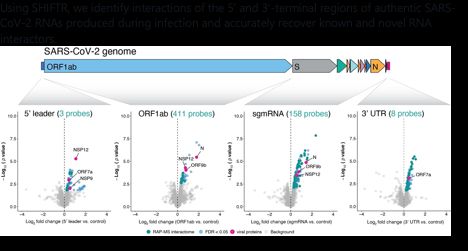
Using SHIFTR, we identify interactions of the 5′ and 3′-terminal regions of authentic SARS-CoV-2 RNAs produced during infection and accurately recover known and novel RNA interactors.
February 12, 2024 at 8:09 AM
Using SHIFTR, we identify interactions of the 5′ and 3′-terminal regions of authentic SARS-CoV-2 RNAs produced during infection and accurately recover known and novel RNA interactors.
SHIFTR works for RNAs of different length and abundance (snRNAs, lncRNAs, mRNAs) and is compatible with sequentially releasing interactomes for multiple target RNAs in a single experiment.
February 12, 2024 at 8:08 AM
SHIFTR works for RNAs of different length and abundance (snRNAs, lncRNAs, mRNAs) and is compatible with sequentially releasing interactomes for multiple target RNAs in a single experiment.
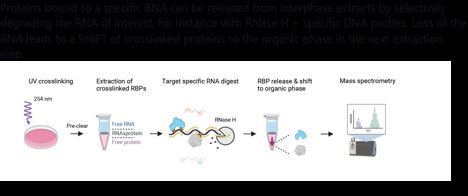
Proteins bound to a specific RNA can be released from interphase extracts by selectively degrading the RNA of interest, for instance with RNase H + specific DNA probes. Loss of the RNA leads to a SHIFT of crosslinked proteins to the organic phase in the next extraction step.
February 12, 2024 at 8:08 AM
Proteins bound to a specific RNA can be released from interphase extracts by selectively degrading the RNA of interest, for instance with RNase H + specific DNA probes. Loss of the RNA leads to a SHIFT of crosslinked proteins to the organic phase in the next extraction step.
In brief, SHIFTR relies on the sequence-independent isolation of crosslinked RNA-protein complexes by organic phase separation as described in OOPS, XRNAX, or PTex.
February 12, 2024 at 8:08 AM
In brief, SHIFTR relies on the sequence-independent isolation of crosslinked RNA-protein complexes by organic phase separation as described in OOPS, XRNAX, or PTex.
With SHIFTR you can identify proteins directly bound to a specific region within any endogenous RNA. In addition to delivering region-resolution, SHIFTR requires orders of magnitude lower input material compared to the state-of-the-art, thus removing a critical bottleneck.
February 12, 2024 at 8:07 AM
With SHIFTR you can identify proteins directly bound to a specific region within any endogenous RNA. In addition to delivering region-resolution, SHIFTR requires orders of magnitude lower input material compared to the state-of-the-art, thus removing a critical bottleneck.
Big shout-out to the lab members leading this effort @Helmholtz_HIRI @Helmholtz_HZI: Nora Schmidt, Sabina Ganskih, Yuanjie Wei and Alex Gabel. We are immensely grateful to our collaborators and funders @ERC_Research and the Helmholtz Association.
October 4, 2023 at 8:44 AM
Big shout-out to the lab members leading this effort @Helmholtz_HIRI @Helmholtz_HZI: Nora Schmidt, Sabina Ganskih, Yuanjie Wei and Alex Gabel. We are immensely grateful to our collaborators and funders @ERC_Research and the Helmholtz Association.
In brief, the host protein SND1 binds the negative-sense RNA intermediates of SARS-CoV-2 and promotes viral RNA synthesis through recruitment of NSP9, which acts as a protein primer for RNA production 🤯.
October 4, 2023 at 8:40 AM
In brief, the host protein SND1 binds the negative-sense RNA intermediates of SARS-CoV-2 and promotes viral RNA synthesis through recruitment of NSP9, which acts as a protein primer for RNA production 🤯.

